Abstract
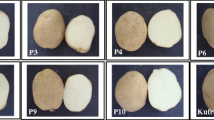
Interspecific potato somatic hybrids (here after referred as ‘cph-hybrids’) derived earlier through protoplast fusion (Solanum tuberosum + S. cardiophyllum) were used in this study. The genetic potential of cph-hybrids was assessed based on the field performance in the Indian sub-tropical conditions. In general, cph-hybrids exhibited higher plant stand, poor plant vigour and late foliage maturity as compared to the control potato var. Kufri Bahar. Yield performance of cph-hybrids was poor as compared to the control, but produced 3–6 times higher marketable tuber yield than the wild parent (S. cardiophyllum). All cph-hybrids possessed significantly higher tuber dry matter content (≥ 24%) than the parents (20.82%) and var. Kufri Bahar (18.52%), excellent keeping quality and showed high resistance to late blight. Thus, based on this study the promising cph-hybrids viz., Crd 6, Crd 10 and Crd16, can be used as parents in breeding for the improvement of important traits viz., higher tuber dry matter content, better keeping quality and high late blight resistance, along with adaptability under sub-tropical conditions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradshaw JE, Bryan GJ, Ramsay G (2006) Genetic resources (including wild and cultivated Solanum species) and progress in their utilisation in potato breeding. Potato Res 49:49–65
Cardi T, Mazzei M, Frusciante L (2002) Field variation in a tetraploid progeny derived by selfing a Solanum commersonii (+) S. tuberosum somatic hybrid: a multivariate analysis. Euphytica 124:111–119
Caruso I, Castaldi L, Caruso G, Frusciante L, Carputo D (2008) Breeding potential of Solanum tuberosum–S. commersonii pentaploid hybrids: fertility studies and tuber evaluation. Euphytica 164:357–363
Chakrabarti SK, Conghua X, Tiwari JK (eds) (2017) The potato genome. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66135-3
Chandel P, Tiwari JK, Ali N, Devi S, Shashi Sharma, Sanjeev Sharma, Luthra SK, Singh BP (2015) Interspecific potato somatic hybrids between Solanum tuberosum and S. cardiophyllum, potential sources of late blight resistance breeding. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult 123:579–589
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research. Wiley, New York, p 680
Gupta VK, Luthra SK, Singh BP (2015) Storage behaviour and cooking quality of Indian potato varieties. J Food Sci Technol 52:4863–4873
Jansky S (2006) Overcoming hybridization barriers in potato. Plant Breed 125:1–12
Luthra SK, Malik K, Gupta VK, Singh BP (2013) Evaluation of potato genotypes under high temperature stress conditions. Crop Improv 40:74–80
Luthra SK, Tiwari JK, Lal M, Chandel P, Kumar V, Singh BP (2016) Breeding potential of potato somatic hybrids: evaluations for adaptability, tuber traits, late blight resistance, keeping quality and backcross (BC1) progenies. Potato Res 59:375–391
Moller C, Frei U, Wenzel G (1994) Field evaluation of tetraploid somatic potato hybrids. Theor Appl Genet 88:147–152
Orczyk W, Przetakiewicz J, Nadoloska-Orczyk A (2003) Somatic hybrids of Solanum tuberosum—application to genetics and breeding. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult 74:1–13
Sarkar D, Tiwari JK, Sharma S, Poonam Sharma S, Gopal J, Singh BP, Luthra SK, Pandey SK, Pattanayak D (2011) Production and characterization of somatic hybrids between Solanum tuberosum L. and S. pinnatisectum Dun. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult 107:427–440
Shaner G, Finney RF (1977) The effect of nitrogen fertilization on the expression of slow mild-mildewing resistance in knox wheat. Phytopathology 67:1051–1056
Singh BP, Bhattacharyya SK (1995) Field resistance to late blight in four Indian potato cultivars. Potato Res 38:171–178
Singh PH (2002) Potato late blight caused by Phytophthora infestans and its management. Meerut College Meerut, CCS University, Meerut
Tiwari JK, Devi S, Ali N, Luthra SK, Kumar V, Bhardwaj V, Singh RK, Rawat S, Chakrabarti SK (2018) Progress in somatic hybridization research in potato during the past 40 years. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult 132:225–238
Tiwari JK, Devi S, Chandel P, Ali N, Bhardwaj V, Singh BP (2016) Organelle genome analysis in somatic hybrids between Solanum tuberosum and S. pinnatisectum revealed diverse cytoplasm type in potato. Agric Res 5:22–28
Tiwari JK, Kumar V, Devi S, Luthra SK, Chakrabarti SK, Rawat S, Nagesh M (2017) Genomics in management and genetic enhancement of potato germplasm. In: Chakrabarti SK, Conghua X, Tiwari JK (eds) The potato genome. Compendium of plant genomes. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66135-3_8
Tiwari JK, Poonam Kumar V, Singh BP, Sharma S, Luthra SK, Bhardwaj V (2013) Evaluation of potato somatic hybrids of dihaploid S. tuberosum (+) S. pinnatisectum for late blight resistance. Potato J 40:176–179
Tiwari JK, Poonam Sarkar D, Pandey SK, Gopal J, Kumar SR (2010) Molecular and morphological characterization of somatic hybrids between Solanum tuberosum L. and S. etuberosum Lindl. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult 103:175–187
Tiwari JK, Saurabh S, Chandel P, Devi S, Ali N, Bist CM, Singh BP (2015) Analysis of genetic and epigenetic changes in potato somatic hybrids between Solanum tuberosum and S. etuberosum by AFLP and MSAP Markers. Agric Res 4:339–346
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Director, ICAR-CPRI, Shimla and the Joint-Director, ICAR-CPRI Regional Station, Modipuram for necessary supports under the Biotechnology Programme (HORTCPRICIL201500300131).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SKL and JKT planned and executed the experiment; VK and ML conducted field/laboratory experiments for late blight testing/evaluations. SKL and JKT prepared the manuscript. All authors read and confirmed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luthra, S.K., Tiwari, J.K., Kumar, V. et al. Evaluation of Interspecific Somatic Hybrids of Potato (Solanum tuberosum) and Wild S. cardiophyllum for Adaptability, Tuber Dry Matter, Keeping Quality and Late Blight Resistance. Agric Res 8, 158–164 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40003-018-0369-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40003-018-0369-8