Abstract
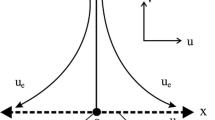
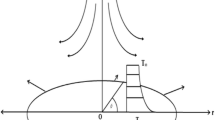
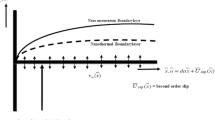
The present investigation deals with two-dimensional boundary layer flow of an incompressible electrically conducting nanofluid induced by a nonlinearly (power-law) shrinking flat surface in the presence of passively controlled nanoparticle boundary condition along with induced magnetic field effect. The similarity transformations developed by Lie group method are used which transforms the set of governing equations into a set of coupled similarity equations. This system of nonlinear ordinary differential equation is solved to obtain multiple solutions using a Runge–Kutta–Fehlberg fourth–fifth-order method (RKF45) with shooting method. This study claims the existence of multiple solutions of velocity and temperature profiles as function of suction (\(s\)) and shrinking parameter (\(\chi\)). The critical points (turning points) have also been reported for suction (\(0 < s_{c} < s\)) and shrinking parameter (\(\chi_{c} < \chi < 0\)) for the default set of other parameters. The temporal stability analysis has been performed to confirm the uniqueness of stable solution.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Timofeeva EV, Yu W, France DM, Singh D, Routbort JL (2011) Nanofluids for heat transfer: an engineering approach. Nanoscale Res Lett 6(1):1–7
Yu W, France DM, Choi SUS, Routbort JL (2007) Review and assessment of nanofluid technology for transportation and other applications (No. ANL/ESD/07-9). Argonne National Laboratory (ANL)
Saidur R, Leong KY, Mohammad HA (2011) A review on applications and challenges of nanofluids. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 15(3):1646–1668
Wan M, Parashar R, Kumar N, Yadav RR, Prakash R, Ngila JC, Parashar V (2015) Heat transfer biofluids: a novel approach towards weed management. Ecol Eng 84:492–495
Li J (2008) Computational analysis of nanofluid flow in microchannels with applications to micro-heat sinks and bio-MEMS. North Carolina State University, ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 3345402
Tsai TH, Kuo LS, Chen PH, Lee DS, Yang CT (2010) Applications of ferro-nanofluid on a micro-transformer. Sensors 10(9):8161–8172
Buongiorno J (2006) Convective transport in nanofluids. J Heat Transfer 128(3):240–250
Kuznetsov AV, Nield DA (2010) Natural convective boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate. Int J Therm Sci 49(2):243–247
Nield DA, Kuznetsov AV (2009) The Cheng–Minkowycz problem for natural convective boundary-layer flow in a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf 52(25):5792–5795
Khan WA, Pop I (2010) Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int J Heat Mass Transf 53(11):2477–2483
Rana P, Bhargava R (2012) Flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid over a nonlinearly stretching sheet: a numerical study. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 17(1):212–226
Hamad MAA, Ferdows M (2012) Similarity solution of boundary layer stagnation-point flow towards a heated porous stretching sheet saturated with a nanofluid with heat absorption/generation and suction/blowing: a Lie group analysis. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 17(1):132–140
Gorla RRS, Chamkha AJ, Rashad AM (2011) Mixed convective boundary layer flow over a vertical wedge embedded in a porous medium saturated with a nanofluid: natural convection dominated regime. Nanoscale Res Lett 6(1):1–9
Kuznetsov AV, Nield DA (2010) Effect of local thermal non-equilibrium on the onset of convection in a porous medium layer saturated by a nanofluid. Transp Porous Media 83(2):425–436
Kuznetsov AV, Nield DA (2011) Double-diffusive natural convective boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate. Int J Therm Sci 50(5):712–717
Nield DA, Kuznetsov AV (2011) The Cheng–Minkowycz problem for the double-diffusive natural convective boundary layer flow in a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54(1):374–378
Nield DA (2011) A note on the onset of convection in a layer of a porous medium saturated by a non-Newtonian nanofluid of power-law type. Transp Porous Media 87(1):121–123
Kuznetsov AV, Nield DA (2013) The Cheng–Minkowycz problem for natural convective boundary layer flow in a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid: a revised model. Int J Heat Mass Transf 65:682–685
Kuznetsov AV, Nield DA (2014) Natural convective boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate: a revised model. Int J Therm Sci 77:126–129
Mustafa M, Mushtaq A, Hayat T, Ahmad B (2014) Nonlinear radiation heat transfer effects in the natural convective boundary layer flow of nanofluid past a vertical plate: a numerical study. PLoS One 9(9):e103946
Mustafa M, Khan JA, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2015) Boundary layer flow of nanofluid over a nonlinearly stretching sheet with convective boundary condition. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 14(1):159–168
Dhanai R, Rana P, Kumar L (2015) Multiple solutions of MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer behavior of nanofluids induced by a power-law stretching/shrinking permeable sheet with viscous dissipation. Powder Technol 273:62–70
Khan JA, Mustafa M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2015) Three-dimensional flow of nanofluid over a non-linearly stretching sheet: an application to solar energy. Int J Heat Mass Transf 86:158–164
Hayat T, Muhammad T, Shehzad SA, Alsaedi A (2015) A mathematical study for three-dimensional boundary layer flow of Jeffrey nanofluid. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A 70(4):225–233
Dhanai R, Rana P, Kumar L (2015) Dual solutions in MHD boundary layer nanofluid flow and heat transfer with heat source/sink considering viscous dissipation. Res J Eng Technol 6(1):142–148
Dhanai R, Rana P, Kumar L (2016) Critical values in slip flow and heat transfer analysis of non-Newtonian nanofluid utilizing heat source/sink and variable magnetic field: multiple solutions. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 58:155–164
Dhanai R, Rana P, Kumar L (2016) Multiple solutions in MHD flow and heat transfer of Sisko fluid containing nanoparticles migration with a convective boundary condition: critical points. Eur Phys J Plus 131(5):1–14
Davidson PA (2001) An introduction to magnetohydrodynamics, 1st edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rossow VJ (1958) On flow of electrically conducting fluids over a flat plate in the presence of a transverse magnetic field. NACA Technical Report 1358
Sparrow EM, Cess RD (1961) The effect of a magnetic field on free convection heat transfer. Int J Heat Mass Transf 3(4):267–274
Pop I, Na TY (1998) A note on MHD flow over a stretching permeable surface. Mech Res Commun 25(3):263–269
Hiemenz K (1911) Grenzschicht an einem in den gleichformingen Flussigkeits-strom einge-tauchten graden Kreiszylinder. Dingler’s Poly J 326:321–324
Wang CY (2008) Stagnation flow towards a shrinking sheet. Int J Non-Linear Mech 43(5):377–382
Jafar K, Ishak A, Nazar R (2011) MHD stagnation-point flow over a nonlinearly stretching/shrinking sheet. J Aerosp Eng 26(4):829–834
Ibrahim W, Shankar B, Nandeppanavar MM (2013) MHD stagnation point flow and heat transfer due to nanofluid towards a stretching sheet. Int J Heat Mass Transf 56(1):1–9
Mustafa M, Hina S, Hayat T, Ahmad B (2014) Influence of induced magnetic field on the peristaltic flow of nanofluid. Meccanica 49(3):521–534
Ibrahim W (2015) The effect of induced magnetic field and convective boundary condition on MHD stagnation point flow and heat transfer of nanofluid past a stretching sheet. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 14(1):178–186
Sandeep N, Sulochana C, Isaac Lare A (2015) Stagnation-point flow of a Jeffrey Nanofluid over a stretching surface with induced magnetic field and chemical reaction. Int J Eng Res Afr 20:93–111 (Trans Tech Publications)
Gireesha BJ, Mahanthesh B, Shivakumara IS, Eshwarappa KM (2015) Melting heat transfer in boundary layer stagnation-point flow of nanofluid toward a stretching sheet with induced magnetic field. Eng Sci Technol Int J 19(1):313–321
Yoshimura A, Prud’homme RK (1988) Wall slip corrections for Couette and parallel disk viscometers. J Rheol (1978-present) 32(1):53–67
Zhu Y, Granick S (2002) No-slip boundary condition switches to partial slip when fluid contains surfactant. Langmuir 18(26):10058–10063
Hayat T, Naz R, Alsaedi A (2014) Effects of slip condition in the channel flow of nanofluid. J Comput Theor Nanosci 11(12):2618–2624
Mansur S, Ishak A, Pop I (2014) Flow and heat transfer of nanofluid past stretching/shrinking sheet with partial slip boundary conditions. Appl Math Mech 35(11):1401–1410
Malvandi A, Ganji DD (2015) Magnetic field and slip effects on free convection inside a vertical enclosure filled with alumina/water nanofluid. Chem Eng Res Des 94:355–364
Weidman PD, Kubitschek DG, Davis AMJ (2006) The effect of transpiration on self similar boundary layer flow over moving surfaces. Int J Eng Sci 44:730–737
Bhattacharyya K, Mukhopadhyay S, Layek GC (2011) Slip effects on boundary layer stagnationpoint flow and heat transfer towards a shrinking sheet. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54:308–313
Dhanai R, Rana P, Kumar L (2016) MHD mixed convection nanofluid flow and heat transfer over an inclined cylinder due to velocity and thermal slip effects: Buongiorno’s model. Powder Technol 288:140–150
Bluman G, Anco S (2002) Symmetry and Integration Methods for Differential Equations, Applied Mathematical Sciences, vol 154. Springer, New York
Uddin MJ, Ferdows M, Rashidi MM, Parsa AB (2016) Group analysis and numerical solution of slip flow of a nanofluid in porous media with heat transfer. Prog Comput Fluid Dyn Int J 16(3):190–200
Animasaun IL, Raju CSK, Sandeep N (2016) Unequal diffusivities case of homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions within viscoelastic fluid flow in the presence of induced magnetic-field and nonlinear thermal radiation. Alexandria Eng J 55(2):1595–1606
Sandeep N, Sulochana C, Animasaun IL (2016) Stagnation-point flow of a Jeffrey nanofluid over a stretching surface with induced magnetic field and chemical reaction. Int J Eng Res Afr 20:93–111
Sandeep N, Sulochana C (2016) Effect of induced magnetic field on MHD stagnation point flow of a nanofluid over a stretching cylinder with suction. J Nanofluids 5(1):68–73
Raju CSK, Sandeep N, Saleem S (2016) Effects of induced magnetic field and homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions on stagnation flow of a Casson fluid. Eng Sci Technol Int J 19(2):875–887
Raju CSK, Sandeep N (2016) Effects of induced magnetic field and nonlinear thermal radiation on Williamson nanofluid past a stretching surface. Int J Appl Eng Res 11(1):41–49
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support from Universiti Sains Malaysia, RU Grant 1001/PMATHS/811252.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Jader Barbosa Jr..
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rana, P., Uddin, M.J., Gupta, Y. et al. Slip effects on MHD Hiemenz stagnation point nanofluid flow and heat transfer along a nonlinearly shrinking sheet with induced magnetic field: multiple solutions. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 39, 3363–3374 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-017-0730-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-017-0730-z