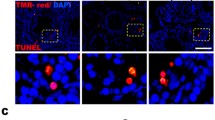
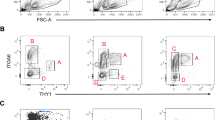
Abstract
Spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs) are essential for spermatogenesis throughout the lifespan of the male. However, the rarity of SSCs has raised the need for an efficient selection method, but little is known about culture conditions that stimulate monkey SSC proliferation in vitro. In this study, we report the development of effective enrichment techniques and in vitro culturing of germ cells from pre-pubertal monkey testes. Testis cells were analyzed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting techniques and were transplanted into the testes of nude mice to characterize SSCs. Thy-1-positive cells showed a higher number of colonies than the unselected control after xenotransplantation. Extensive colonization of monkey cells in the mouse testes indicated the presence of highly enriched populations of SSCs in the Thy-1-positive sorted cells. Furthermore, monkey testis cells were enriched by differential plating using extracellular matrix, laminin, and gelatin, and then cultured under various conditions. Isolation of monkey testicular germ cells by differential plating increased germ cell purity by 2.7-fold, following the combinational isolation method using gelatin and laminin. These enriched germ cells actively proliferated under culture conditions involving StemPro medium supplemented with bFGF, GDNF, LIF, and EGF at 37 °C. These results suggest that the enrichment and in vitro culture method proposed in the present study for harvesting a large number of functionally active monkey SSCs can be applied as the basis for efficient in vitro expansion of human SSCs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clermont Y, Leblond CP. Differentiation and renewal of spermatogonia in the monkey, Macacus rhesus. Am J Anat. 1959;104:237–73.
Heller CG, Clermont Y. Spermatogenesis in man: an estimate of its duration. Science. 1963;140:184–6.
Simorangkir DR, Marshall GR, Ehmcke J, Schlatt S, Plant TM. Prepubertal expansion of dark and pale type A spermatogonia in the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) results from proliferation during infantile and juvenile development in a relatively gonadotropin independent manner. Biol Reprod. 2005;73:1109–15.
Zhengwei Y, McLachlan RI, Bremner WJ, Wreford NG. Quantitative (stereological) study of the normal spermatogenesis in the adult monkey (Macaca fascicularis). J Androl. 1997;18:681–7.
Maki CB, Pacchiarotti J, Ramos T, Pascual M, Pham J, Kinjo J, et al. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of spermatogonial stem cells in adult primate testes. Hum Reprod. 2009;24:1480–91.
Ryu BY, Orwig KE, Kubota H, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL. Phenotypic and functional characteristics of spermatogonial stem cells in rats. Dev Biol. 2004;274:158–70.
Ryu BY, Kubota H, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL. Conservation of spermatogonial stem cell self-renewal signaling between mouse and rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:14302–7.
Orwig KE, Shinohara T, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL. Functional analysis of stem cells in the adult rat testis. Biol Reprod. 2002;66:944–9.
Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Toyokuni S, Shinohara T. CD9 is a surface marker on mouse and rat male germline stem cells. Biol Reprod. 2004;70:70–5.
Kim YH, Kim BJ, Kim BG, Lee YA, Kim KJ, Chung HJ, et al. Stage-specific embryonic antigen-1 expression by undifferentiated spermatogonia in the prepubertal boar testis. J Anim Sci. 2013;91:3143–54.
Brinster RL, Avarbock MR. Germline transmission of donor haplotype following spermatogonial transplantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:11303–7.
Brinster RL, Zimmermann JW. Spermatogenesis following male germ-cell transplantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:11298–302.
Kim BG, Kim YH, Lee YA, Kim BJ, Kim KJ, Jung SE, et al. Production of transgenic spermatozoa by lentiviral transduction and transplantation of porcine spermatogonial stem cells. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2014;11:458–66.
Kaul G, Kaur J, Rafeeqi TA. Ultrasound guided transplantation of enriched and cryopreserved spermatogonial cell suspension in goats. Reprod Domest Anim. 2010;45:e249–54.
Izadyar F, Den Ouden K, Stout TA, Stout J, Coret J, Lankveld DP, et al. Autologous and homologous transplantation of bovine spermatogonial stem cells. Reproduction. 2003;126:765–74.
Kim BG, Cho CM, Lee YA, Kim BJ, Kim KJ, Kim YH, et al. Enrichment of testicular gonocytes and genetic modification using lentiviral transduction in pigs. Biol Reprod. 2010;82:1162–9.
Kim KJ, Cho CM, Kim BG, Lee YA, Kim BJ, Kim YH, et al. Lentiviral modification of enriched populations of bovine male gonocytes. J Anim Sci. 2014;92:106–18.
Kubota H, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL. Growth factors essential for self-renewal and expansion of mouse spermatogonial stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:16489–94.
Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Ogonuki N, Inoue K, Miki H, Ogura A, Toyokuni S, et al. Long-term proliferation in culture and germline transmission of mouse male germline stem cells. Biol Reprod. 2003;69:612–6.
Oatley JM, de Avila DM, McLean DJ, Griswold MD, Reeves JJ. Transplantation of bovine germinal cells into mouse testes. J Anim Sci. 2002;80:1925–31.
Nagano M, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL. Pattern and kinetics of mouse donor spermatogonial stem cell colonization in recipient testes. Biol Reprod. 1999;60:1429–36.
Hermann BP, Sukhwani M, Simorangkir DR, Chu T, Plant TM, Orwig KE. Molecular dissection of the male germ cell lineage identifies putative spermatogonial stem cells in rhesus macaques. Hum Reprod. 2009;24:1704–16.
Kubota H, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL. Culture conditions and single growth factors affect fate determination of mouse spermatogonial stem cells. Biol Reprod. 2004;71:722–31.
Tolkunova EN, Malashicheva AB, Chikhirzhina EV, Kostyleva EI, Zeng W, Luo J, et al. E-cadherin as a novel surface marker of spermatogonial stem cells. Tsitologiia. 2009;51:212–8.
Shinohara T, Orwig KE, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL. Spermatogonial stem cell enrichment by multiparameter selection of mouse testis cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:8346–51.
Dobrinski I, Ogawa T, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL. Computer assisted image analysis to assess colonization of recipient seminiferous tubules by spermatogonial stem cells from transgenic donor mice. Mol Reprod Dev. 1999;53:142–8.
Reding SC, Stepnoski AL, Cloninger EW, Oatley JM. THY1 is a conserved marker of undifferentiated spermatogonia in the pre-pubertal bull testis. Reproduction. 2010;139:893–903.
He Z, Kokkinaki M, Jiang J, Dobrinski I, Dym M. Isolation, characterization, and culture of human spermatogonia. Biol Reprod. 2010;82:363–72.
Costoya JA, Hobbs RM, Barna M, Cattoretti G, Manova K, Sukhwani M, et al. Essential role of Plzf in maintenance of spermatogonial stem cells. Nat Genet. 2004;36:653–9.
Shinohara T, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL. beta1- and alpha6-integrin are surface markers on mouse spermatogonial stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:5504–9.
Kubota H, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL. Spermatogonial stem cells share some, but not all, phenotypic and functional characteristics with other stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:6487–92.
Ogawa T, Arechaga JM, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL. Transplantation of testis germinal cells into mouse seminiferous tubules. Int J Dev Biol. 1997;41:111–22.
Brinster RL, Nagano M. Spermatogonial stem cell transplantation, cryopreservation and culture. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 1998;9:401–9.
Hamra FK, Schultz N, Chapman KM, Grellhesl DM, Cronkhite JT, Hammer RE, et al. Defining the spermatogonial stem cell. Dev Biol. 2004;269:393–410.
Wrobel KH. Prespermatogenesis and spermatogoniogenesis in the bovine testis. Anat Embryol (Berl). 2000;202:209–22.
Tokunaga Y, Imai S, Torii R, Maeda T. Cytoplasmic liberation of protein gene product 9.5 during the seasonal regulation of spermatogenesis in the monkey (Macaca fuscata). Endocrinology. 1999;140:1875–83.
Hynes RO. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992;69:11–25.
Haruyama E, Suda M, Ayukawa Y, Kamura K, Mizutamari M, Ooshima Y, et al. Testicular development in cynomolgus monkeys. Toxicol Pathol. 2012;40:935–42.
Shinohara T, Orwig KE, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL. Germ line stem cell competition in postnatal mouse testes. Biol Reprod. 2002;66:1491–7.
Curtis SK, Amann RP. Testicular development and establishment of spermatogenesis in Holstein bulls. J Anim Sci. 1981;53:1645–57.
Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Muneto T, Lee J, Takenaka M, Chuma S, Nakatsuji N, et al. Long-term culture of male germline stem cells from hamster testes. Biol Reprod. 2008;78:611–7.
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the Korean Health Technology R&D Project (HI12C0055), Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea. We also appreciate the Chung-Ang University Research Scholarship Grant in 2017, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Ethical statement
All animal procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Chung-Ang University (IACUC no. 2015-00016) in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Agricultural Animals in Agricultural Research and the Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YH., Kang, HG., Kim, BJ. et al. Enrichment and In Vitro Culture of Spermatogonial Stem Cells from Pre-Pubertal Monkey Testes. Tissue Eng Regen Med 14, 557–566 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-017-0058-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-017-0058-x