Abstract
Introduction
Improvement of health in human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) patients on antiretroviral therapy (ART) is characterised by an increase in CD4 cell counts and a decrease in viral load to undetectable levels. In modelling HIV/AIDS progression in patients, researchers mostly deal with either viral load levels only or CD4 cell counts only, as they expect these two variables to be collinear. In this study, both variables will be in one model.
Methods
Principal component variables are created by fitting a regression model of CD4 cell counts on viral load levels to improve the efficiency of the model. The new orthogonal covariate is included to represent the CD4 cell counts covariate for the continuous time-homogeneous Markov model defined. Viral load levels are categorised to define the states for the Markov model.
Results
The likelihood ratio test and the estimated AICs show that the model with the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate gives a better prediction of mortality than the model in which the covariate is excluded. The study further revealed high accelerated mortality rates from undetectable viral load levels as well as accelerated risks of viral rebound from undetectable viral level for patients with lower CD4 cell counts than expected.
Conclusion
Inclusion of both viral load levels and CD4 cell counts, monitoring and management in time homogeneous Markov models help in the prediction of mortality in HIV/AIDS patients on ART. Higher CD4 cell counts improve the health and consequently survival of HIV/AIDS patients.
Similar content being viewed by others

Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The development of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) has substantially reduced morbidity and mortality in the human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) population [1]. HAART reduces the viral load of circulating HIV by blocking replication at multiple points in the virus life cycle [2], resulting in an increase in CD4 cell counts and increased life expectancy of individuals infected with HIV. Thus, making CD4 cell counts and viral load the fundamental laboratory markers regularly used for patient monitoring and management [3], in addition to predicting HIV/AIDS disease progression or treatment outcomes [4].
However, although the primary predictor of HIV transmission is HIV viral load, relatively fewer HIV modelling studies include a detailed description of the dynamics of HIV viral load along stages of HIV disease progression. This could be due to the unavailability of data on viral load, particularly from low- and middle-income countries that have historically relied on monitoring CD4 cell counts for patients on ART because of higher costs of viral load testing [5]. However, sometimes, both CD4 cell counts and viral load covariates information is available.
Estill et al. [6] investigated the benefits of viral load routine monitoring for reducing HIV transmission. They developed a stochastic mathematical model representing 1000 simulations for both CD4 cell counts monitoring and viral load routine monitoring. Their findings revealed that viral load routine monitoring and managing in patients reduce both cohort viral load and transmissions by 31%. Rose et al. [7] investigated frameworks for the analysis of viral load. They came up with two frameworks: the single measure viral load and the repeated measure viral load. Their findings indicated that the repeated measure viral load has more precision than the single measure viral load because it utilises all available viral load data, has more statistical power, and also avoids subjectivity of defining a “window”. Thus, in this study, we propose a repeated measure viral load monitoring and management using a Markov stochastic model.
Mathematical models have been extensively used in research into the epidemiology of HIV/AIDS, because they play an important role in improving our understanding of major factors contributing to the spread of this virus. It has also been argued that multi-state stochastic models are useful tools for studying complex dynamics such as chronic disease and also in determining factors associated with the progression between different stages of the disease [8, 9]. A Markov process is defined as a type of stochastic process in which a system changes in a random manner between different states. However, for most of these studies, states of the Markov processes are based on CD4 cell counts. For example, Titus analysed HIV dynamics using a discrete-time Markov chain mathematical model based on simulated CD4 states [10]. Dessie [9] used a CD4-based Markov model to determine the factors associated with the progression between different stages of the disease for individuals on antiretroviral therapy (ART).
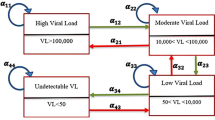
In this study, a continuous-time-homogeneous Markov process is used to model the progression of HIV/AIDS patients. We define HIV/AIDS progression based on five viral load states, measured in copies/µL, followed by the end point, death. More importantly, among the determinants of HIV/AIDS, both the viral load counts and CD4 cell counts are included in the same model, thus making this research different from previous studies. The CD4 cell count covariate is included and the effect of collinearity with viral load is corrected for using the principal component approach. In addition to that, effects of non-adherence to treatment, viral load baseline (VLBL), age and gender on transition intensities is assessed. Transitions between the viral load states is considered to be bi-directional using data recorded from a cohort of 320 HIV+ patients from a wellness clinic in Bela Bela, South Africa.
Continuous-Time Markov Processes
Transitions between states are assumed to follow a stochastic Markov process, that is, transitions to the next state depend only on the current state occupied by a patient. The previous states occupied by an individual do not matter; that is, the memoryless property of the Markov models. These transitions are described using the transition probabilities (\(p_{ij} (t)\)), transition intensities (\(\alpha_{ij}\)), from state i to state j. The functions \(p_{ij} (t)\) are continuously differentiable and are subject to the initial condition:
where \(\delta_{ij}\) is a kronecker delta, \(p_{ij} \left( 0 \right) = 1, \,\,\,\,i = j\) means the patient’s state definitely does not change when no time elapses and \(p_{ij} \left( 0 \right) = 0,\,\,\,i \,{\ne}\,\, j\) means that, when no time elapses, we are sure that the patient’s state cannot change with certainty. The transition intensity is defined as;
and \(\alpha_{ii} (t) = - \sum\nolimits_{j \ne i} {\alpha_{ij} (t)}\) for each \(i \in C\). In this study, transition probabilities depend only on the elapsed time and not on the chronological time. Thus, the Markov process is time-homogeneous, implying that \(p_{ij} \left( {t,t + s} \right) = p_{ij} \left( s \right)\) and \(\alpha_{ij} \left( t \right) = \alpha_{ij}\).
The effect of the above explanatory variables (covariates) on the transition intensities is modelled using the proportional intensities:
where \(\varvec{Z}\) is a \(k\)-dimensional vector of explanatory variables, \(\beta_{ij}\) is a vector of \(k\) regression parameters relating to the instantaneous rate of transitions from state \(i\) to state \(j\) to the covariates \(\varvec{Z},\) and \(\alpha_{ij}^{(0)}\) is the baseline transition intensities with covariates set to their means.
Methods
Data Description
The model is applied to data from a heterosexual group of 320 HIV patients on HAART from a Wellness clinic in Bela Bela, South Africa, from 2005 to 2010. These patients were observed after 3 months of treatment uptake and every 6 months thereafter. This yielded 2259 observations. Of these patients, 224 were females and 96 were males, 172 were aged between 15 and 45 years and 72 were over 45 years. The mean age of the patients at enrolment was 40.62 years. A total of 267 had a VLBL above 10,000 copies/µL and 49 had a VLBL below 10,000 copies/µL. At enrolment, the mean viral load was 138 208 copies/µL with a maximum of 818,600 copies/µL. A total of 226 patients had a CD4 baseline below 200 cells/mm3 and 96 had a CD4 baseline above 200 cells/mm3. During the course of treatment, a number of factors were considered. These include non-adherence to treatment therapy, treatment change, treatment line and resistance to treatment, with 36 showing some signs of non-adherence to treatment which influenced the need for treatment change.
For each and every assessment time point, blood samples were obtained from each patient, and the plasma HIV RNA was measured using an Amplicor HIV-1 monitor assay kit which has a lower limit of sensitivity of 50 copies/µL. Thus, HIV RNA below 50 copies/µL is undetectable.
At \(t = 0\), the regimens that were mostly administered to patients were the triple combination therapy, d4T-3TC-EFV (208 patients) and d4T-3TC-NVP (92 patients). d4T and 3TC represent Stavudine and Lamivudine, respectively, which fall into the nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTI) class. EFV and NVP stand for Efavirenz and Nevirapine, respectively, and are from the non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTI) class.
In patients who showed some signs of non-adherence, d4T was substituted by AZT (Zidovudine). A switch from d4T-3TC-EFV to AZT-3TC-EFV was most common, rising from 10 patients in the first 6 months to 92 patients at 30 months. During the same period, the number of patients who switched from d4T-3TC-NVP to AZT-3TC-NVP rose from 6 to 45. After 1 year of treatment uptake, 1 patient was introduced to FTC-TDF-EFV and, after 3.5 years, the frequency increased to 10 patients. Another combination of FTC-TDF-NVP was also introduced to 3 patients after 2 years, and the number rose to 7 after 3 years. AZT-3TC-LPV/r was also administered, and at t = 0, 2 patients were administered with this triple combination. Other treatment combinations that were administered include FTC-TDF-NVP, AZT-ddI-LPV/r, d4T-3TC-LPV/r, ddI-d4T-3TC, and FTC-TDF-LPV/r. However, these were not administered frequently.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
The procedures used in this study were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the University of Venda, South Africa (Protocol number SMNS/13/MBY/01/0625), in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its subsequent amendments. Additionally, permission to access health facilities was obtained from the Limpopo Provincial Department of Health, South Africa, and the collaborating health facilities. Informed consent was obtained from the study participants prior to their involvement, and the data obtained were stripped of personal identifiers to ensure the confidentiality of the participants.
Principal Component Analysis
Principal component analysis is a technique used to combine highly correlated factors into principal components that are much less highly correlated with each other, which improves the efficiency of the model.
In this study, the predictive power of viral load values (\(I_{1}\)) and CD4 values (\(I_{2}\)) is explored. Two new, uncorrelated factors, \(I_{1}^{*}\) and \(I_{2}^{*}\), can be constructed as follows:
Then, we carry out a linear regression analysis to determine the parameters \(\gamma_{1}\) and \(\gamma_{2}\) in the equation:
\(\gamma_{1}\) and \(\gamma_{2}\) are the intercept and slope parameters of the regression model, respectively, and \(\varepsilon_{1}\) is the ‘error’ term or residual, which by definition is independent of \(I_{1}^{*} = I_{1}\).
We then set:
By construction, \(I_{2}^{*}\) is uncorrelated with the viral load values (\(I_{1}\)), since \(I_{2}^{*} = \varepsilon_{1}\), the residual term in the equation. \(I_{2}^{*}\) in the model explains the component of mortality or HIV/AIDS progression that cannot be explained by the viral load values alone (or in the absence of CD4 cell counts).
The residuals (\(I_{2}^{*}\)) from the fitted model are included with the original HIV data as the new orthogonal variable, the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate (residuals). These residuals are coded as “1” for negative residuals and “0” for positive residuals. A continuous-time Markov model for the effects of age, gender, VLBL, non-adherence (NA), and orthogonal CD4 cell counts (\(I_{2}^{*}\)) on HIV progression based on the viral load is fitted using the “msm” package for multistate modelling in R. The variables in the model are coded as follows:
A negative CD4 cell count residual implies that the observed CD4 cell count is lower than the expected CD4 cell count, given the viral load levels of the patient, and a positive residual means having a higher CD4 cell count than expected.
Model Formulation
Consider a stochastic process \(\{ V\left( t \right), t \in [0, 5){\text{years}}\}\) defined on a finite state space \(V = \{ 1,2,3,4,5,6\}\) based on viral load states as defined above. \(V\left( t \right)\) represents the viral load state of an HIV/AIDS patient at time \(t\). This process represents a Markov process if \(\forall s,t \ge 0\) and for every \(i,j \in V\)
The above equation implies that a Markov process is memoryless, that is, the future transitions depend on the entire history only through the present state.
HIV/AIDS progression is based on viral load states, and possible transitions between these states are shown in Fig. 1. The transition between states is assumed to be bi-directional, that is, movement from state i to state \(i \pm 2\) is always via state \(i \pm 1,\) where \(i = 1,2,3,4,5\) define the live states based on viral load. The model allows for reverse transition due to the efficacy of treatment and forward due to non-adherence to treatment. Transitions between states are shown by the arrows.
Based on Fig. 1, the transition rates are defined as follows:
Q is a 6×6 matrix and its elements \(\alpha_{ij}\) are the instantaneous rates of transition from one state to another subject to the conditions that \(\alpha_{ij} = 0, i \ne j\) and \(\sum\nolimits_{j = 1}^{6} {\alpha_{ij} } = 0\) so that \(\alpha_{ii} = - \sum\nolimits_{i \ne j} {\alpha_{ij} ,} \quad i \in V\backslash 6\). \(\alpha_{ij}\) is independent of time because the process is assumed to be homogeneous with respect to time. In the next section, the parameters of our models are estimated including the transition rates.
The effect of the above explanatory variables (covariates) on the transition intensities is modelled using the proportional intensities:
where \(\varvec{Z}\) is a \(k = 5\)-dimensional vector of explanatory variables \({\text{VLBL}}, {\text{Gender}},\,\,{\text{Age}},\,\,{\text{Non-adherence}}, {\text{CD}}4 {\text{orthogonal }}(I_{2}^{*} )\). Thus, the transition intensity for a patient \(h\) in this study is given by the model:
For this model, \(\alpha_{ij}^{(0)}\) are the baseline transition intensities that refer to a patient with age category 0 (over 45 years old), gender = 0 (female), VLBL = 0 (below 10,000 copies/µL, adherence to treatment and positive \(I_{2}^{*}\), \(\beta_{ij}\) is a vector of \(k\) regression parameters relating the instantaneous rate of transitions from state \(i\) to state \(j\) to the covariates \(\varvec{Z}\). The transition intensities,\(\alpha_{ij}\), are presented in rates per year. \(\alpha_{ij}\) are the elements of a \(6 \times 6\) transition intensity matrix \(Q\) from a continuous time-homogeneous Markov process.
An important aspect is the inclusion of both \({\text{VLBL}}_{\text{h}}\) and \(I_{2}^{*}\) (the orthogonal CD4 covariate) derived after allowing for collinearity.
Assessment of the Fitted Models
Based on Eq. (1), two nested models are fitted: one of the models excludes the effect of the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate (nested model) and the other includes all covariates including the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate. These models are compared using their Akaike information criteria (AICs) defined as follows:
where \(- 2 \times {\text{Log}}\left( {\text{likelihood}} \right)\) represents the bias, \(2k\) represents the variance and \(k\) is the number of estimated parameters in the fitted model. The model with the minimum AIC is considered as the better model. Further assessment of the fitted nested models is carried out using the likelihood ratio test (LRT). The value of the \({\text{LRT}} = - 2\log_{\text{e}} \left( {\frac{{L_{s} (\hat{\theta })}}{{L_{f} (\hat{\theta })}}} \right)\), where \(L_{s} (\hat{\theta })\) is the simple model (no CD4 cell count orthogonal) and \(L_{f} (\hat{\theta })\) is the full model (with CD4 cell count orthogonal).
Convergence of a Time-Homogeneous Markov Model
If a Markov model fails to converge, optimisation criteria result in a failure to calculate standard errors leading to the exclusion in the calculation of confidence intervals for the estimated parameters. After running the analysis using the ‘msm’ package in R, the statistical package warns if ‘optimisation has probably not converged to the maximum likelihood—Hessian matrix not positive definite.’ To ensure that the model converges, a scaling factor is used to normalise the likelihood and to prevent the overflow within the optimisation process.
Results
In this section, the combined effect of viral load and CD4 cell counts in the progression of HIV in patients on treatment is analysed. This is carried out by first fitting a time-homogeneous Markov model for the effects of the covariates, VLBL and NA, on HIV/AIDS progression based on viral load states. Secondly, a time-homogeneous Markov model for the effects of covariates, VLBL, NA, age and the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate is fitted. Comparison of these models is based on their −2 × Log-likelihood, AIC, likelihood ratio tests and also the percentage prevalence plots. The results are shown in the following subsections.
Time-Homogeneous Markov Model with the Effects of Orthogonal CD4 Cell Counts Covariate Excluded
A time-homogeneous Markov model is fitted for HIV/AIDS progression defined by viral load states. In this model, the effects of the covariates VLBL and NA, to the progression of HIV are considered. The relationship between these covariates and the transition intensities is defined by the following equation:
where \(\varvec{Z} = [{\text{VLBL}}, {\text{Gender}},\,\,\,{\text{Age}},\,\,\,{\text{Non-adherence }}]\) is a \(k = 4\)-dimensional vector of covariates and \(\beta_{ij}\) is a vector of \(k\) regression parameters relating the instantaneous rate of transitions from state \(i\) to state \(j\) to the covariates \(\varvec{Z}\) and baseline intensities \(\alpha_{ij}^{(0)}\) relating to the baseline transition from state \(i\) to state \(j\).
When fitting the time-homogeneous Markov model, the gender and age of HIV patients have no significant effects to HIV progression, hence their exclusion from the results (Table 1), in which the first column represents possible transitions from state i to state j, where i = 1,…,5 and j = 1,…,6. The second column represents the baseline transition intensities (with confidence intervals), the third column gives coefficients (with confidence intervals) to represents the effects of non-adherence to HIV progression, and the fourth column gives coefficients (with confidence intervals) to represent the effects of having a VLBL above 10,000 copies/µL to HIV progression. The results are given in Table 1.
The results from Table 1 show that, when a patient’s viral load is above 10,000 copies/µL (states 3, 4 and 5), rates of viral load suppression are higher than rates of viral load rebound. However, from state 2 (viral load between 50 and 10,000 copies/µL), the rates of viral rebound are higher than the rates of viral suppression. The rates of viral rebound are increased for patients who had problems in adhering to treatment therapy regardless of the original state.
Patients who started therapy with VLBL above 10,000 copies/µL experienced higher rates of viral rebound than patients who started therapy with VLBL below 10,000 copies/µL. Having a viral load above 10,000 copies/µL also accelerates the rates of transition to death from the undetectable viral load (state 1). The same group also experienced high risks of transition from state 2 and state 3, although the risk is lower than when the patients are in state 1.
The results from Table 1 also show a significant reduction in the rate of attaining an undetectable viral load for patients who were non-adherent to treatment (state 2-1). This is indicated by the exclusion of zero in the confidence interval of the estimated parameter. Although not significant, transitions to death for patients who were non-adherent are higher compared to that of adherent patients.
The results show wide confidence intervals for transitions to death from each of the live states. This indicates a relatively poor prediction of mortality by the fitted model. To obtain a better picture of how the fitted model predicts mortality, percentage prevalence in each state are plotted to compare the observed data from the expected data. The percentage prevalence plots are shown in Fig. 2.
Figure 2 shows that the expected percentage prevalence give a good fit of the observed percentage prevalence only for the live states, that is states 2, 3, 4 and 5. However, the expected percentage prevalence underestimates the observed prevalence for the death state and overestimates the observed prevalence for state 1. The other anomaly is that of experiencing more than 40% deaths towards the end of the study. This is a cause for concern since these patients were receiving antiretroviral therapy. This is a further confirmation that the model does not give a good prediction of mortality. A decision to include the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate in our model was made and is discussed in the next subsection.
Time-Homogeneous Markov Model with the Effects of Orthogonal CD4 Cell Counts Covariate Included
The orthogonal components for this model are obtained by regressing CD4 cell count on viral load as discussed earlier. The residuals from this model are then used to represent the orthogonal covariate, CD4 cell counts, and is now incorporated in the continuous-time Markov model.
The results from Table 2 show a significant model confirming correlation between CD4 cell counts and the viral load. After regressing CD4 cell counts on viral load, the residuals from the model are taken to represent the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate. These residuals are included with the original covariates and then coded as “1” for negative residuals and “0” for positive residuals. A negative CD4 residual implies having lower CD4 cell count than the expected given the viral load levels. A positive residual means having a higher CD4 cell count than the expected. The orthogonal covariate is then used together with the other covariates to determine the progression of HIV/AIDS based on the viral load states.
The relationship between these covariates and the transition intensities is defined by the following equation:
where \(\varvec{Z} = [{\text{VLBL}}, {\text{Gender}},{\text{Age}},{\text{Non-adherence}},{\text{orthogonal CD}}4 {\text{cell counts covariate }}]\) is a \(k = 5\)-dimensional vector of the covariates and \(\beta_{ij}\) is a vector of \(k\) regression parameters relating the instantaneous rate of transitions from state \(i\) to state \(j\) to the covariates \(\varvec{Z}\) and baseline intensities \(\alpha_{ij}^{(0)}\) relating to the baseline transition from state \(i\) to state \(j\). The inclusion of the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate has resulted in the significant effects of age on the progression of HIV, hence its inclusion in Table 3. However, the covariate gender is still not significant. The inclusion of the gender covariate together with the use of a scaling factor of 4000 resulted in a failure of convergence to a maximum likelihood and a non-positive Hessian matrix. The adjustment of the scaling factor to 5000 resulted in normalising the likelihood, leading to the convergence of the Markov model. Thus, the gender covariate is included after adjusting the scaling factor. The results are shown in Table 3.
The results from Table 3 show that, when the patient’s viral load is above 10,000 copies/µL, represented by states 3, 4 and 5, the rates of viral suppression are higher than the rates of viral rebound. However, once the viral load is below 10,000 copies/µL (states 2 and 1), patients experience higher rates of viral rebound than rates of viral suppression. This is a cause for concern, since state 1 represents the undetectable viral load level.
Table 3 shows that the risk of viral rebound from states 1 and 2 is higher in patients who initiated therapy with a VLBL above 10,000 copies/µL than in patients who initiated therapy with lower viral loads. Other factors that accelerate viral rebound from state 1 are negative CD4 residuals and non-adherence to treatment. From state 2, males experience higher risks of viral rebound than their female counterparts. However, when viral load is above 10,000 copies/µL, males have increased rates of transitions to good states and reduced rates of transition to bad states than females.
The results also show increased rates of transitions to death (state 6) from state 1. This is mainly caused by non-adherence to treatment followed by having a viral load above 10,000 copies/µL, age and then orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate. Thus, younger patients, below the age of 45 years, and patients with CD4 cell counts lower than expected have accelerated risks of death from state 1.
The estimated parameters in Table 3 have narrow confidence intervals for transitions that took place between live states: transitions from \(i \,{\text{to}} j\), where \(j\) is not an absorbing state. Transitions to death have wider confidence intervals. For transitions between live states, the estimated parameters for the variable CD4 cell counts orthogonal have narrow confidence intervals, indicating that the inclusion of the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate gives rise to more precise estimates than the first model. The model with the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate has a lower − 2 × Log-likelihood than the model without the covariate.
Figure 3 shows the percentage prevalence plots for each of the states given that CD4 residual is included in the model. Figure 3 helps in assessing whether the expected percentage prevalence gives a better fit of the observed prevalence in the death state (state 6) compared to the results in Fig. 2.
The results from Fig. 3 show that, if HIV progression is defined by viral load states with the inclusion of the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate, this results in a better fit of the observed prevalence. As a result, for the death state, the expected percentage prevalence state explains the observed percentage prevalence better than the model without the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate .
Assessment of the fitted models
The fitted models were assessed to identify the model that best describes the data. Assessment of the fitted models is carried using the likelihood ratio test and estimates of AICs. The model with the lowest AIC is considered as the best model for the observed data. Table 4 shows the results.
The likelihood ratio tests from Table 4 show that the continuous-time-homogeneous Markov model defined by viral load states with the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate, and including the gender variable, gives the best fit to the data. However, since the interest is in the lowest AIC for our model, the model with the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate, while excluding the gender variable, is the best model. Thus, a gender difference was not a good predictor of HIV progression based on viral load states together with the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate.
Discussion
In this study, a time-homogeneous Markov model has been developed to explain and predict the probability of death for HIV/AIDS patients. The states of the Markov model are based on viral load levels. A model for HIV/AIDS progression for the effects of VLBL, NA, gender and age is fitted first. From this model, the covariates age and gender were excluded, since they failed to predict HIV/AIDS progression based on viral load levels since their coefficients were insignificant. Next, we used a time-homogeneous model for the effects of the same covariates with the orthogonal CD4 covariate included. This resulted in the variable age contributing significantly to the HIV/AIDS progression. The variable gender had significant effects after adjusting the scaling factor from 4000 to 5000 to ensure convergence of the optimisation process. Randarajan et al. [11], in their study, also revealed the non-significant effects of the variable gender in viral suppression. However, this may not be comparable to our studies because they used a logistic regression model, while our findings are based on a continuous-time-homogeneous Markov model. Construction of the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate used the principal component approach to address the issue of collinearity of the viral load and the CD4 cell counts covariates. Most researchers deal with either of the two variables when developing models
The results from the analysis showed that, if HIV progression is defined by viral load states and the variable CD4 cell count is excluded from the model, the expected percentage prevalence underestimates mortality from a period of 0.5 years of treatment uptake. This resulted in a death prevalence of over 40% which is unrealistic considering patients were on ART.
The orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate was included in the continuous-time Markov model defined by viral load levels so that HIV mortality is explained and predicted in a better way. The results from the fitted model showed an improvement in the – 2 Log-likelihood compared to the model without the orthogonal CD4 cell counts covariate. The model also had the lowest AIC. The death prevalence from this model was lower than 20%.
The results also show high risks of viral rebound from undetectable viral load levels which was mainly caused by non-adherence to treatment, having negative CD4 residuals and starting therapy when the VLBL was above 10,000 copies/µL. Having CD4 cell counts that are lower than expected increases the rates of viral rebound from undetectable levels. These findings are also corroborated by the studies of Silveira et al. [12] which showed that a higher prevalence of undetectable viral load levels have been associated with lower levels of VLBL at the beginning of treatment. This supports the issues raised by Chesney [13] that, without proper adherence, antiretroviral agents are not maintained at a sufficient concentration to suppress HIV replication. Pasternak et al. [14], in their study, also demonstrated that incomplete ART adherence is associated with increased levels of cell-associated HIV-1 RNA.
Our findings also showed high risks of mortality from the undetectable viral load for non-adherent patients, patients who initiated therapy with a viral load level above 10,000 copies/µL, younger patients below the age of 45 years and patients whose CD4 cell counts were lower than expected. This could be due to the findings by Mujugira et al. [15], whose study revealed delayed ART initiation, failure to achieve viral suppression, and virologic rebound among young patients.
Continuous-time-homogeneous Markov models have the ability to handle multiple outcomes compared to the Kaplan–Meier and Cox proportional hazards models. However, its memoryless property places limitations on the disease history behaviour, especially when dealing with HIV patients on ART whose adherence to treatment is likely to improve with time.
The other limitation is that the study was limited to one centre.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the findings reveal the importance of Principal components approach in treating collinearity of the viral load and CD4 cell counts covariates when both are in the one model. As a result, we have discovered that having lower CD4 cell counts than expected results in accelerated risks of viral rebound from undetectable viral load levels,and also accelerated deaths from undetectable viral load levels. Thus, higher CD4 cell counts improve the health and consequently the survival of HIV/AIDS patients. The inclusion of both viral load and CD4 cell count in the one model give a better prediction of mortality.
Change history
06 December 2018
In the original publication, the following text was missing from the beginning of the Methods section in the main text “This study uses similar methods to those previously published.
References
Palella FJ Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, Loveless MO, Fuhrer J, Satten GA, Aschman DJ, Holmberg SD. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–60.
Cole SR, Hernan MA, Anastos K, Jamieson BD, Robins JM. Determining the effects of hghly actictive antiretroviral therapy on change in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA viral koad using a marginal structural left-censored mean model. Am J Epidemiol. 2007;166(2):219–27.
Mathieu E, Foucher Y, Dellamanica P, Doures JP. Parametric and non homogeneous semi-Markov process for HIV control. Methodol Comput Appl Probab. 2007;9:389–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11009-007-9033-7.
Hoffman RM, Black V, Technau K, et al. Effects of highly active antiretroviral therapy duration and regimen on risk for mother-to-child transmission of HIV in Johannesburg, South Africa. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2010;54(1):35–41.
Lecher S, Williams J, Fonjungo PN (2016) Progress with scale-up of HIV viral load monitoring—seven Sub-Saharan African Countries, January 2015–June 2016. Morbid Mortal Week Rep 65(47).
Estill J, Aubrière C, Egger M, Johnson L, Wood R, et al. Viral load monitoring of antiretroviral therapy, cohort viral load and HIV transmission in Southern Africa: a mathematical modelling analysis. AIDS. 2012;26:1403–13.
Rose CE, Gardener L, Girde JCS, et al. A comparison of methods for analysing viral load data in studies of HIV patients. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(6):e0130090.
Naresh R, Tripathi A, Omar S. Modelling the spread of AIDS epidemic with vertical transmission. Appl Math Comput. 2006;178:262–72.
Dessie ZG. Modeling HIV dynamics evolution using non-homogeneous semi-Markov pr0cess. Springer Plus. 2014;3:537.
Titus RK. Mathematical modeling of the spread of HIV/AIDS by Markov chain process. Am J Appl Math. 2016;4:235–46.
Randarajan S, Colby DJ, Truong G, et al. Factors associated ith HIV viral loads suppression on antiretroviral therapy in Vietman. J Virus Erad. 2016;2:94–101.
Silveira MPT, de Lourdes Draschler M, de Carvalho Leite J C, Pinheiro CAT, da Silveira VL. Predictors of undetectable plasma viral load in HIV-positive adults receiving antiretroviral therapy in Southern Brazil. Braz J Infect Dis. 2002;6(4):164–71.
Chesney M. Factors affecting adherence to antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;30(Suppl 2):S171–6.
Pasternak AO, de Bruin M, Jurriaans S, Bakker M, Berkhout B, Prins JM, Lukashov VV. Modest nonadherence to antiretroviral therapy promotes residual HIV-1 replication in the absence of virological rebound in plasma. J Infect Dis. 2012;206:1443–52.
Mujugira A, Celum C, Tappero JW, Ronald A, Mugo N, Baeten JM. Younger age predicts failure to achieve viral suppression and virologic rebound among HIV-1-infected persons in serodiscordant partnerships. Aids Res Human Retrovir. 2016;32(2):5. https://doi.org/10.1089/aid.2015.0296.
Acknowledgements
We thank the participants of the study.
Funding
No funding or sponsorship was received for this study or publication of this article.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Authorship Contributions
Claris Shoko devised the initial idea and drafted the first manuscript. Delson Chikobvu finalised and proofread the article. Claris Shoko and Delson Chikobvu contributed to the analysis and interpretation of the data. Pascal O. Bessong collected the data used in the current study and aided with both revisions to and proofreading of the final manuscript. All authors participated in critical revision of the manuscript drafts and approved the final version.
Disclosures
Claris Shoko, Delson Chikobvu and Pascal O. Bessong have nothing to disclose.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
The procedures used in this study were as approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the University of Venda, South Africa (Protocol number SMNS/13/MBY/01/0625), in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its subsequent amendments. Additionally, permission to access health facilities was obtained from the Limpopo Provincial Department of Health, South Africa, and the collaborating health facilities. Informed consent was obtained from study participants prior to their involvement; and data obtained was stripped of personal identifiers to ensure the confidentiality of the participants.
Data Availability
The datasets during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced Digital Features
To view enhanced digital features for this article go to https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.7172264.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Shoko, C., Chikobvu, D. & Bessong, P.O. A Markov Model to Estimate Mortality Due to HIV/AIDS Using Viral Load Levels-Based States and CD4 Cell Counts: A Principal Component Analysis Approach. Infect Dis Ther 7, 457–471 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40121-018-0217-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40121-018-0217-y