Abstract
Purpose of Review
For decades, treatment of compressive optic nerve neuropathy was conservative and involved the intravenous application of high-dose corticoids, which was combined with nerve growth factors in later years. If surgery was considered, transcranial and transfacial access to the orbital apex and the optic nerve were achieved using classical approaches. Over the past decade, endonasal endoscopic procedures have increasingly come into force, based on favorable experiences with functional endoscopic sinus surgery and as a result of innovative developments in endoscopy and image guidance. The purpose of this review is to address the latest literature in this field with regard to the indications, techniques, results, and complications associated with this procedure.
Recent Findings
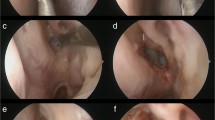
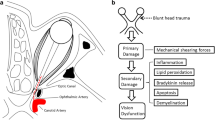
There are basically two approaches for endoscopic optic nerve decompression: the extradural supraorbital “keyhole” approach, which provides access to the optic nerve canal roof and which is usually performed by neurosurgeons, and the endonasal endoscopic approach, which is widely used by otorhinolaryngologists. The development and application of endonasal endoscopic surgery was only possible with extensive knowledge of the topographic anatomy. The most important anatomical landmarks and topography have been described based on either cadaveric or CT scan studies, and include the opticocarotid recess, the distance between the optic nerve canal and the internal carotid artery, the ophthalmic artery, and the length of the optic nerve canal. There are two main indications for endonasal endoscopic optic nerve decompression: (1) traumatic optic nerve neuropathy (TON), and (2) optic nerve neuropathy from non-traumatic causes (nTON), such as tumorous conditions, inflammatory diseases, or idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH). In trauma cases, rates of postoperative visual improvement of 40–80% have been reported. Factors influencing the outcome include the severity of the injury, initial visual acuity (light perception or better vs. no light perception), the time interval between trauma and intervention, and the type of injury, such as fracture lines directly through the optic nerve canal or probable avulsion trauma. nTON cases generally have a slightly better prognosis, with vision improvement of 54–100% reported. The procedure should be performed before any optic nerve atrophy can occur. In IIH cases, all major symptoms, including vision loss, headache, visual field deterioration, and papilla edema, improved after optic nerve decompression, with rates of 60–100% reported. Earlier studies reported the occurrence of major complications such as cerebral fluid leakage, severe hemorrhage, or optic nerve injury at rates of about 3%. However, more recent studies postulate that no major complications occur, which may reflect the increasing use of the endonasal endoscopic route to the optic nerve and skull base as standard procedure, so that surgeons are becoming more comfortable with the technique.
Summary
Endonasal endoscopic optic nerve decompression is a safe and highly effective treatment to reduce hydrostatic pressure on the optic nerve in cases of optic nerve neuropathy of various etiologies. In TON cases, about 50% of patients will benefit from the procedure, with vision improvement possible in some cases even with an interval of some days between trauma and surgery. Non-trauma cases have a slightly better prognosis. The intervention should be performed prior to optic nerve atrophy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Deichmüller C, Welkoborsky HJ. Traumatic optic nerve neuropathy. In: Welkoborsky HJ, Wiechens B, Hinni ML, editors. Interdisciplinary management of orbital diseases: Thieme Intl; 2017. p. 140.
Deichmüller C, Welkoborsky HJ. Orbital traumatology. HNO. 2018;66:721–9.
He ZH, Lan ZB, Xiong A, Hou GK, Pan YW, Li Q, et al. Endoscopic decompression of the optic canal for traumatic optic neuropathy. Chin J Traumatol. 2016;19(6):330–2.
Yu B, Ma Y, Tu Y, Wu W. The outcome of endoscopic transethmosphenoid optic canal decompression for indirect traumatic optic neuropathy with no-light-perception. J Ophthalmol. 2016;2016:6492858.
• Yu B, Chen Y, Ma Y, Tu Y, Wu W. Outcome of endoscopic trans-ethmosphenoid optic canal decompression for indirect traumatic optic neuropathy in children. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018;18(1):152. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0792-4. Important paper on a large case series of indirect TON in children and the outcome following endoscopic optic nerve decompression.
• Sofferman RA. Sphenoethmoid approach to the optic nerve. Laryngoscope. 1981;91:184–96. Recommended paper. It is one of the first papers in the literature describing the endonasal sphenoethmoid approach.
•• Luxenberger W, Stammberger H, Jebeles JA, Walch C. Endoscopic optic nerve decompression: the Graz experience. Laryngoscope. 1998;108:873–82. One of the “key” papers describing the endoscopic endonasal route and technique for optic nerve decompression.
Maurer J, Hinni M, Mann W, Pfeiffer N. Optic nerve decompression in trauma and tumor patients. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1999;256:341–5.
•• Castelnuovo P, Turri-Zanoni M, Battaglia P, Locatelli D, Dallan I. Endoscopic Endonasal Management of Orbital Pathologies. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2015;26(3):463–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nec.2015.03.001. Important paper elucidating the surgical technique and outcome of the endonasal endoscopic approach to the optic nerve canal.
Horiguchi K, Murai H, Hasegawa Y, Mine S, Yamakami I, Saeki N. Endoscopic endonasal trans-sphenoidal optic nerve decompression for traumatic optic neuropathy--technical note. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2010;50(6):518–22.
• Locatelli M, Caroli M, Pluderi M, Motta F, Gaini SM, Tschabitscher M, et al. Endoscopic transsphenoidal optic nerve decompression: an anatomical study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2011;33(3):257–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0734-1. Important study describing topographic anatomy and anatomical landmarks.
• Hart CK, Theodosopoulos PV, Zimmer LA. Anatomy of the optic canal: a computed tomography study of endoscopic nerve decompression. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2009;118(12):839–44. Important CT-based study to identify the most important anatomical landmarks and topography.
• Gogela SL, Zimmer LA, Keller JT, Andaluz N. Refining operative strategies for optic nerve decompression: a morphometric analysis of transcranial and endoscopic endonasal techniques using clinical parameters. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2018;14(3):295–302. https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opx093. Very important CT-based study on the decompression circumference that can be achieved by different surgical techniques.
Di Somma A, Andaluz N, Gogela SL, Cavallo LM, Keller JT, Prats-Galino A, et al. Surgical freedom evaluation during optic nerve decompression: laboratory investigation. World Neurosurg. 2017a;101:227–35.
Di Somma A, Cavallo LM, de Notaris M, Solari D, Topczewski TE, Bernal-Sprekelsen M, et al. Endoscopic endonasal medial-to-lateral and transorbital lateral-to-medial optic nerve decompression: an anatomical study with surgical implications. J Neurosurg. 2017b;127(1):199–208. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.8.JNS16566.
Mesquita Filho PM, Prevedello DM, Prevedello LM, Ditzel Filho LF, Fiore ME, Dolci RL, et al. Optic canal decompression: comparison of 2 surgical techniques. World Neurosurg. 2017;104:745–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.04.171.
• Zhao Y, Duan H, Liu J, Cheng K, Han Y, Li Y. Three-dimensional radiologic study on index measurement of endonasal endoscopic optic nerve decompression. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(6):1598–602. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000003932. Important study elucidating the anatomy and topography of the optic nerve canal and posterior ethmoid/sphenoid based on CT scans.
• Abhinav K, Acosta Y, Wang WH, Bonilla LR, Koutourousiou M, Wang E, et al. Endoscopic endonasal approach to the optic canal: anatomic considerations and surgical relevance. Neurosurgery. 2015;11(Suppl 3):431–445; discussion 445–6. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000900. Important paper on the anatomy and topography of the optic nerve canal and its effect on the endoscopic endonasal technique.
Wang X, Wu W, Zhang H, Lan Q. Endoscopic optic nerve decompression through supraorbital keyhole extradural approach: a cadaveric study. Turk Neurosurg. 2017;27(2):212–6. https://doi.org/10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.15298-15.1.
• Bleier BS, Healy DY Jr, Chhabra N, Freitag S. Compartmental endoscopic surgical anatomy of the medial intraconal orbital space. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014;4(7):587–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.21320. Important study regarding identification of the neurovascular bundle and supply of the medial rectus muscle.
Gaab MR. Instrumentation: endoscopes and equipment. World Neurosurg. 2013;79(2 Suppl):S14.e11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2012.02.032.
Jacquesson T, Abouaf L, Berhouma M, Jouanneau E. How I do it: the endoscopic endonasal optic nerve and orbital apex decompression. Acta Neurochir. 2014;156(10):1891–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2199-1.
Garg R, Varshney R, Lee JT, Krantz K, Keschner DB. New instrumentation in endoscopic medial orbital decompression. Laryngoscope. 2016;126(9):1981–3. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.25939.
• Liu Y, Yu H, Zhen H. Navigation-assisted, endonasal, endoscopic optic nerve decompression for the treatment of nontraumatic optic neuropathy. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2018.12.009. Important study evaluating the impact of the use of a navigation system on the effect of decompression in non-traumatic optic neuropathy.
Jacquesson T, Berhouma M, Jouanneau E. Response to: "considerations about endoscopic endonasal optic nerve and orbital apex decompression". Acta Neurochir. 2015;157(4):631–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-015-2357-0.
Ference EH, Sindwani R, Tan BK, Chandra RK, Kern RC, Conley D, et al. Open versus endoscopic medial orbital decompression: utilization, cost, and operating room time. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2016;30(5):360–6. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2016.30.4350.
Reich SS, Null RC, Timoney PJ, Sokol JA. Trends in orbital decompression techniques of surveyed American Society of Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Members. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;32(6):434–7.
Chen M, Jiang Y, Pang WH, Li N, Niu YZ, Zhao H. A 212 cases analysis of treatment for traumatic optic neuropathy by nasal endoscopic opticnerve decompression. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017;31(18):1411–4. https://doi.org/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2017.18.008.
Gupta D, Gadodia M. Transnasal endoscopic optic nerve decompression in post traumatic optic neuropathy. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;70(1):49–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-017-1211-5.
• DeKlotz TR, Stefko ST, Fernandez-Miranda JC, Gardner PA, Snyderman CH, Wang EW. Endoscopic endonasal optic nerve decompression for fibrous dysplasia. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2017;78(1):24–9. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1584078. Important paper on optic nerve decompression in patients with fibrous dysplasia.
Sowerby LJ, Rajakumar C, Allen L, Rotenberg BW. Urgent endoscopic orbital decompression for vision deterioration in dysthyroid optic neuropathy. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anorl.2018.08.007.
Chen F, Zuo K, Feng S, Guo J, Fan Y, Shi J, et al. A modified surgical procedure for endoscopic optic nerve decompression for the treatment of traumatic optic neuropathy. N Am J Med Sci. 2014;6(6):270–3. https://doi.org/10.4103/1947-2714.134372.
Ponto KA, Zwiener I, Al-Nawas B, Kahaly GJ, Otto AF, Karbach J, et al. Piezosurgery for orbital decompression surgery in thyroid associated orbitopathy. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;42(8):1813–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2014.06.020.
Kong DS, Shin HJ, Kim HY, Chung SK, Nam DH, Lee JI, et al. Endoscopic optic canal decompression for compressive optic neuropathy. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18(11):1541–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2011.02.042.
Beer-Furlan A, Evins AI, Rigante L, Burrell JC, Anichini G, Stieg PE, et al. Endoscopic extradural anterior clinoidectomy and optic nerve decompression through a pterional port. J Clin Neurosci. 2014;21(5):836–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2013.10.006.
Berhouma M, Jacquesson T, Abouaf L, Vighetto A, Jouanneau E. Endoscopic endonasal optic nerve and orbital apex decompression for nontraumatic optic neuropathy: surgical nuances and review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus. 2014;37(4):E19. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.7.FOCUS14303.
Sia DI, Chan WO, Wormald PJ, Davis G, Selva D. Decompression of benign orbital apex lesion via medial endoscopic approach. Orbit. 2012;31(5):344–6. https://doi.org/10.3109/01676830.2012.678920.
Hathiram BT, Khattar VS, Sonawane HP, Watve PJ. Traumatic optic neuropathy—our experience. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;62(3):229–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-010-0072-y.
Guy WM, Soparkar CN, Alford EL, Patrinely JR, Sami MS, Parke RB. Traumatic optic neuropathy and second optic nerve injuries. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014;132(5):567–71. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2014.82.
•• Yan W, Chen Y, Qian Z, Selva D, Pelaez D, Tu Y, et al. Incidence of optic canal fracture in the traumatic optic neuropathy and its effect on the visual outcome. Br J Ophthalmol. 2017;101(3):261–7. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2015-308043. Largest retrospective comparative cases series on endoscopic optic nerve decompression in patients with TON with and without optic nerve canal fracture.
Welkoborsky HJ, Möbius H, Bauer L, Wiechens B. Traumatic optic nerve neuropathy. Longterm results following microsurgical optic nerve decompression. HNO. 2011;59(10):997–1004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00106-011-2266-3.
• Yu-Wai-Man P, Griffiths PG. Surgery for traumatic optic neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;19:CD005024. Cochrane database review of the results of optic nerve decompression in TON patients. Additional information about spontaneous recovery and axonotmesis.
Jiang N, Zhao G, Yang S, Lin J, Hu L, Che C, et al. A retrospective analysis of eleven cases of invasive rhino-orbito-cerebral mucormycosis presented with orbital apex syndrome initially. BMC Ophthalmol. 2016;16:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-016-0189-1.
Medsinge A, Sylvester C, Tyler-Kabara E, Stefko ST. Bilateral endoscopic optic nerve decompression in an infant with osteopetrosis. J AAPOS. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2018.05.012.
• Tarrats L, Hernández G, Busquets JM, Portela JC, Serrano LA, González-Sepúlveda L, et al. Outcomes of endoscopic optic nerve decompression in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017;7(6):615–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.21927. Large cases series elucidating the results of endoscopic optic nerve decompression in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension.
Xie D, Yu H, Ju J, Zhang L. The outcome of endoscopic optic nerve decompression for bilateral traumatic optic neuropathy. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(4):1024–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000003743.
• Dhaliwal SS, Sowerby LJ, Rotenberg BW. Timing of endoscopic surgical decompression in traumatic optic neuropathy: a systematic review of the literature. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016;6(6):661–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.21706. Meta-analysis with a systematic review of the literature to elucidate the possible impact of the interval between trauma and surgery on functional outcome.
Tong Y, Chen G, Jiang F, Wu W. Successful delayed treatment of the traumatic orbital apex syndrome by nasal endoscopic decompression surgery. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2015;63(9):728–30. https://doi.org/10.4103/0301-4738.171005.
Emanuelli E, Bignami M, Digilio E, Fusetti S, Volo T, Castelnuovo P. Post-traumatic optic neuropathy: our surgical and medical protocol. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015;272(11):3301–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3408-5.
• Xu R, Chen F, Zuo K, Ye X, Yang Q, Shi J, et al. Endoscopic optic nerve decompression for patients with traumatic optic neuropathy: is nerve sheath incision necessary? ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2014;76(1):44–9. https://doi.org/10.1159/000358305. Important study examining the effect of nerve sheath incision on outcome in patients with TON.
• Song Y, Li H, Ma Y, Li W, Zhang X, Pan X, et al. Analysis of prognostic factors of endoscopic optic nerve decompression in traumatic blindness. Acta Otolaryngol. 2013;133(11):1196–200. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2013.822556. Recommended paper elucidating preoperative blindness vs. preoperative residual vision as a prognostic factor for functional outcome following optic nerve decompression in TON.
• Yang QT, Zhang GH, Liu X, Ye J, Li Y. The therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic optic nerve decompression and its effects on the prognoses of 96 cases of traumatic optic neuropathy. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72(5):1350–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3182493c70. Large case series elucidating prognostic factors of endoscopic nerve decompression in patients with TON.
Peng A, Li Y, Hu P, Wang Q. Endoscopic optic nerve decompression for traumatic optic neuropathy in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;75(8):992–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2011.05.004.
Mabuchi F, Aihara M, Mackey MR, Lindsey JD, Weinreb RN. Optic nerve damage in experimental mouse ocular hypertension. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:4321–30.
Levin LA. Intrinsic survival mechanisms for retinal ganglion cells. Eur J Ophthalmol. 1999;9(Suppl. I):12–6.
Wu W, Sia DI, Cannon PS, Selva D, Tu Y, Qu J. Visual acuity recovery in traumatic optic neuropathy following endoscopic optic nerve decompression: a case report. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;27(1):e13–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0b013e3181dc8323.
Neo WL, Chin DCW, Huang XY. Rhinogenous optic neuritis with full recovery of vision – the role of endoscopic optic nerve decompression and a review of literature. Am J Otolaryngol. 2018;39(6):791–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2018.08.008.
Holl DC, Hardillo JAU, Dammers R, van der Schroeff MP, van der Lugt A. Cystic degeneration of craniofacial fibrous dysplasia. World Neurosurg. 2018;120:159–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.08.175.
Shibata T, Tanikawa M, Sakata T, Mase M. Urgent optic nerve decompression via an endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach for craniopharyngioma in a 12-month-old infant: a case report. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2018;53(3):182–7. https://doi.org/10.1159/000487086.
Li E, Howard MA, Vining EM, Becker RD, Silbert J, Lesser RL. Visual prognosis in compressive optic neuropathy secondary to sphenoid sinus mucocele: a systematic review. Orbit. 2018;37(4):280–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/01676830.2017.1423087.
Lin CC, Chao TK, Chen TH, Wang JK. Compressive optic neuropathy caused by cholesterol granuloma in the posterior ethmoid sinus. Eye Sci. 2015;30(1):31–3.
Aldea S, Bică D, Gobej I, Bennis S, Baussart B, Mireau E, et al. Bilateral orbital and optic nerve endoscopic endonasal decompression for nonspecific inflammatory orbital disease: case report. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2013;74(Suppl 1):e133–5. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1327446.
Yildirim AE, Karaoglu D, Divanlioglu D, Secen AE, Gurcay AG, Cagil E, et al. Endoscopic endonasal optic nerve decompression in a patient with pseudotumor cerebri. J Craniofac Surg. 2015;26(1):240–2. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000001294.
Sencer A, Akcakaya MO, Basaran B, Yorukoglu AG, Aydoseli A, Aras Y, et al. Unilateral endoscopic optic nerve decompression for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a series of 10 patients. World Neurosurg. 2014;82(5):745–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2014.03.045.
• Steinsapir KD, Goldberg RA. Traumatic optic neuropathy: an evolving understanding. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011;151:928–33. Important paper for understanding the pathophysiology of traumatic optic neuropathy.
Kozub J, Shen JH, Joos KM, Prasad R, Hutson MS. Optic nerve sheath fenestration using a Raman-shifted alexandrite laser. Lasers Surg Med. 2016;48(3):270–80. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.22456.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Endoscopic Orbital Surgery
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Welkoborsky, H.J., Kuestermeyer, J., Steinke, K.V. et al. Endoscopic Optic Nerve Decompression: Indications, Technique, Results. Curr Otorhinolaryngol Rep 7, 153–164 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40136-019-00235-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40136-019-00235-z