Abstract
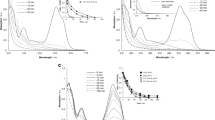
Dye wastewaters contain significant amounts of toxic organic species and intense color. Electrochemical oxidation has a proven potential to degrade these bio-resistant pollutants. This paper presents the results of indirect electrochemical oxidation of Reactive Black 5 (RB 5) recalcitrant dye wastewater using NaCl, KBr and Na2SO4 as supporting electrolytes. The studies were performed in an undivided batch reactor using indigenously prepared Ti/CoOx–RuO2–SnO2–Sb2O5 electrode classified as dimensionally stable anode (DSA). Characterization of the catalytic coating was performed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and energy-dispersive X-ray (EDAX) analysis. Similar operating conditions like electrolyte concentration, pH, current density and electrolysis time were used for all studies. The progress of dye degradation was monitored by estimating reduction in chemical oxygen demand (COD), total organic carbon (TOC) and color. Other performance indicators like average current efficiency (ACE) and energy consumption (EC) were also analyzed. The rate of COD removal followed pseudo-first-order kinetics. The present investigation exhibited highest treatment effectiveness in the presence of chloride compared to bromide and sulfate as degradation was dependent on the generation of highly electroactive oxidative species.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Mohan, N. Balasubramanian, C.A. Basha, Electrochemical oxidation of textile wastewater and its reuse. J. Hazard. Mater. 147(1–2), 644–651 (2007)
M. Panizza, G. Cerisola, Removal of colour and COD from wastewater containing acid blue 22 by electrochemical oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 153(1–2), 83–88 (2008)
A.I. del Rio, M.J. Benimeli, J. Molina, J. Bonastre, F. Cases, Electrochemical treatment of C.I. reactive black 5 solutions on stabilized doped Ti/SnO2 electrodes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 7(12), 13074–13092 (2012)
E. Chatzisymeon, N.P. Xekoukoulotakis, A. Coz, N. Kalogerakis, D. Mantzavinos, Electrochemical treatment of textile dyes and dyehouse effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 137(2), 998–1007 (2006)
R.G. Da Silva, S.A. Neto, A.R. De Andrade, Electrochemical degradation of reactive dyes at different DSA® compositions. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 22(1), 126–133 (2011)
A.J. Mendez-Martinez, M.M. Davila-Jimenez, O. Ornelas-Davila, M.P. Elizalde-Gonzalez, U. Arroyo-Abad, I. Sires, E. Brillas, Electrochemical reduction and oxidation pathways for Reactive Black 5 dye using nickel electrodes in divided and undivided cells. Electrochim. Acta 59, 140–149 (2012)
E. Brillas, C.A. Martínez-Huitle, Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. An updated review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 166–167, 603–643 (2015)
H. Jalife-Jacobo, R. Feria-Reyes, O. Serrano-Torres, S. Gutierrez-Granados, J.M. Peralta-Hernandez, Diazo dye Congo Red degradation using a Boron-doped diamond anode: an experimental study on the effect of supporting electrolytes. J. Hazard. Mater. 319, 78–83 (2016)
S. Aquino Neto, A.R. de Andrade, Electrooxidation of glyphosate herbicide at different DSA®compositions: pH, concentration and supporting electrolyte effect. Electrochim. Acta 54(7), 2039–2045 (2009)
M.S. Morsi, A.A. Al-Sarawy, W.A.S. El-Dein, Electrochemical degradation of some organic dyes by electrochemical oxidation on a Pb/PbO2 electrode. Desalin. Water Treat. 26(1–3), 301–308 (2011)
A. Uranga-Flores, C. De La Rosa-Juarez, S. Gutierrez-Granados, D.C. De Moura, C.A. Martinez-Huitle, J.M. Peralta Hernández, Electrochemical promotion of strong oxidants to degrade Acid Red 211: effect of supporting electrolytes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 738, 84–91 (2015)
F.L. Guzman-Duque, R.E. Palma-Goyes, I. Gonzalez, G. Penuela, R.A. Torres-Palma, Relationship between anode material, supporting electrolyte and current density during electrochemical degradation of organic compounds in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 278, 221–226 (2014)
D. Rajkumar, K. Palanivelu, N. Mohan, Electrochemical degradation of resorcinol using mixed oxide coated titanium electrode for wastewater treatment—a kinetic study. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 10, 396–401 (2003)
C.A. Martinez-Huitle, E. Brillas, Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods: a general review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 87(3–4), 105–145 (2009)
W. Wu, Z.H. Huang, T.T. Lim, Recent development of mixed metal oxide anodes for electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants in water. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 480, 58–78 (2014)
S. Garcia-Segura, J.D. Ocon, M.N. Chong, Electrochemical oxidation remediation of real wastewater effluents—a review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 113, 48–67 (2018)
F.C. Moreira, R.A.R. Boaventura, E. Brillas, V.J.P. Vilar, Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: a review on their application to synthetic and real wastewaters. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 202, 217–261 (2017)
D. Rajkumar, J.G. Kim, K.K. Kim, A study on electrochemical oxidation of catechol in chloride medium for wastewater treatment application. Environ. Eng. Res. 9(6), 279–287 (2004)
V.M. Vasconcelos, F.L. Ribeiro, F.L. Migliorini, S.A. Alves, J.R. Steter, M.R. Baldan, N.G. Ferreira, M.R.V. Lanza, Electrochemical removal of Reactive Black 5 azo dye using non-commercial boron-doped diamond film anodes. Electrochim. Acta 178, 484–493 (2015)
C.R. Costa, C.M.R. Botta, E.L.G. Espindola, P. Olivi, Electrochemical treatment of tannery wastewater using DSA® electrodes. J. Hazard. Mater. 153, 616–627 (2008)
H. Bai, P. He, J. Chen, K. Liu, H. Lei, X. Zhang, F. Dong, H. Li, Electrocatalytic degradation of bromocresol green wastewater on Ti/SnO2–RuO2 electrode. Water Sci. Technol. 77(7), 1–8 (2016)
S. Chen, Y. Zheng, S. Wang, X. Chen, Ti/RuO2–Sb2O5–SnO2 electrodes for chlorine evolution from seawater. J. Chem. Eng. 172, 47–51 (2011)
Y. Zhang, C. Meng, Facile fabrication of Fe3O4 and Co3O4 microspheres and their influence on the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. J. Alloys Compd. 674, 259–265 (2016)
A.K. Srivastava, B. Yadav, Humidity sensing properties of TiO2–Sb2O5 nanocomposite. Mater. Sci. 28, 491–502 (2010)
A.N. Subba Rao, V.T. Venkatarangaiah, Metal oxide-coated anodes in wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 21(5), 3197–3217 (2014)
D. Rajkumar, J.G. Kim, Oxidation of various reactive dyes with in situ electro-generated active chlorine for textile dyeing industry wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 136(2), 203–212 (2006)
A.H. Gemeay, Kinetics and mechanism of the reduction of some azo-dyes by inorganic oxysulfur compounds. Dyes Pigments 54(3), 201–212 (2002)
F.L. Souza, D.W. Miwa, M.A. Rodrigo, A.J. Motheo, Electrochemical degradation of dimethyl phthalate ester on a DSA® electrode. Braz. Chem. Soc. 25(3), 492–501 (2014)
M. Sun, G.V. Lowry, K.B. Gregory, Selective oxidation of bromide in wastewater brines from hydraulic fracturing. Water Res. 47(11), 3723–3731 (2013)
G. Bhaskar Raju, M. Thalamadai Karuppiah, S.S. Latha, D. Latha Priya, S. Parvathy, S. Prabhakar, Electrochemical pretreatment of textile effluents and effect of electrode materials on the removal of organics. Desalination 249(1), 167–174 (2009)
M. Holcapek, K. Volna, D. Vanerkova, Effects of functional groups on the fragmentation of dyes in electrospray and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectra. Dyes Pigments 75(1), 156–165 (2007)
D. Vanerkova, A. Sakalis, M. Holcapek, P. Jandera, A. Voulgaropoulos, Analysis of electrochemical degradation products of sulphonated azo dyes using high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 20, 2807–2815 (2006)
D. Jager, D. Kupka, M. Vaclavikova, L. Ivanicova, G. Gallios, Degradation of Reactive Black 5 by electrochemical oxidation. Chemosphere 190, 405–416 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saxena, P., Ruparelia, J. Influence of Supporting Electrolytes on Electrochemical Treatability of Reactive Black 5 Using Dimensionally Stable Anode. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. A 100, 299–310 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-019-00360-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-019-00360-4