Abstract
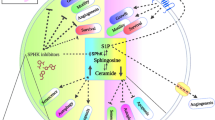
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) can regulate several physiological and pathological processes. S1P signaling via its cell surface receptor S1PR1 has been shown to enhance tumorigenesis and stimulate growth, expansion, angiogenesis, metastasis, and survival of cancer cells. S1PR1-mediated tumorigenesis is supported and amplified by activation of downstream effectors including STAT3, interleukin-6, and NF-κB networks. S1PR1 signaling can also trigger various other signaling pathways involved in carcinogenesis including activation of PI3K/AKT, MAPK/ERK1/2, Rac, and PKC/Ca, as well as suppression of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). It also induces immunological tolerance in the tumor microenvironment, while the immunosuppressive function of S1PR1 can also lead to the generation of pre-metastatic niches. Some tumor cells upregulate S1PR1 signaling pathways, which leads to drug resistant cancer cells, mainly through activation of STAT3. This signaling pathway is also implicated in some inflammatory conditions leading to the instigation of inflammation-driven cancers. Furthermore, it can also increase survival via induction of anti-apoptotic pathways, for instance, in breast cancer cells. Therefore, S1PR1 and its signaling pathways can be considered as potential anti-tumor therapeutic targets, alone or in combination therapies. Given the oncogenic nature of S1PR1 and its distribution in a variety of cancer cell types along with its targeting advantages over other molecules of this family, S1PR1 should be considered a favorable target in therapeutic approaches to cancer. This review describes the role of S1PR1 in cancer development and progression, specifically addressing breast cancer, glioma, and hematopoietic malignancies. We also discuss the potential use of S1P signaling modulators as therapeutic targets in cancer therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weichand B, Popp R, Dziumbla S, Mora J, Strack E, Elwakeel E, et al. S1PR1 on tumor-associated macrophages promotes lymphangiogenesis and metastasis via NLRP3/IL-1beta. J Exp Med. 2017;214(9):2695–713. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20160392.
Kunkel GT, Maceyka M, Milstien S, Spiegel S. Targeting the sphingosine-1-phosphate axis in cancer, inflammation and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12(9):688–702. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4099.
Takabe K, Paugh SW, Milstien S, Spiegel S. “Inside-out” signaling of sphingosine-1-phosphate: therapeutic targets. Pharmacol Rev. 2008;60(2):181–95. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.107.07113.
Calis IU, Cosan DT, Mutlu F. Effects of S1P1 and S1P3 in ER(+) and ER(−) breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2017;37(10):5469–75. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.11976.
Brocklyn JR. Regulation of cancer cell migration and invasion by sphingosine-1-phosphate. World J Biol Chem. 2010;1(10):307–12. https://doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v1.i10.307.
Goparaju SK, Jolly PS, Watterson KR, Bektas M, Alvarez S, Sarkar S, et al. The S1P2 receptor negatively regulates platelet-derived growth factor-induced motility and proliferation. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(10):4237–49. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.25.10.4237-4249.2005.
Patmanathan SN, Johnson SP, Lai SL, Panja Bernam S, Lopes V, Wei W, et al. Aberrant expression of the S1P regulating enzymes, SPHK1 and SGPL1, contributes to a migratory phenotype in OSCC mediated through S1PR2. Sci Rep. 2016;6:25650. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep25650.
Jin L, Liu WR, Tian MX, Fan J, Shi YH. The SphKs/S1P/S1PR1 axis in immunity and cancer: more ore to be mined. World J Surg Oncol. 2016;14:131. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-016-0884-7.
Lee H, Deng J, Kujawski M, Yang C, Liu Y, Herrmann A, et al. STAT3-induced S1PR1 expression is crucial for persistent STAT3 activation in tumors. Nat Med. 2010;16(12):1421–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2250.
Paik JH, Nam SJ, Kim TM, Heo DS, Kim CW, Jeon YK. Overexpression of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and phospho-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is associated with poor prognosis in rituximab-treated diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:911. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-14-911.
Brinkmann V. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors in health and disease: mechanistic insights from gene deletion studies and reverse pharmacology. Pharmacol Ther. 2007;115(1):84–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.04.006.
Dong H, Claffey KP, Brocke S, Epstein PM. Inhibition of breast cancer cell migration by activation of cAMP signaling. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015;152(1):17–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3445-9.
Go H, Kim PJ, Jeon YK, Cho YM, Kim K, Park BH, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1PR1) expression in non-muscle invasive urothelial carcinoma: association with poor clinical outcome and potential therapeutic target. Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England: 1990). 2015;51(14):1937–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2015.07.021.
Deng J, Liu Y, Lee H, Herrmann A, Zhang W, Zhang C, et al. S1PR1-STAT3 signaling is crucial for myeloid cell colonization at future metastatic sites. Cancer Cell. 2012;21(5):642–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2012.03.039.
Sabbadini R. Targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate for cancer therapy. Br J Cancer. 2006;95(9):1131.
Liang J, Nagahashi M, Kim EY, Harikumar KB, Yamada A, Huang WC, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate links persistent STAT3 activation, chronic intestinal inflammation, and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell. 2013;23(1):107–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2012.11.013.
White C, Alshaker H, Cooper C, Winkler M, Pchejetski D. The emerging role of FTY720 (Fingolimod) in cancer treatment. Oncotarget. 2016;7(17):23106–27. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7145.
Yester JW, Tizazu E, Harikumar KB, Kordula T. Extracellular and intracellular sphingosine-1-phosphate in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011;30(3–4):577–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-011-9305-0.
Maceyka M, Harikumar KB, Milstien S, Spiegel S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and its role in disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2012;22(1):50–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2011.09.003.
Watters RJ, Wang HG, Sung SS, Loughran TP, Liu X. Targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors in cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011;11(9):810–7.
Neves SR, Ram PT, Iyengar R. G protein pathways. Science (New York, NY). 2002;296(5573):1636–9. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1071550.
Siehler S, Manning DR. Pathways of transduction engaged by sphingosine 1-phosphate through G protein-coupled receptors. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2002;1582(1–3):94–9.
O’Sullivan C, Dev KK. The structure and function of the S1P1 receptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013;34(7):401–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2013.05.002.
Moore CA, Milano SK, Benovic JL. Regulation of receptor trafficking by GRKs and arrestins. Annu Rev Physiol. 2007;69:451–82. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.69.022405.154712.
Waters CM, Connell MC, Pyne S, Pyne NJ. c-Src is involved in regulating signal transmission from PDGFbeta receptor-GPCR(s) complexes in mammalian cells. Cell Signal. 2005;17(2):263–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2004.07.011.
Pyne NJ, Pyne S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 signaling in mammalian cells. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). 2017;22(3):344. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030344.
Aoki M, Aoki H, Ramanathan R, Hait NC, Takabe K. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in immune cells and inflammation: roles and therapeutic potential. Mediat Inflamm. 2016;2016:8606878. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8606878.
Takuwa Y. Subtype-specific differential regulation of Rho family G proteins and cell migration by the Edg family sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2002;1582(1–3):112–20.
Zu Heringdorf DM, Vincent ME, Lipinski M, Danneberg K, Stropp U, Wang DA, et al. Inhibition of Ca(2+) signalling by the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor S1P(1). Cell Signal. 2003;15(7):677–87.
Singleton PA, Dudek SM, Ma SF, Garcia JG. Transactivation of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors is essential for vascular barrier regulation. Novel role for hyaluronan and CD44 receptor family. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(45):34381–93. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m603680200.
Igarashi J, Erwin PA, Dantas AP, Chen H, Michel T. VEGF induces S1P1 receptors in endothelial cells: Implications for cross-talk between sphingolipid and growth factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100(19):10664–9. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1934494100.
Rodriguez YI, Campos LE, Castro MG, Aladhami A, Oskeritzian CA, Alvarez SE. Sphingosine-1 phosphate: a new modulator of immune plasticity in the tumor microenvironment. Front Oncol. 2016;6:218. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2016.00218.
Kazemi T, Younesi V, Jadidi-Niaragh F, Yousefi M. Immunotherapeutic approaches for cancer therapy: an updated review. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016;44(3):769–79.
Xie Z, Liu H, Geng M. Targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling for cancer therapy. Sci China Life Sci. 2017;60(6):585–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-017-9046-6.
Priceman SJ, Shen S, Wang L, Deng J, Yue C, Kujawski M, et al. S1PR1 is crucial for accumulation of regulatory T cells in tumors via STAT3. Cell Rep. 2014;6(6):992–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.02.016.
Rathinasamy A, Domschke C, Ge Y, Bohm HH, Dettling S, Jansen D, et al. Tumor specific regulatory T cells in the bone marrow of breast cancer patients selectively upregulate the emigration receptor S1P1. Cancer Immunol Immunother CII. 2017;66(5):593–603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-017-1964-4.
Yang XO, Panopoulos AD, Nurieva R, Chang SH, Wang D, Watowich SS, et al. STAT3 regulates cytokine-mediated generation of inflammatory helper T cells. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(13):9358–63. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C600321200.
Maeda Y, Seki N, Kataoka H, Takemoto K, Utsumi H, Fukunari A, et al. IL-17-producing Vgamma4+ gammadelta T cells require sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 for their egress from the lymph nodes under homeostatic and inflammatory conditions. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md: 1950). 2015;195(4):1408–16. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1500599.
Yonesu K, Kawase Y, Inoue T, Takagi N, Tsuchida J, Takuwa Y, et al. Involvement of sphingosine-1-phosphate and S1P1 in angiogenesis: analyses using a new S1P1 antagonist of non-sphingosine-1-phosphate analog. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009;77(6):1011–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2008.12.007.
Chae SS, Paik JH, Furneaux H, Hla T. Requirement for sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 in tumor angiogenesis demonstrated by in vivo RNA interference. J Clin Investig. 2004;114(8):1082–9. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci22716.
LaMontagne K, Littlewood-Evans A, Schnell C, O’Reilly T, Wyder L, Sanchez T, et al. Antagonism of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors by FTY720 inhibits angiogenesis and tumor vascularization. Can Res. 2006;66(1):221–31. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-05-2001.
Reinhard NR, Mastop M, Yin T, Wu Y, Bosma EK, Gadella TWJ Jr, et al. The balance between Galphai-Cdc42/Rac and Galpha12/13-RhoA pathways determines endothelial barrier regulation by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Mol Biol Cell. 2017;28(23):3371–82. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E17-03-0136.
Sanna MG, Wang SK, Gonzalez-Cabrera PJ, Don A, Marsolais D, Matheu MP, et al. Enhancement of capillary leakage and restoration of lymphocyte egress by a chiral S1P1 antagonist in vivo. Nat Chem Biol. 2006;2(8):434–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio804.
He P, Philbrick MJ, An X, Wu J, Messmer-Blust AF, Li J. Endothelial differentiation gene-1, a new downstream gene is involved in RTEF-1 induced angiogenesis in endothelial cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88143. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088143.
Williams PA, Stilhano RS, To VP, Tran L, Wong K, Silva EA. Hypoxia augments outgrowth endothelial cell (OEC) sprouting and directed migration in response to sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). PLoS One. 2015;10(4):e0123437. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123437.
Jung B, Obinata H, Galvani S, Mendelson K, Ding BS, Skoura A, et al. Flow-regulated endothelial S1P receptor-1 signaling sustains vascular development. Dev Cell. 2012;23(3):600–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2012.07.015.
Gaengel K, Niaudet C, Hagikura K, Lavina B, Muhl L, Hofmann JJ, et al. The sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor S1PR1 restricts sprouting angiogenesis by regulating the interplay between VE-cadherin and VEGFR2. Dev Cell. 2012;23(3):587–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2012.08.005.
Sarkisyan G, Gay LJ, Nguyen N, Felding BH, Rosen H. Host endothelial S1PR1 regulation of vascular permeability modulates tumor growth. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014;307(1):C14–24. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00043.2014.
Hobson JP, Rosenfeldt HM, Barak LS, Olivera A, Poulton S, Caron MG, et al. Role of the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor EDG-1 in PDGF-induced cell motility. Science (New York, NY). 2001;291(5509):1800–3. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1057559.
Waters C, Sambi B, Kong KC, Thompson D, Pitson SM, Pyne S, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) act via PDGF beta receptor-sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor complexes in airway smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(8):6282–90. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M208560200.
Bergelin N, Lof C, Balthasar S, Kalhori V, Tornquist K. S1P1 and VEGFR-2 form a signaling complex with extracellularly regulated kinase 1/2 and protein kinase C-alpha regulating ML-1 thyroid carcinoma cell migration. Endocrinology. 2010;151(7):2994–3005. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2009-1387.
Nikkhoo A, Rostami N, Hojjat-Farsangi M, Azizi G, Yousefi B, Ghalamfarsa G, et al. Smac mimetics as novel promising modulators of apoptosis in the treatment of breast cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28205.
Wang H, Huang H, Ding SF. Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes the proliferation and attenuates apoptosis of endothelial progenitor cells via S1PR1/S1PR3/PI3K/Akt pathway. Cell Biol Int. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.10991.
Liu Y, Deng J, Wang L, Lee H, Armstrong B, Scuto A, et al. S1PR1 is an effective target to block STAT3 signaling in activated B cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2012;120(7):1458–65. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-12-399030.
Yu H, Kortylewski M, Pardoll D. Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: role of STAT3 in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(1):41–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1995.
Ding BB, Yu JJ, Yu RY, Mendez LM, Shaknovich R, Zhang Y, et al. Constitutively activated STAT3 promotes cell proliferation and survival in the activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood. 2008;111(3):1515–23. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-04-087734.
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(11):798–809. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2734.
Selvam SP, Ogretmen B. Sphingosine kinase/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling in cancer therapeutics and drug resistance. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2013;216:3–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-1511-4_1.
Yu H, Lee H, Herrmann A, Buettner R, Jove R. Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: new and unexpected biological functions. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14(11):736–46. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3818.
Cheng N, Wang GH. miR-133b, a microRNA targeting S1PR1, suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(4):1469–74. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2016.3043.
Sukocheva OA. Expansion of sphingosine kinase and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor function in normal and cancer cells: from membrane restructuring to mediation of estrogen signaling and stem cell programming. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020420.
Guan H, Liu L, Cai J, Liu J, Ye C, Li M, et al. Sphingosine kinase 1 is overexpressed and promotes proliferation in human thyroid cancer. Mol Endocrinol (Baltimore, Md). 2011;25(11):1858–66. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2011-1048.
Baudhuin LM, Cristina KL, Lu J, Xu Y. Akt activation induced by lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine-1-phosphate requires both mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and is cell-line specific. Mol Pharmacol. 2002;62(3):660–71.
Huang YL, Huang WP, Lee H. Roles of sphingosine 1-phosphate on tumorigenesis. World J Biol Chem. 2011;2(2):25–34. https://doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v2.i2.25.
Nagahashi M, Hait NC, Maceyka M, Avni D, Takabe K, Milstien S, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate in chronic intestinal inflammation and cancer. Adv Biol Regul. 2014;54:112–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbior.2013.10.001.
Masjedi A, Hashemi V, Hojjat-Farsangi M, Ghalamfarsa G, Azizi G, Yousefi M, et al. The significant role of interleukin-6 and its signaling pathway in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:1415–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.177.
Sanada Y, Mizushima T, Kai Y, Nishimura J, Hagiya H, Kurata H, et al. Therapeutic effects of novel sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor agonist W-061 in murine DSS colitis. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e23933. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0023933.
Song J, Matsuda C, Kai Y, Nishida T, Nakajima K, Mizushima T, et al. A novel sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonist, 2-amino-2-propanediol hydrochloride (KRP-203), regulates chronic colitis in interleukin-10 gene-deficient mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;324(1):276–83. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.106.119172.
Danese S, Furfaro F, Vetrano S. Targeting S1P in Inflammatory bowel disease: new avenues for modulating intestinal leukocyte migration. J Crohn’s Colitis. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx107.
Blaho VA, Hla T. An update on the biology of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors. J Lipid Res. 2014;55(8):1596–608. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R046300.
Durham AL, Adcock IM. The relationship between COPD and lung cancer. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam, Netherlands). 2015;90(2):121–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.08.017.
Houghton AM, Mouded M, Shapiro SD. Common origins of lung cancer and COPD. Nat Med. 2008;14(10):1023–4. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1008-1023.
Hsu CK, Lee IT, Lin CC, Hsiao LD, Yang CM. Sphingosine-1-phosphate mediates COX-2 expression and PGE2 /IL-6 secretion via c-Src-dependent AP-1 activation. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230(3):702–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24795.
Sukocheva O, Wadham C, Holmes A, Albanese N, Verrier E, Feng F, et al. Estrogen transactivates EGFR via the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor Edg-3: the role of sphingosine kinase-1. J Cell Biol. 2006;173(2):301–10. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200506033.
Sukocheva OA, Wang L, Albanese N, Pitson SM, Vadas MA, Xia P. Sphingosine kinase transmits estrogen signaling in human breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol (Baltimore, Md). 2003;17(10):2002–12. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2003-0119.
Sukocheva O, Wadham C, Gamble J, Xia P. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 transmits estrogens’ effects in endothelial cells. Steroids. 2015;104:237–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2015.10.009.
Rutherford C, Childs S, Ohotski J, McGlynn L, Riddick M, MacFarlane S, et al. Regulation of cell survival by sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor S1P1 via reciprocal ERK-dependent suppression of Bim and PI-3-kinase/protein kinase C-mediated upregulation of Mcl-1. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e927. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2013.455.
Xiao S, Yang J. Preclinical study of the antitumor effect of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 antibody (S1PR1-antibody) against human breast cancer cells. Investig New Drugs. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-018-0618-5.
Lei FJ, Cheng BH, Liao PY, Wang HC, Chang WC, Lai HC, et al. Survival benefit of sphingosin-1-phosphate and receptors expressions in breast cancer patients. Cancer Med. 2018;7(8):3743–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1609.
Mahajan-Thakur S, Bien-Moller S, Marx S, Schroeder H, Rauch BH. Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) signaling in glioblastoma multiforme—a systematic review. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(11):2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112448.
Bien-Moller S, Lange S, Holm T, Bohm A, Paland H, Kupper J, et al. Expression of S1P metabolizing enzymes and receptors correlate with survival time and regulate cell migration in glioblastoma multiforme. Oncotarget. 2016;7(11):13031–46. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7366.
Yoshida Y, Nakada M, Sugimoto N, Harada T, Hayashi Y, Kita D, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor type 1 regulates glioma cell proliferation and correlates with patient survival. Int J Cancer. 2010;126(10):2341–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24933.
Sordillo LA, Sordillo PP, Helson L. Sphingosine kinase inhibitors as maintenance therapy of glioblastoma after ceramide-induced response. Anticancer Res. 2016;36(5):2085–95.
Bernhart E, Damm S, Wintersperger A, Nusshold C, Brunner AM, Plastira I, et al. Interference with distinct steps of sphingolipid synthesis and signaling attenuates proliferation of U87MG glioma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015;96(2):119–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2015.05.007.
Kim K, Kim YL, Sacket SJ, Kim HL, Han M, Park DS, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) induces shape change in rat C6 glioma cells through the S1P2 receptor: development of an agonist for S1P receptors. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2007;59(7):1035–41. https://doi.org/10.1211/jpp.59.7.0017.
Young N, Pearl DK, Van Brocklyn JR. Sphingosine-1-phosphate regulates glioblastoma cell invasiveness through the urokinase plasminogen activator system and CCN1/Cyr61. Mol Cancer Res MCR. 2009;7(1):23–32. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.mcr-08-0061.
Yoshida Y, Nakada M, Harada T, Tanaka S, Furuta T, Hayashi Y, et al. The expression level of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor type 1 is related to MIB-1 labeling index and predicts survival of glioblastoma patients. J Neurooncol. 2010;98(1):41–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0064-5.
Cinamon G, Matloubian M, Lesneski MJ, Xu Y, Low C, Lu T, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 promotes B cell localization in the splenic marginal zone. Nat Immunol. 2004;5(7):713–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1083.
Shiow LR, Rosen DB, Brdickova N, Xu Y, An J, Lanier LL, et al. CD69 acts downstream of interferon-alpha/beta to inhibit S1P1 and lymphocyte egress from lymphoid organs. Nature. 2006;440(7083):540–4. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04606.
Visentin B, Vekich JA, Sibbald BJ, Cavalli AL, Moreno KM, Matteo RG, et al. Validation of an anti-sphingosine-1-phosphate antibody as a potential therapeutic in reducing growth, invasion, and angiogenesis in multiple tumor lineages. Cancer Cell. 2006;9(3):225–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2006.02.023.
Matloubian M, Lo CG, Cinamon G, Lesneski MJ, Xu Y, Brinkmann V, et al. Lymphocyte egress from thymus and peripheral lymphoid organs is dependent on S1P receptor 1. Nature. 2004;427(6972):355–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02284.
Koresawa R, Yamazaki K, Oka D, Fujiwara H, Nishimura H, Akiyama T, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for patients with primary testicular diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2016;174(2):264–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.14054.
Kortylewski M, Swiderski P, Herrmann A, Wang L, Kowolik C, Kujawski M, et al. In vivo delivery of siRNA to immune cells by conjugation to a TLR9 agonist enhances antitumor immune responses. Nat Biotechnol. 2009;27(10):925–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1564.
Patrussi L, Capitani N, Martini V, Pizzi M, Trimarco V, Frezzato F, et al. Enhanced chemokine receptor recycling and impaired S1P1 expression promote leukemic cell infiltration of lymph nodes in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Can Res. 2015;75(19):4153–63. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-15-0986.
Borge M, Remes Lenicov F, Nannini PR, de los Rios Alicandu MM, Podaza E, Ceballos A, et al. The expression of sphingosine-1 phosphate receptor-1 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells is impaired by tumor microenvironmental signals and enhanced by piceatannol and R406. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md: 1950). 2014;193(6):3165–74. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1400547.
Sic H, Kraus H, Madl J, Flittner KA, von Munchow AL, Pieper K, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors control B-cell migration through signaling components associated with primary immunodeficiencies, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and multiple sclerosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134(2):420–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2014.01.037.
Capitani N, Patrussi L, Trentin L, Lucherini OM, Cannizzaro E, Migliaccio E, et al. S1P1 expression is controlled by the pro-oxidant activity of p66Shc and is impaired in B-CLL patients with unfavorable prognosis. Blood. 2012;120(22):4391–9. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-04-425959.
Wasik AM, Wu C, Mansouri L, Rosenquist R, Pan-Hammarstrom Q, Sander B. Clinical and functional impact of recurrent S1PR1 mutations in mantle cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2018;2(6):621–5. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2017014860.
Chang BY, Francesco M, De Rooij MF, Magadala P, Steggerda SM, Huang MM, et al. Egress of CD19(+)CD5(+) cells into peripheral blood following treatment with the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib in mantle cell lymphoma patients. Blood. 2013;122(14):2412–24. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-02-482125.
Zhao X, Lwin T, Silva A, Shah B, Tao J, Fang B, et al. Unification of de novo and acquired ibrutinib resistance in mantle cell lymphoma. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14920. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14920.
Kluk MJ, Ryan KP, Wang B, Zhang G, Rodig SJ, Sanchez T. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 in classical Hodgkin lymphoma: assessment of expression and role in cell migration. Lab Investig. 2013;93(4):462–71. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2013.7.
Vrzalikova K, Ibrahim M, Vockerodt M, Perry T, Margielewska S, Lupino L, et al. S1PR1 drives a feedforward signalling loop to regulate BATF3 and the transcriptional programme of Hodgkin lymphoma cells. Leukemia. 2018;32(1):214–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.275.
Feng H, Stachura DL, White RM, Gutierrez A, Zhang L, Sanda T, et al. T-lymphoblastic lymphoma cells express high levels of BCL2, S1P1, and ICAM1, leading to a blockade of tumor cell intravasation. Cancer Cell. 2010;18(4):353–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2010.09.009.
Matsuzaki K, Fujita K, Hayashi Y, Matsushita M, Nojima S, Jingushi K, et al. STAT3 expression is a prognostic marker in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. PLoS One. 2018;13(8):e0201256. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0201256.
McCann GA, Naidu S, Rath KS, Bid HK, Tierney BJ, Suarez A, et al. Targeting constitutively-activated STAT3 in hypoxic ovarian cancer, using a novel STAT3 inhibitor. Oncoscience. 2014;1(3):216–28. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncoscience.26.
Dai L, Liu Y, Xie L, Wu X, Qiu L, Di W. Sphingosine kinase 1/sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P)/S1P receptor axis is involved in ovarian cancer angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(43):74947–61. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20471.
Campos LS, Rodriguez YI, Leopoldino AM, Hait NC, Lopez Bergami P, Castro MG, et al. Filamin A expression negatively regulates sphingosine-1-phosphate-induced NF-kappaB activation in melanoma cells by inhibition of Akt signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 2016;36(2):320–9. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00554-15.
Suwanwela J, Osathanon T. Inflammation related genes are upregulated in surgical margins of advanced stage oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2017;7(3):193–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobcr.2017.05.003.
Lin Q, Wei Y, Zhong Y, Zhu D, Ren L, Xu P, et al. Aberrant expression of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 correlates with metachronous liver metastasis and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(10):9743–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2267-4.
Zhu Y, Luo G, Jiang B, Yu M, Feng Y, Wang M, et al. Apolipoprotein M promotes proliferation and invasion in non-small cell lung cancers via upregulating S1PR1 and activating the ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;501(2):520–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.029.
Lankadasari MB, Aparna JS, Mohammed S, James S, Aoki K, Binu VS, et al. Targeting S1PR1/STAT3 loop abrogates desmoplasia and chemosensitizes pancreatic cancer to gemcitabine. Theranostics. 2018;8(14):3824–40. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.25308.
Lifshitz V, Priceman SJ, Li W, Cherryholmes G, Lee H, Makovski-Silverstein A, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1 promotes environment-mediated and acquired chemoresistance. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017;16(11):2516–27. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-17-0379.
Watson C, Long JS, Orange C, Tannahill CL, Mallon E, McGlynn LM, et al. High expression of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors, S1P1 and S1P3, sphingosine kinase 1, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 is associated with development of tamoxifen resistance in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patients. Am J Pathol. 2010;177(5):2205–15. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2010.100220.
Akao Y, Banno Y, Nakagawa Y, Hasegawa N, Kim TJ, Murate T, et al. High expression of sphingosine kinase 1 and S1P receptors in chemotherapy-resistant prostate cancer PC3 cells and their camptothecin-induced up-regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;342(4):1284–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.02.070.
Alshaker H, Wang Q, Srivats S, Chao Y, Cooper C, Pchejetski D. New FTY720-docetaxel nanoparticle therapy overcomes FTY720-induced lymphopenia and inhibits metastatic breast tumour growth. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017;165(3):531–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-017-4380-8.
Tarrason G, Auli M, Mustafa S, Dolgachev V, Domenech MT, Prats N, et al. The sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1 antagonist, W146, causes early and short-lasting peripheral blood lymphopenia in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011;11(11):1773–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2011.07.004.
Foss FW, Snyder AH, Davis MD, Rouse M, Okusa MD, Lynch KR, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of γ-aminophosphonates as potent, subtype-selective sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonists and antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007;15(2):663–77.
Huwiler A, Zangemeister-Wittke U. The sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator fingolimod as a therapeutic agent: recent findings and new perspectives. Pharmacol Ther. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.11.001.
Jadidi-Niaragh F, Mirshafiey A. Therapeutic approach to multiple sclerosis by novel oral drugs. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2011;5(1):66–80. https://doi.org/10.2174/187221311794474900.
Azuma H, Takahara S, Ichimaru N, Wang JD, Itoh Y, Otsuki Y, et al. Marked prevention of tumor growth and metastasis by a novel immunosuppressive agent, FTY720, in mouse breast cancer models. Can Res. 2002;62(5):1410–9.
Lukas S, Patnaude L, Haxhinasto S, Slavin A, Hill-Drzewi M, Horan J, et al. No differences observed among multiple clinical S1P1 receptor agonists (functional antagonists) in S1P1 receptor down-regulation and degradation. J Biomol Screen. 2014;19(3):407–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087057113502234.
Sobel K, Monnier L, Menyhart K, Bolinger M, Studer R, Nayler O, et al. FTY720 phosphate activates sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 and selectively couples to Galpha12/13/Rho/ROCK to induce myofibroblast contraction. Mol Pharmacol. 2015;87(6):916–27. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.114.097261.
Mehling M, Brinkmann V, Antel J, Bar-Or A, Goebels N, Vedrine C, et al. FTY720 therapy exerts differential effects on T cell subsets in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2008;71(16):1261–7. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000327609.57688.ea.
Mousseau Y, Mollard S, Richard L, Nizou A, Faucher-Durand K, Cook-Moreau J, et al. Fingolimod inhibits PDGF-B-induced migration of vascular smooth muscle cell by down-regulating the S1PR1/S1PR3 pathway. Biochimie. 2012;94(12):2523–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2012.07.002.
Rosa R, Marciano R, Malapelle U, Formisano L, Nappi L, D’Amato C, et al. Sphingosine kinase 1 overexpression contributes to cetuximab resistance in human colorectal cancer models. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(1):138–47. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-12-1050.
Kim YM, Sachs T, Asavaroengchai W, Bronson R, Sykes M. Graft-versus-host disease can be separated from graft-versus-lymphoma effects by control of lymphocyte trafficking with FTY720. J Clin Investig. 2003;111(5):659–69. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci16950.
Ushitora Y, Tashiro H, Ogawa T, Tanimoto Y, Kuroda S, Kobayashi T, et al. Suppression of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after rat liver transplantation by FTY720, a sphingosine-1-phosphate analog. Transplantation. 2009;88(8):980–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e3181b9ca69.
Lu Z, Wang J, Zheng T, Liang Y, Yin D, Song R, et al. FTY720 inhibits proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cholangiocarcinoma by inactivating STAT3 signaling. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:783. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-14-783.
Hait NC, Avni D, Yamada A, Nagahashi M, Aoyagi T, Aoki H, et al. The phosphorylated prodrug FTY720 is a histone deacetylase inhibitor that reactivates ERalpha expression and enhances hormonal therapy for breast cancer. Oncogenesis. 2015;4:e156. https://doi.org/10.1038/oncsis.2015.16.
Kappos L, Radue EW, O’Connor P, Polman C, Hohlfeld R, Calabresi P, et al. A placebo-controlled trial of oral fingolimod in relapsing multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(5):387–401. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0909494.
Ubai T, Azuma H, Kotake Y, Inamoto T, Takahara K, Ito Y, et al. FTY720 induced Bcl-associated and Fas-independent apoptosis in human renal cancer cells in vitro and significantly reduced in vivo tumor growth in mouse xenograft. Anticancer Res. 2007;27(1a):75–88.
Azuma H, Takahara S, Horie S, Muto S, Otsuki Y, Katsuoka Y. Induction of apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells in vitro and in vivo caused by FTY720 treatment. J Urol. 2003;169(6):2372–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000064938.32318.91.
Bahrami B, Hojjat-Farsangi M, Mohammadi H, Anvari E, Ghalamfarsa G, Yousefi M, et al. Nanoparticles and targeted drug delivery in cancer therapy. Immunol Lett. 2017;190:64–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2017.07.015.
Jadidi-Niaragh F, Atyabi F, Rastegari A, Kheshtchin N, Arab S, Hassannia H, et al. CD73 specific siRNA loaded chitosan lactate nanoparticles potentiate the antitumor effect of a dendritic cell vaccine in 4T1 breast cancer bearing mice. J Control Release. 2017;246:46–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.12.012.
Jadidi-Niaragh F, Atyabi F, Rastegari A, Mollarazi E, Kiani M, Razavi A, et al. Downregulation of CD73 in 4T1 breast cancer cells through siRNA-loaded chitosan-lactate nanoparticles. Tumor Biol. 2016;37(6):8403–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4732-0.
Mao Y, Wang J, Zhao Y, Wu Y, Kwak KJ, Chen CS, et al. A novel liposomal formulation of FTY720 (fingolimod) for promising enhanced targeted delivery. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med. 2014;10(2):393–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2013.08.001.
Peyrin-Biroulet L, Christopher R, Behan D, Lassen C. Modulation of sphingosine-1-phosphate in inflammatory bowel disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16(5):495–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2017.03.007.
Bigaud M, Dincer Z, Bollbuck B, Dawson J, Beckmann N, Beerli C, et al. Pathophysiological consequences of a break in S1P1-Dependent homeostasis of vascular permeability revealed by S1P1 competitive antagonism. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0168252.
Davis MD, Clemens JJ, Macdonald TL, Lynch KR. Sphingosine 1-phosphate analogs as receptor antagonists. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(11):9833–41. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M412356200.
Balthasar S, Samulin J, Ahlgren H, Bergelin N, Lundqvist M, Toescu EC, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor expression profile and regulation of migration in human thyroid cancer cells. Biochem J. 2006;398(3):547–56. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20060299.
Wei SH, Rosen H, Matheu MP, Sanna MG, Wang SK, Jo E, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate type 1 receptor agonism inhibits transendothelial migration of medullary T cells to lymphatic sinuses. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(12):1228–35. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1269.
Wang H, Huang H, Ding SF. Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes the proliferation and attenuates apoptosis of Endothelial progenitor cells via S1PR1/S1PR3/PI3K/Akt pathway. Cell Biol Int. 2018;42(11):1492–502. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.10991.
Kawa Y, Nagano T, Yoshizaki A, Dokuni R, Katsurada M, Terashita T, et al. Role of S1P/S1PR3 axis in release of CCL20 from human bronchial epithelial cells. PLoS One. 2018;13(9):e0203211. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203211.
Kurano M, Tsuneyama K, Morimoto Y, Shimizu T, Jona M, Kassai H, et al. Apolipoprotein M protects lipopolysaccharide-treated mice from death and organ injury. Thromb Haemost. 2018;118(6):1021–35. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1641750.
Imeri F, Blanchard O, Jenni A, Schwalm S, Wunsche C, Zivkovic A, et al. FTY720 and two novel butterfly derivatives exert a general anti-inflammatory potential by reducing immune cell adhesion to endothelial cells through activation of S1P(3) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. 2015;388(12):1283–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1159-5.
Hughes JE, Srinivasan S, Lynch KR, Proia RL, Ferdek P, Hedrick CC. Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces an antiinflammatory phenotype in macrophages. Circ Res. 2008;102(8):950–8. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.107.170779.
Huwiler A, Pfeilschifter J. New players on the center stage: sphingosine 1-phosphate and its receptors as drug targets. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;75(10):1893–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2007.12.018.
Khattar M, Deng R, Kahan BD, Schroder PM, Phan T, Rutzky LP, et al. Novel sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator KRP203 combined with locally delivered regulatory T cells induces permanent acceptance of pancreatic islet allografts. Transplantation. 2013;95(7):919–27. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e3182842396.
Pan S, Mi Y, Pally C, Beerli C, Chen A, Guerini D, et al. A monoselective sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1 agonist prevents allograft rejection in a stringent rat heart transplantation model. Chem Biol. 2006;13(11):1227–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.09.017.
Nishi T, Miyazaki S, Takemoto T, Suzuki K, Iio Y, Nakajima K, et al. Discovery of CS-0777: a potent, selective, and orally active S1P1 agonist. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2011;2(5):368–72. https://doi.org/10.1021/ml100301k.
Fujii Y, Hirayama T, Ohtake H, Ono N, Inoue T, Sakurai T, et al. Amelioration of collagen-induced arthritis by a novel S1P1 antagonist with immunomodulatory activities. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md: 1950). 2012;188(1):206–15. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1101537.
Jin J, Hu J, Zhou W, Wang X, Xiao Q, Xue N, et al. Development of a selective S1P1 receptor agonist, Syl930, as a potential therapeutic agent for autoimmune encephalitis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;90(1):50–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2014.04.010.
Xiao Q, Jin J, Wang X, Hu J, Xi M, Tian Y, et al. Synthesis, identification, and biological activity of metabolites of two novel selective S1P1 agonists. Bioorg Med Chem. 2016;24(10):2273–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2016.03.059.
Lien YH, Yong KC, Cho C, Igarashi S, Lai LW. S1P(1)-selective agonist, SEW2871, ameliorates ischemic acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2006;69(9):1601–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5000360.
Rolin J, Sand KL, Knudsen E, Maghazachi AA. FTY720 and SEW2871 reverse the inhibitory effect of S1P on natural killer cell mediated lysis of K562 tumor cells and dendritic cells but not on cytokine release. Cancer Immunol Immunother CII. 2010;59(4):575–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-009-0775-7.
Hosseini M, Haji-Fatahaliha M, Jadidi-Niaragh F, Majidi J, Yousefi M. The use of nanoparticles as a promising therapeutic approach in cancer immunotherapy. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016;44(4):1051–61.
Siahmansouri H, Somi MH, Babaloo Z, Baradaran B, Jadidi-Niaragh F, Atyabi F, et al. Effects of HMGA 2 si RNA and doxorubicin dual delivery by chitosan nanoparticles on cytotoxicity and gene expression of HT-29 colorectal cancer cell line. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016;68(9):1119–30.
Li MH, Sanchez T, Yamase H, Hla T, Oo ML, Pappalardo A, et al. S1P/S1P1 signaling stimulates cell migration and invasion in Wilms tumor. Cancer Lett. 2009;276(2):171–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2008.11.025.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
There was no funding.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors (NR, AN, AA, GA, MHF, GG, BY, MY, and FJN) have any conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rostami, N., Nikkhoo, A., Ajjoolabady, A. et al. S1PR1 as a Novel Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer Therapy. Mol Diagn Ther 23, 467–487 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-019-00401-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-019-00401-5