Abstract
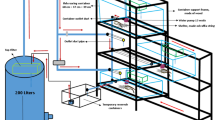
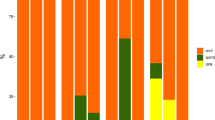
The present study investigated feed efficiency and growth performance of juvenile Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) cultured in tanks with different colors. Triplicate groups of experimental fish were distributed into 12 tanks, which showed four different tank colors, i.e. red, blue, green, and yellow. All the fish in the trial received the same diet for a period of 60 days. Forty fish with an average weight of 44 g were stocked in the tank. All experimental tanks were supplied with seawater of 22 ppt salinity with temperature ranging between 17–20 °C during the course of the experiment. Tank water volume in the experimental facility of the recirculating aquaculture system (RAS) was set to 40 L. The RAS system consisted of bio-filtration, UV filtration and gravel-mechanic filtration units. Results in the present study demonstrated that growth performance and feed utilization were affected by the tank colors tested in the trial. It is concluded that the selection of appropriate tank color might affect economic benefits in aquaculture facilities.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brännäs E, Alanärä A, Magnhagen C (2001) The social behaviour of fish. In: Keeling LJ, Gonyou HW (eds) Social behaviour in farm animals. CABI publishing, New York, pp 275–304
De Silva SS, Anderson TA (1994) Fish nutrition in aquaculture. Chapman & Hall, London, p 319
Chatain B, Ounais-Guschemann N (1991) The relationships between light and larvae of Sparus aurata. Spec Publ Eur Aquac Soc 15:310–313
Tamazouzt L, Chatain B, Fontainea P (2000) Tank wall colour and light level affect growth and survival of Eurasian perch larvae (Perca fluviatilis L.). Aquaculture 182(1–2):85–90
Pedreira MM, Sipaúba-Tavares LH (2001) Effect of light green and dark brown colored tanks on survival rates and development of tambaqui larvae, Colossoma macropomum (Osteichthyes, Serrasalmidae). Maringá 23(2):521–525
Howell BR (1979) Experiments on the rearing of larval turbot, Scophthalmus maximus L. Aquaculture 18:215–225
Matsuda H, Tsujigado A, Yamakawa T (1987) Effect of environmental factors on the survival and growth of larvae of stone founder Kareius bicoloratus. Bull Fish Res Inst Mie 2:45–50
Henne JP, Watanabe WO (2003) Effects of light intensity and salinity on growth, survival, and whole body osmolality of larval southern flounder Paralichthys lethostigma. J World Aquac Soc 34:450–465
Jentoft S, Oxnevad S, Aastveit AH, Andersen O (2006) Effects of tank wall color and up-welling water flow on growth and survival of Eurasian perch larvae (Perca fluviatilis). J World Aquac Soc 37:313–317
Papoutsoglou SE, Mylonakis G, Miliou H, Karakatsouli NP, Chadio S (2000) The effect of background colour on growth performances and physiological responses of scaled carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) reared in a closed circulated system. Aquac Eng 22:309–318
Papoutsoglou SE, Karakatsouli N, Chiras G (2005) Dietary l-tryptophan and tank colour effects on growth performance of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) juveniles reared in a recirculating system. Aquac Eng 32:277–284
Rotllant J, Tort L, Montero D, Pavlidis M, Martinez SE, Wendelaar B, Balm PHM (2003) Background colour influence on the stress response in cultured red porgy Pagrus pagrus. Aquaculture 223:129–139
Portz DE, Woodley CM, Cech JJ Jr (2006) Stress-associated impacts of short-term holding on fishes. Rev Fish Biol Fish 16:125–170
Strand Å, Alanärä A, Staffan F, Magnhagen C (2007) Effects of tank colour and light intensity on feed intake, growth rate and energy expenditure of juvenile Eurasian perch, Perca fluviatilis L. Aquaculture 272:312–318
Yigit M, Erdem M, Koshio S, Ergün S, Türker A, Karaali B (2006) Substituting fish meal with poultry by-product meal in diets for Black Sea turbot Psetta maeotica. Aquac Nutr 12:340–347
Okumuş İ, Mazlum MD (2002) Evaluation of commercial trout feeds: feed consumption, growth, feed conversion, carcass composition and bio-economic analysis. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 2:101–107
Yigit M, Erdem M, Aral O, Karaali B (2005) Nitrogen excretion patterns and postprandial ammonia profiles in Black Sea turbot (Scophthalmus maeoticus) under controlled conditions. Isr J Aquac Bamidgeh 57:231–240
Almendras JME (1994) Ammonia excretion rates of the sea bass, Lates calcarifer, in fresh and sea water. Isr J Aquac Bamidgeh 46:76–83
Howell BR (1979) Experiments on the rearing of larval turbot, Scophthalmus maximus L. Aquaculture 18:215–225
Duray MN, Estudillo CB, Alpasan LG (1996) The effect of bacground color and rotifer density on rotifer intake, growth and survival oft he grouper (Epinephelus suillus) larvae. Aquaculture 146:217–224
McLean E, Cotter P, Thain C, King N (2008) Tank color impacts performance of cultured fish. Ribarstvo 2:43–54
Imanpoor MR, Abdollahi M (2011) Effects of tank color on growth, stress response and skin color of juvenile caspian kutum Rutilus frisii Kutum. Glob Vet 6(2):118–125
Karakatsouli N, Papoutsoglou SE, Manolessos G (2007) Combined effects of rearing density and tank colour on the growth and welfare of juvenile white sea bream Diplodus sargus L. in a recirculating water system. Aquac Res 38:1152–1160
Arends RJ, Rotllant J, Metz JR, Mancera JM, Wendelaar Bonga SE, Flik G (2000) Α-MSH acetylation in the pitutitary gland oft he sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) in response to different backgrounds, confinement and air exposure. J Endocrinol 166:427–435
Höglund E, Balm PHM, Winberg S (2002) Behavioural and neuroendocrine effects of enviromental background colour and social interaction in Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus). J Exp Biol 205:2535–2543
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University, Marine Science and Technology Faculty to use their facility for the experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kesbiç, O.S., Yiğit, M. & Acar, Ü. Effects of Tank Color on Growth Performance and Nitrogen Excretion of European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Juveniles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 86, 205–210 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-014-0441-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-014-0441-5