Abstract
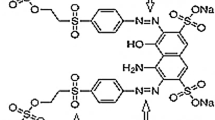
Electrochemical oxidation is a promising alternative for the degradation of reactive dyestuffs in residual dyeing liquid, which contains organic dyes, as well as salts such as sodium chloride and sodium sulfate. In this work, three kinds of salts, Na2SO4, NaCl and FeSO4, were selected to study the influence of electrolytes on the electrochemical oxidation of recalcitrant reactive red X-3B, using graphite cathode and dimensionally stable anode or graphite anode. The removals of color and chemical oxygen demand have been evaluated. Color removals were 99.97% and 99.84% with graphite anode and dimensionally stable anode in Na2SO4 and NaCl electrolyte. The corresponding chemical oxygen demand removals were 93.60% and 100%. In contrast, the maximum color and chemical oxygen demand removals were 97.32% and 68.76% in FeSO4 electrolyte. It was found that a combination of NaCl and FeSO4 achieved complete oxygen demand removal for both graphite anode and dimensionally stable anode. During the electrochemical oxidation process, anode and electrolyte exhibited a great effect on pH variations. Based on the cyclic voltammetry and active oxidative species investigations, the oxidation of reactive red X-3B was attributed to indirect oxidation of active chlorine and reactive oxygen species.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DSA:
-
Dimensionally stable anode
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- BDD:
-
Boron-doped diamond
- SHE:
-
Standard hydrogen electrode
References
Abdel-Aziz MH, Nirdosh I, Sedahmed GH (2018) Liquid–solid mass transfer behaviour of heterogeneous reactor made of a rotating tubular packed bed of spheres. Int J Heat Mass Transf 126:1129–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.05.050
An H, Cui H, Zhang W, Zhai J, Qian Y, Xie X, Li Q (2012) Fabrication and electrochemical treatment application of a microstructured TiO2-NTs/Sb–SnO2/PbO2 anode in the degradation of CI Reactive Blue 194 (RB 194). Chem Eng J 209:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.07.089
Babaei-Sati R, Basiri Parsa J (2017) Electrogeneration of H2O2 using graphite cathode modified with electrochemically synthesized polypyrrole/MWCNT nanocomposite for electro-Fenton process. J Ind Eng Chem 52:270–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.03.056
Bengani-Lutz P, Zaf RD, Culfaz-Emecen PZ, Asatekin A (2017) Extremely fouling resistant zwitterionic copolymer membranes with ~ 1nm pore size for treating municipal, oily and textile wastewater streams. J Membr Sci 543:184–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.08.058
Bensalah N, Louhichi B, Abdel-Wahab A (2012) Electrochemical oxidation of succinic acid in aqueous solutions using boron doped diamond anodes. Int J Environ Sci Technol 9:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-011-0007-5
Bravo-Yumi N, Espinoza-Montero P, Picos-Benítez A, Navarro-Mendoza R, Brillas E, Peralta-Hernández JM (2020) Synthesis and characterization of Sb2O5-doped Ti/SnO2-IrO2 anodes toward efficient degradation tannery dyes by in situ generated oxidizing species. Electrochim Acta 358:136904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136904
Burkinshaw SM, Salihu G (2018) The role of auxiliaries in the immersion dyeing of textile fibres: part 10 the influence of inorganic electrolyte on the wash-off of reactive dyes. Dyes Pigm 149:652–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2017.11.034
Carneiro JF, Aquino JM, Silva AJ, Barreiro JC, Cass QB, Rocha-Filho RC (2018) The effect of the supporting electrolyte on the electrooxidation of enrofloxacin using a flow cell with a BDD anode: kinetics and follow-up of oxidation intermediates and antimicrobial activity. Chemosphere 206:674–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.031
Çeçen F, Gül G (2020) Biodegradation of five pharmaceuticals: estimation by predictive models and comparison with activated sludge data. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02820-y
Davarpanah A, Zarei M, Valizadeh K, Mirshekari B (2019) CFD design and simulation of ethylene dichloride (EDC) thermal cracking reactor. Energy Sourc Part A Recov Util Environ Eff 41:1573–1587. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2018.1549133
Dotto J, Fagundes-Klen MR, Veit MT, Palácio SM, Bergamasco R (2019) Performance of different coagulants in the coagulation/flocculation process of textile wastewater. J Clea Prod 208:656–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.112
Escalona-Durán F, Ribeiro da Silva D, Martínez-Huitle CA, Villegas-Guzman P (2020) The synergic persulfate-sodium dodecyl sulfate effect during the electro-oxidation of caffeine using active and non-active anodes. Chemosphere 253:126599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126599
Escalona-Durán F, Villegas-Guzman P, dos Santos EV, da Silva DR, Martínez-Huitle CA (2019) Intensification of petroleum elimination in the presence of a surfactant using anodic electrochemical treatment with BDD anode. J Electroanal Chem 832:453–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.11.045
Guo S, Zhu X, Yang C, Zhang J, Zhang F, Li X (2019) Synthesis and characterization of L-arginine/Fe3O4 adsorbent for the removal of methyl orange from aqueous solutions. Ionics 25:1323–1330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-02844-6
Huang L, Li D, Liu J, Yang L, Dai C, Ren N, Feng Y (2021) CFD simulation of mass transfer in electrochemical reactor with mesh cathode for higher phenol degradation. Chemosphere 262:127626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127626
Jager D, Kupka D, Vaclavikova M, Ivanicova L, Gallios G (2018) Degradation of reactive black 5 by electrochemical oxidation. Chemosphere 190:405–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.126
Kaur P, Kushwaha JP, Sangal VK (2018) Electrocatalytic oxidative treatment of real textile wastewater in continuous reactor: degradation pathway and disposability study. J Hazard Mater 346:242–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.12.044
Kumar G, Huy M, Bakonyi P, Bélafi-Bakó K, Kim S-H (2018) Evaluation of gradual adaptation of mixed microalgae consortia cultivation using textile wastewater via fed batch operation. Biotechnol Rep 20:e00289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2018.e00289
Leal TW, Lourenço LA, Scheibe AS, de Souza SMAGU, de Souza AAU (2018) Textile wastewater treatment using low-cost adsorbent aiming the water reuse in dyeing process. J Environ Chem Eng 6:2705–2712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.04.008
Li D, Sun T, Wang L, Wang N (2018) Enhanced electro-catalytic generation of hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radical for degradation of phenol wastewater using MnO2/Nano-G|Foam-Ni/Pd composite cathode. Electrochim Acta 282:416–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.06.075
Liu N, Wu Y (2019) Removal of methylene blue by electrocoagulation: a study of the effect of operational parameters and mechanism. Ionics 25:3953–3960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-02915-8
Manojlović D et al (2020) Efficiency of homely synthesized magnetite: carbon composite anode toward decolorization of reactive textile dyes. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:2455–2462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02654-8
Moreira FC, Boaventura RAR, Brillas E, Vilar VJP (2017) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: a review on their application to synthetic and real wastewaters. Appl Catal B 202:217–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.037
Moreno-Palacios AV, Palma-Goyes RE, Vazquez-Arenas J, Torres-Palma RA (2019) Bench-scale reactor for Cefadroxil oxidation and elimination of its antibiotic activity using electro-generated active chlorine. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103173
Nidheesh PV, Gandhimathi R, Sanjini NS (2014) NaHCO3 enhanced Rhodamine B removal from aqueous solution by graphite–graphite electro Fenton system. Sep Purif Technol 132:568–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2014.06.009
Pieczyńska A, Ossowski T, Bogdanowicz R, Siedlecka E (2019) Electrochemical degradation of textile dyes in a flow reactor: effect of operating conditions and dyes chemical structure. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:929–942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1704-0
Radi MA, Nasirizadeh N, Mirjalili M, Rohani Moghadam M (2019) Ultrasound-assisted electrochemical decolorization of anthraquinone dye CI Reactive Blue 49, its optimization and synergic effect: a comparative study. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:2455–2464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1638-y
Rajkumar D, Kim JG (2006) Oxidation of various reactive dyes with in situ electro-generated active chlorine for textile dyeing industry wastewater treatment. J Hazard Mater 136:203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.11.096
Roozbahani MM, Nassiri P, Shalkouhi PJ (2009) Risk assessment of workers exposed to noise pollution in a textile plant International. J Environ Sci Technol 6:591–596. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326099
Rueffer M, Bejan D, Bunce NJ (2011) Graphite: an active or an inactive anode? Electrochim Acta 56:2246–2253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.11.071
Salazar R, Ureta-Zañartu MS, González-Vargas C, Brito CdN, Martinez-Huitle CA (2018) Electrochemical degradation of industrial textile dye disperse yellow 3: Role of electrocatalytic material and experimental conditions on the catalytic production of oxidants and oxidation pathway. Chemosphere 198:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.092
Sen SK, Patra P, Das CR, Raut S, Raut S (2019) Pilot-scale evaluation of bio-decolorization and biodegradation of reactive textile wastewater: an impact on its use in irrigation of wheat crop. Water Resour Ind 21:100106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2019.100106
Soni BD, Ruparelia JP (2013) Decolourization and mineralization of reactive black-5 with transition metal oxide coated electrodes by electrochemical oxidation. Procedia Eng 51:335–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.01.046
Valizadeh K, Farahbakhsh S, Bateni A, Zargarian A, Davarpanah A, Alizadeh A, Zarei M (2020) A parametric study to simulate the non-Newtonian turbulent flow in spiral tubes. Energy Sci Eng 8:134–149. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.514
Verma AK (2017) Treatment of textile wastewaters by electrocoagulation employing Fe–Al composite electrode. J Water Process Eng 20:168–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2017.11.001
Wang J, Zhang T, Mei Y, Pan B (2018) Treatment of reverse-osmosis concentrate of printing and dyeing wastewater by electro-oxidation process with controlled oxidation-reduction potential (ORP). Chemosphere 201:621–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.051
Yaseen DA, Scholz M (2019) Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: a critical review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:1193–1226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2130-z
Zarei M, Davarpanah A, Mokhtarian N, Farahbod F (2020) Integrated feasibility experimental investigation of hydrodynamic, geometrical and operational characterization of methanol conversion to formaldehyde. Energy Sour Part A Recov Util Environ Eff 42:89–103. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2019.1587057
Zhou L, Hu Z, Zhang C, Bi Z, Jin T, Zhou M (2013) Electrogeneration of hydrogen peroxide for electro-Fenton system by oxygen reduction using chemically modified graphite felt cathode. Sep Purif Technol 111:131–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.03.038
Zhou L, Zhou H, Yang X (2019) Preparation and performance of a novel starch-based inorganic/organic composite coagulant for textile wastewater treatment. Sep Purif Technol 210:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.07.089
Zou J, Peng X, Li M, Xiong Y, Wang B, Dong F, Wang B (2017) Electrochemical oxidation of COD from real textile wastewaters: kinetic study and energy consumption. Chemosphere 171:332–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.065
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFC0400502), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (19D111321, 20D111318) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and Graduate Student Innovation Fund of Donghua University (CUSF-DH-D-2020068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsibility editor: Samareh Mirkia.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Y., Chen, Q. & Zhou, J. Influence of typical electrolytes on electrooxidation of bio-refractory reactive dye. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 1799–1810 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03184-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03184-7