Abstract
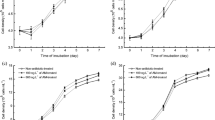
Previous reports suggested that coexisting antibiotics could enhance cyanobacterial growth and cyanotoxin production, but the influence of antibiotics on cyanobacterial removal has not been reported. This study investigated regulation effects and mechanisms of mixed antibiotics (ciprofloxacin, amoxicillin, sulfamethoxazole, tetracycline and spiramycin) in Microcystis aeruginosa exposed to UV-B and UV-C radiation at their current contamination level of 200 ng L−1. Mixed antibiotics alleviated growth inhibition effects of 240–480 mJ cm−2 of UV-B and 48–144 mJ cm−2 of UV-C, while enhanced the growth inhibition effects of 240 mJ cm−2 of UV-C. Responses of chlorophyll-a suggested that mixed antibiotics may regulate the toxicity of UV radiation via photosynthesis. Mixed antibiotics increased the production of microcystins in UV-treated M. aeruginosa, which may cause further hazard to the aquatic environment. Superoxide dismutase activity, growth rate and cell density varied in a similar pattern under exposure to UV radiation and mixed antibiotics, suggesting the correlation between cyanobacterial growth and reactive oxygen species during the UV treatment regulated by antibiotics. Responses of malondialdehyde suggested a higher toxicity of UV-C than UV-B to M. aeruginosa under the regulation of mixed antibiotics. With the coexistence of antibiotic contaminants, the radiation dose should be increased during the removal of M. aeruginosa by UV treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badri H, Monsieurs P, Coninx I, Nauts R, Wattiez R, Leys N (2015) Temporal gene expression of the cyanobacterium arthrospira in response to gamma rays. PLoS ONE 10:29
Bainor A, Chang L, McQuade TJ, Webb B, Gestwicki JE (2011) Bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay in low volume. Anal Biochem 410:310–312
Carmichael WW, Boyer GL (2016) Health impacts from cyanobacteria harmful algae blooms: implications for the North American Great Lakes. Harmful Algae 54:194–212
Deng C, Pan X, Zhang D (2015) Influence of ofloxacin on photosystems I and II activities of Microcystis aeruginosa and the potential role of cyclic electron flow. J Biosci Bioeng 119:159–164
Dias E, Oliveira M, Jones-Dias D, Vasconcelos V, Ferreira E, Manageiro V, Canica M (2015) Assessing the antibiotic susceptibility of freshwater Cyanobacteria spp. Front Microbiol 6:11
Ding Y, Song L, Sedmak B (2013) UVB radiation as a potential selective factor favoring microcystin producing bloom forming Cyanobacteria. PLoS ONE 8:e73919
Dirany A, Sires I, Oturan N, Ozcan A, Oturan MA (2012) Electrochemical treatment of the antibiotic sulfachloropyridazine: kinetics, reaction pathways, and toxicity evolution. Environ Sci Technol 46:4074–4082
Farré M, Pérez S, Kantiani L, Barceló D (2008) Fate and toxicity of emerging pollutants, their metabolites and transformation products in the aquatic environment. Trac Trends Anal Chem 27:991–1007
Gao QT, Tam NF (2011) Growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant responses of two microalgal species, Chlorella vulgaris and Selenastrum capricornutum, to nonylphenol stress. Chemosphere 82:346–354
Garcia-Galan MJ, Anfruns A, Gonzalez-Olmos R, Rodriguez-Mozaz S, Comas J (2016) Advanced oxidation of the antibiotic sulfapyridine by UV/H(2)O(2): characterization of its transformation products and ecotoxicological implications. Chemosphere 147:451–459
Gonzalez-Pleiter M, Gonzalo S, Rodea-Palomares I, Leganes F, Rosal R, Boltes K, Marco E, Fernandez-Pinas F (2013) Toxicity of five antibiotics and their mixtures towards photosynthetic aquatic organisms: implications for environmental risk assessment. Water Res 47:2050–2064
Grenni P, Ancona V, Barra Caracciolo A (2018) Ecological effects of antibiotics on natural ecosystems: a review. Microchem J 136:25–39
Gulkowska A, Leung HW, So MK, Taniyasu S, Yamashita N, Yeunq LWY, Richardson BJ, Lei AP, Giesy JP, Lam PKS (2008) Removal of antibiotics from wastewater by sewage treatment facilities in Hong Kong and Shenzhen, China. Water Res 42:395–403
Jiang HB, Qiu BS (2011) Inhibition of photosynthesis by UV-B exposure and its repair in the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. J Appl Phycol 23:691–696
Kataria S, Jajoo A, Guruprasad KN (2014) Impact of increasing Ultraviolet-B (UV-B) radiation on photosynthetic processes. J Photochem Photobiol B 137:55–66
Liu Y, Zhang J, Gao B (2015) Cellular and transcriptional responses in Microcystis aeruginosa exposed to two antibiotic contaminants. Microb Ecol 69:535–543
Liu Y, Chen S, Zhang J, Li X, Gao B (2017) Stimulation effects of ciprofloxacin and sulphamethoxazole in Microcystis aeruginosa and isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation-based screening of antibiotic targets. Mol Ecol 26:689–701
Moon BR, Kim TK, Kim MK, Choi J, Zoh KD (2017) Degradation mechanisms of Microcystin-LR during UV-B photolysis and UV/H2O2 processes: byproducts and pathways. Chemosphere 185:1039–1047
Qian HF, Li JJ, Pan XJ, Sun ZQ, Ye CB, Jin GQ, Fu ZW (2012) Effects of streptomycin on growth of algae Chlorella vulgaris and Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ Toxicol 27:229–237
Rastogi RP, Madamwar D, Incharoensakdi A (2015) Bloom dynamics of cyanobacteria and their toxins: environmental health impacts and mitigation strategies. Front Microbiol 6:22
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury J, Herdman M, Stanier R (1979) Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 111:1–61
Sakai H, Oguma K, Katayama H, Ohgaki S (2007) Effects of low- or medium-pressure ultraviolet lamp irradiation on Microcystis aeruginosa and Anabaena variabilis. Water Res 41:11–18
Sakai H, Katayama H, Oguma K, Ohgaki S (2009) Kinetics of Microcystis aeruginosa growth and intracellular microcystins release after UV irradiation. Environ Sci Technol 43:896–901
Schmitt FJ, Renger G, Friedrich T, Kreslavski VD, Zharmukhamedov SK, Los DA, Kuznetsov VV, Allakhverdiev SI (2014) Reactive oxygen species: re-evaluation of generation, monitoring and role in stress-signaling in phototrophic organisms. Biochim Biophys Acta-Bioenerg 1837:835–848
Sheeba SVP, Srivastava PK, Prasad SM (2011) Differential physiological and biochemical responses of two cyanobacteria Nostoc muscorum and Phormidium foveolarum against oxyfluorfen and UV-B radiation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:1981–1993
Sinha RP, Häder DP (2008) UV-protectants in cyanobacteria. Plant Sci 174:278–289
Tao Y, Zhang X, Au DW, Mao X, Yuan K (2010) The effects of sub-lethal UV-C irradiation on growth and cell integrity of cyanobacteria and green algae. Chemosphere 78:541–547
Tao Y, Mao X, Hu J, Mok HOL, Wang L, Au DWT, Zhu J, Zhang X (2013) Mechanisms of photosynthetic inactivation on growth suppression of Microcystis aeruginosa under UV-C stress. Chemosphere 93:637–644
Trovó AG, Nogueira RFP, Aguera A, Fernandez-Alba AR, Malato S (2011) Degradation of the antibiotic amoxicillin by photo-Fenton process—chemical and toxicological assessment. Water Res 45:1394–1402
Wan J, Guo P, Zhang S (2014) Response of the cyanobacterium Microcystis flos-aquae to levofloxacin. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:3858–3865
Wan J, Guo P, Peng X, Wen K (2015) Effect of erythromycin exposure on the growth, antioxidant system and photosynthesis of Microcystis flos-aquae. J Hazard Mater 283:778–786
Wang M, Zhang Y, Guo P (2017) Effect of florfenicol and thiamphenicol exposure on the photosynthesis and antioxidant system of Microcystis flos-aquae. Aquat Toxicol 186:67–76
Wang Z, Chen Q, Hu L, Wang M (2018) Combined effects of binary antibiotic mixture on growth, microcystin production, and extracellular release of Microcystis aeruginosa: application of response surface methodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:736–748
Xie ZM, Wang YX, Liu YD, Liu YM (2009) Ultraviolet-B exposure induces photo-oxidative damage and subsequent repair strategies in a desert cyanobacterium Microcoleus vaginatus Gom. Eur J Soil Biol 45:377–382
Xiong JQ, Kurade MB, Kim JR, Roh HS, Jeon BH (2017) Ciprofloxacin toxicity and its co-metabolic removal by a freshwater microalga Chlamydomonas mexicana. J Hazard Mater 323:212–219
Yang W, Tang Z, Zhou F, Zhang W, Song L (2013) Toxicity studies of tetracycline on Microcystis aeruginosa and Selenastrum capricornutum. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 35:320–324
Yang Z, Kong F, Shi X, Yu Y, Zhang M (2015) Effects of UV-B radiation on microcystin production of a toxic strain of Microcystis aeruginosa and its competitiveness against a non-toxic strain. J Hazard Mater 283:447–453
Ye J, Zhang Y, Chen S, Liu C, Zhu Y, Liu W (2014) Enantioselective changes in oxidative stress and toxin release in Microcystis aeruginosa exposed to chiral herbicide diclofop acid. Aquat Toxicol 146:12–19
Ye J, Du Y, Wang L, Qian J, Chen J, Wu Q, Hu X (2017) Toxin release of cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa after exposure to typical tetracycline antibiotic contaminants. Toxins 9(2):53
Zeeshan M, Prasad SM (2009) Differential response of growth, photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation to UV-B radiation in three cyanobacteria. S Afr J Bot 75:466–474
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51679130) and partly by the Fundamental Research Funds of Shandong University (2017WLJH35).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Xiao-Zhang Yu.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Liu, Y., Zhang, J. et al. Regulation of five-antibiotic mixture on Microcystis aeruginosa exposed to sublethal doses of ultraviolet radiation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 8229–8238 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02318-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02318-2