Abstract
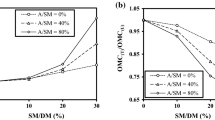
Contribution of cement manufacturing industries to global warming by emission of carbon dioxide gas has raised global concerns. In that case, geopolymer concrete (GPC) can act as an alternative to cement concrete. This paper presents mechanical and durability properties of GPC using 14 M sodium hydroxide solution. Optimum molarity is achieved replacing fly ash by silica fume by mass fractions of 5%, 10% and 15%. The mechanical properties of the concrete are obtained by conducting compressive, split tensile and flexural strength test. The durability properties are investigated by exposing the concrete specimens to aggressive chemical solutions of 2% sulphuric acid, 2% magnesium sulphate and 5% sodium chloride. The compressive strength of fly ash-based GPC at the age of 28 days varies from 16 to 38.5 MPa, whereas those of silica fume-blended GPC achieved up to 42.6 MPa. Further, the silica fume-blended GPC is found excellent resistance to chemical attack. It is observed that blending of silica fume with fly ash in GPC improves strength as well as exhibits satisfactory behaviour in aggressive environment, i.e. curing temperature of 70 °C. The concrete matrix is also investigated by conducting ultrasonic pulse velocity test and observing scanning electron microscopic images.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.G.S. Van Jaarsveld, J.S.J. Van Deventer, L. Lorenzen, The potential use of geopolymeric materials to immobilize toxic metals. Miner. Eng. 10(7), 659–669 (1997)
K.T. Nguyen, N. Ahn, T.A. Le, K. Lee, Theoretical and experimental study on mechanical properties and flexural strength of fly ash geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 106, 65–77 (2016)
M. Albitar, M.S.M. Ali, P. Visintin, M. Drechsler, Durability evaluation of geopolymer and conventional concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 136, 374–385 (2017)
A. Mehta, R. Siddique, Sulfuric acid resistance of fly ash based geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 146, 136–143 (2017)
D.V. Reddy, J.B. Edouard, K. Sobhan, Durability of fly ash-based geopolymer structural concrete in the marine environment. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 25(6), 781–787 (2013)
P. Nath, P.K. Sarker, V.B. Rangan, Early age properties of low-calcium fly ash geopolymer concrete suitable for ambient curing. Proc. Eng. 125, 601–607 (2015)
P. Nath, P.K. Sarker, Flexural strength and elastic modulus of ambient-cured blended low-calcium fly ash geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 130, 22–31 (2017)
A.A. Aliabdo, A.E.M.A. Elmoaty, H.A. Salem, Effect of water addition, plasticizer and alkaline solution constitution on fly ash based geopolymer concrete performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 121, 694–703 (2016)
P. Topark-Ngarm, P. Chindaprasirt, V. Sata, Setting time, strength and bond of high calcium fly ash GPC. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 27(7), 04014198 (2015)
F.U.A. Shaikh, Mechanical and durability properties of fly ash geopolymer concrete containing recycled coarse aggregate. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 5, 277–287 (2016)
A. Karthik, K. Sudalaimani, C.T.V. Kumar, Investigation on mechanical properties of fly ash-ground granulated blast furnace slag based self curing bio- geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 149, 338–349 (2017)
P. Nath, P.K. Sarker, Effect of GGBFS on setting, workability and early strength properties of fly ash geopolymer concrete cured in ambient condition. Constr. Build. Mater. 66, 163–171 (2014)
F.N. Okoye, J. Durgaprasad, N.B. Singh, Effect of silica fume on the mechanical properties of fly ash based geopolymer concrete. Ceram. Int. 42, 3000–3006 (2016)
M. Rostami, K. Behfarnia, The effect of silica fume on durability of alkali activated slag concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 134, 262–268 (2017)
F.A. Memon, M.F. Nuruddin, N. Shafiq, Effect of silica fume on the fresh and hardened properties of fly ash based self-compacting geopolymer concrete. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 20(2), 205–213 (2013)
F.N. Okoye, J. Durgaprasad, N.B. Singh, Mechanical properties of alkali activated fly ash/kaolin based geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 98, 685–691 (2015)
ASTM C618-08, Standard specification for coal fly ash and raw or calcined natural pozzolan for use in concrete (American society for testing and materials, Philadelphia, America, 2008)
IS: 3812 (Part I), Specifications for pulverized fuel ash (for use as pozzolana in cement, cement mortar and concrete)(Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi, India, 2003)
IS: 15388, Silica fume—Specification (Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi, India, 2003)
IS: 1727, Methods of test for pozzolanic materials (Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi, India, 1967)
IS: 383, Specification for coarse and fine aggregates from natural sources for concrete (Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi, India, 1970)
IS: 2720 (Part III), Methods of test for soil (Specific gravity of fine, medium and coarse grained soil) (Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi, India, 1980)
IS: 1199, Methods of sampling and analysis of concrete (Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi, India, 1959)
M. Albitar, P. Visintin, M.S.M. Ali, M. Drechsler, Assessing behaviour of fresh and hardened geopolymer concrete mixed with class-F fly ash. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 19(5), 1445–1455 (2015)
R.H. Haddad, O. Alshbuol, Production of geopolymer concrete using natural pozzolan: a parametric study. Constr. Build. Mater. 114, 699–707 (2016)
IS: 2185 (Part I) Concrete masonry units—Specifications (Hollow and solid concrete blocks) (Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi, India, 2005)
IS: 516, Methods of test for strength of concrete (Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi, India, 1959)
IS: 5816 Splitting tensile strength of concrete—method of test (Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi, India, 1999)
IS: 13311 (Part I), Non-destructive testing of concrete—methods of test (Ultrasonic pulse velocity) (Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi, India, 1992)
D.M.J. Sumajouw, D. Hardjito, S.E. Wallah, B.V. Rangan, Fly ash-based geopolymer concrete: study of slender reinforced columns. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 3124–3130 (2007)
D.M.J. Sumajouw, D. Hadrjito, S.E. Wallah, B.V Rangan, Flexural behaviour of reinforced fly ash-based geopolymer concrete beams, in: Concr. 05, CIA 22nd Bienn. Conf., 2005
E.H. Chang, P. Sarker, N. Lloyd, B.V. Rangan, Bond behaviour of reinforced fly ash-based geopolymer concrete beams, in: Proc. 24th Bienn. Conf. Concr. Inst. Aust., Concrete Institute of Australia, 2009
K. Andri, Alkali-activation of Fly Ash/MIRHA Blend in Geopolymer Concrete for In-situ Application [Dissertation], Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, Kuala Lumpur, 2012
B.S. Choo, J.B. Newman, Advanced concrete technology: constituent materials (Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2003)
Z.X. Yang, N.R. Ha, M.S. Jang, K.H. Hwang, J.K. Lee, The effect of SiO2 on the performance of inorganic sludge-based structural concretes. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 10, 266–268 (2009)
D. Dutta, S. Thokchom, P. Ghosh, S. Ghosh, Effect of silica fume additions on porosity of fly ash geopolymers. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 5, 74–79 (2010)
H.M. Khater, Effect of silica fume on the characterization of the geopolymer materials. Int. J. Adv. Struct. Eng. 5, 12 (2013)
T. Bakharev, Durability of geopolymer materials in sodium and magnesium sulfate solutions. Cem. Concr. Res. 35, 1233–1246 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jena, S., Panigrahi, R. & Sahu, P. Mechanical and Durability Properties of Fly Ash Geopolymer Concrete with Silica Fume. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. A 100, 697–705 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-019-00400-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-019-00400-z