Abstract
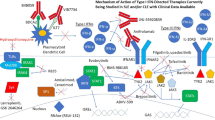
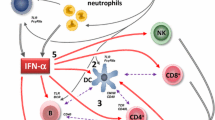
Anifrolumab (anifrolumab-fnia; Saphnelo™) is a monoclonal antibody antagonist of the type 1 interferon receptor (IFNAR). It is being developed by AstraZeneca (under license from Medarex, now Bristol-Myers Squibb) for the treatment of autoimmune disorders, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis, the underlying pathogenesis of which involves type 1 interferon. In July 2021, intravenous anifrolumab was approved in the USA for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe SLE who are receiving standard therapy. Anifrolumab (intravenous or subcutaneous) continues to be assessed in clinical studies in SLE in various countries, and the intravenous formulation is under regulatory review in the EU and Japan. This article summarizes the milestones in the development of anifrolumab leading to this first approval for the treatment of moderate to severe SLE.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Justiz Vaillant AA, Goyal A, Bansal P, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus [online book]. 2020. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535405/#article-24526.s2. Accessed 11 Aug 2021.
Ronnblom L, Leonard D. Interferon pathway in SLE: one key to unlocking the mystery of the disease. Lupus Sci Med. 2019;6(1):e000270.
AstraZeneca. Saphnelo (anifrolumab-fnia): US prescribing information. 2021. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/. Accessed 11 Aug 2021.
AstraZeneca. Saphnelo (anifrolumab) approved in the US for moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus [media release]. 2 Aug 2021. https://www.astrazeneca.com.
MedImmune Inc. MedImmune and Medarex announce collaboration to develop and commercialize fully human antibodies for autoimmune diseases [media release]. 23 Nov 2004. http://www.medimmune.com.
Medarex Inc. Medarex to receive milestone payment from MedImmune for allowance of an Investigational New Drug Application for MEDI-546 [media release]. 2 Feb 2009. http://www.medarex.com.
AstraZeneca. Type I interferon inhibition in systemic lupus erythematosus. 2020. https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2021094378A1/en?q=Anifrolumab&assignee=astrazeneca. Accessed 11 Aug 2021.
AstraZeneca. Type I interferon-mediated disorders. 2020. https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2020165437A1/en?q=Anifrolumab&assignee=astrazeneca. Accessed 11 Aug 2021.
Medimmune, LLC. Stable anti-ifnar1 formulation. 2016. https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2017031288A1/en. Accessed 11 Aug 2021.
Medarex Inc. Form 10-K Medarex Inc. 2009. https://sec.report/Document/0001047469-09-002127/. Accessed 11 Aug 2021.
Peng L, Oganesyan V, Wu H, et al. Molecular basis for antagonistic activity of anifrolumab, an anti-interferon-alpha receptor 1 antibody. MAbs. 2015;7(2):428–39.
Riggs JM, Hanna RN, Rajan B, et al. Characterisation of anifrolumab, a fully human anti-interferon receptor antagonist antibody for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus Sci Med. 2018;5(1):e000261.
Casey KA, Guo X, Smith MA, et al. Type I interferon receptor blockade with anifrolumab corrects innate and adaptive immune perturbations of SLE. Lupus Sci Med. 2018;5(1):e000286.
Guo X, Higgs BW, Bay-Jensen AC, et al. Suppression of T cell activation and collagen accumulation by an anti-IFNAR1 mAb, anifrolumab, in adult patients with systemic sclerosis. J Investig Dermatol. 2015;135(10):2402–9.
Guo X, Wang S, Wang L. Effects of anifrolumab on oxidative stress and macrophage activation: novel biomarkers and impact of type I interferon blockade in systemic lupus erythematosus [abstract no. FRI0256]. In: 19th Annual Congress of the European League Against Rheumatism. 2018.
Furie RA, Morand EF, Bruce IN, et al. Type I interferon inhibitor anifrolumab in active systemic lupus erythematosus (TULIP-1): a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Rheumatol. 2019;1(4):e208–19.
Morand EF, Furie R, Tanaka Y, et al. Trial of anifrolumab in active systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(3):211–21.
Furie R, Khamashta M, Merrill JT, et al. Anifrolumab, an anti-interferon-alpha receptor monoclonal antibody, in moderate-to-severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69(2):376–86.
Tummala R, Rouse T, Berglind A, et al. Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of subcutaneous and intravenous anifrolumab in healthy volunteers. Lupus Sci Med. 2018;5(1):e000252.
Morand EF, Furie R, Tanaka Y, et al. Efficacy of anifrolumab in active systemic lupus erythematosus: patient subgroup analysis of BICLA response in 2 phase 3 trials [abstract no. OP0049]. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(Suppl 1):32.
Morand EF, Furie R, Bruce I, et al. Early and sustained responses with anifrolumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in 2 phase 3 trials [abstract no. P186]. Lupus Sci Med. 2020;7(Suppl 1):A120–1.
Werth V, Furie R, Morand E, et al. Early and sustained reduction in severity of skin disease with anifrolumab treatment in patients with active SLE measured by the Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index (CLASI): pooled data from 2 phase 3 studies [abstract no. 0985]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(Suppl 10):1975–8.
Furie R, Morand EF, Askanase AD, et al. Anifrolumab reduces flare rates in patients with moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2021;30(8):1254–63.
Merrill JT, Werth V, Furie R, et al. Anifrolumab effects on rash and arthritis in patients with SLE and impact of interferon signal in pooled data from phase 3 trials [abstract no. OP0131]. In: 22nd Annual Congress of the European League Against Rheumatism. 2021.
Morand EF, Furie R, Tanaka Y, et al. Effects of anifrolumab on renal disease in patients with SLE [abstract no. POS0691]. In: 22nd Annual Congress of the European League Against Rheumatism. 2021.
Morand E, Furie R, Bruce I, et al. Comprehensive efficacy of anifrolumab across organ domains in patients with active SLE: pooled data from 2 phase 3 trials [abstract no. 1828]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(Suppl 10):3676–9.
Merrill JT, Furie R, Werth VP, et al. Anifrolumab effects on rash and arthritis: impact of the type I interferon gene signature in the phase IIb MUSE study in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus Sci Med. 2018;5(1):e000284.
Chatham WW, Furie R, Saxena A, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of anifrolumab in adults with systemic lupus erythematosus: results of a phase II open-label extension study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73(5):816–25.
Furie R, Kalunian K, Merrill J, et al. Lupus disease activity after cessation of anifrolumab treatment during the phase 2b MUSE trial follow-up period [abstract no. 1829]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(Suppl 10):3679–81.
Tanaka Y, Takeuchi T, Okada M, et al. Safety and tolerability of anifrolumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting type I interferon receptor, in Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a multicenter, phase 2, open-label study. Mod Rheumatol. 2020;30(1):101–8.
Bruce IN, Nami A, Schwetje E, et al. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of subcutaneous anifrolumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, active skin disease, and high type I interferon gene signature: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021;3(2):e101–10.
Jayne D, Rovin BH, Mysler E, et al. Randomized, controlled, phase 2 trial of type 1 IFN inhibitor anifrolumab in patients with active proliferative lupus nephritis [abstract no. POS0690]. In: 22nd Annual Congress of the European League Against Rheumatism. 2021.
Tummala R, Abreu G, Pineda L, et al. Safety profile of anifrolumab in patients with active SLE: an integrated analysis of phase II and III trials. Lupus Sci Med. 2021;8(1):02.
Merrill J, Kalunian K, Furie R, et al. Herpes zoster events with anifrolumab in patients with active SLE: an integrated analysis of phase 2 and phase 3 trials [abstract no. 0849]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(Suppl 10):1672–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Authorship and Conflict of interest
During the peer review process the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on the article. Changes resulting from any comments received were made by the authors on the basis of scientific completeness and accuracy. Emma Deeks is a contracted employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature, and declares no relevant conflicts of interest. All authors contributed to the review and are responsible for the article content.
Ethics approval, Consent to participate, Consent to publish, Availability of data and material, Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
This profile has been extracted and modified from the AdisInsight database. AdisInsight tracks drug development worldwide through the entire development process, from discovery, through pre-clinical and clinical studies to market launch and beyond.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deeks, E.D. Anifrolumab: First Approval. Drugs 81, 1795–1802 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-021-01604-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-021-01604-z