Abstract
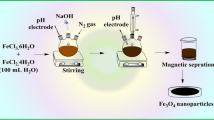
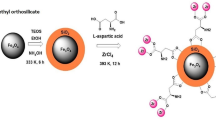
In the present work, selective magnetic solid-phase extraction speciation of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) from aqueous solution with synthesized magnetic nanoparticles modified with 1,5-diphenylcarbazide (DPC). Cr(VI) could be separated from Cr(III) due to its complexation with 1,5-diphenylcarbazide. Fe3O4@SiO2@DPC with an average size of 22 nm has been characterized by X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The optimized conditions for adsorption were established by adjusting the parameters affecting speciation of Cr(VI) and Cr(III), such as pH, sample volume, metal ion concentration, adsorbent dosage, and time. The modified magnetic nanoparticles preferably adsorbed Cr(VI) at pH = 2.5 and made it possible to speciate it from Cr(III). Four times recovery of magnetic solid phase was investigated by eluting Fe3O4@SiO2@DPC with different concentrations of HCl, HNO3 and H2SO4 and it was found that 10 mL of 1 M HNO3 was the best eluent. The obtained data fitted with Langmuir isotherm of adsorption which indicates that the adsorption of Cr(VI) onto Fe3O4@SiO2@DPC is a type of monolayer sorption. Finally, magnetic nanoparticles were evaluated for chromium electroplating wastewater where it showed a sufficient ability to work in a real media.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker JS (2005) Trace and ultratrace analysis in liquids by atomic spectrometry TrAC. Trends Anal Chem 24:243–254
Beyki MH, Bayat M, Miri S, Shemirani F, Alijani H (2014) Synthesis, characterization, and silver adsorption property of magnetic cellulose xanthate from acidic solution: prepared by one step and biogenic approach. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:14904–14912
Brown RJ, Milton MJ (2005) Analytical techniques for trace element analysis: an overview TrAC. Trends Anal Chem 24:266–274
Bulut V, Duran C, Tufekci M, Elci L, Soylak M (2007) Speciation of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) after column solid phase extraction on Amberlite XAD-2010. J Hazard Mater 143:112–117
Cohen MD, Kargacin B, Klein CB, Costa M (1993) Mechanisms of chromium carcinogenicity and toxicity CRC. Crit Rev Toxicol 23:255–281
Cui C, He M, Chen B, Hu B (2014) Chitosan modified magnetic nanoparticles based solid phase extraction combined with ICP-OES for the speciation of Cr(III) and Cr(VI). Anal Methods 6:8577–8583
Dada A, Olalekan A, Olatunya A, Dada O (2012) Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of Zn2 + unto phosphoric acid modified rice husk. J Appl Chem 3:38–45
Dai J, Ren F, Tao C (2012) Adsorption of Cr(VI) and speciation of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) in aqueous solutions using chemically modified chitosan Int J Env Res. Public Health 9:1757–1770
Darwish M, Mohammadi A, Assi N (2016) Integration of nickel doping with loading on graphene for enhanced adsorptive and catalytic properties of CdS nanoparticles towards visible light degradation of some antibiotics. J Hazard Mater 320:304–314
Dayan A, Paine A (2001) Mechanisms of chromium toxicity, carcinogenicity and allergenicity: review of the literature from 1985 to 2000. Hum Exp Toxicol 20:439–451
Fan Z-J et al (2010) Facile synthesis of graphene nanosheets via Fe reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. ACS Nano 5:191–198
Fan S et al (2017) Facile synthesis of tea waste/Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticle composite for hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 7:7576–7590
Gabriel K, Salifoglou A (2005) A chromium (iii)-citrate complex from aqueous solutions. J Agroaliment Process Technol 11:57–60
Ghembaza H, Zerga A, Saïm R (2012) Effects of thickness and chemical quality of SiO2 barrier on POCl3 diffusion during the formation of emitter. Energy Procedia 18:733–740
Janssen L, Koene L (2002) The role of electrochemistry and electrochemical technology in environmental protection. Chem Eng J 85:137–146
Kadirvelu K, Faur-Brasquet C, Cloirec PL (2000) Removal of Cu (II), Pb(II), and Ni (II) by adsorption onto activated carbon cloths. Langmuir 16:8404–8409
Kara A, Demirbel E (2012) Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic analysis on adsorption of Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions by synthesis and characterization of magnetic-poly (divinylbenzene-vinylimidazole) microbeads. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:2387–2403
Li Y, Gao B, Wu T, Sun D, Li X, Wang B, Lu F (2009) Hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solution by adsorption on aluminum magnesium mixed hydroxide. Water Res 43:3067–3075
Li L, Duan H, Wang X, Luo C (2014) Adsorption property of Cr (vi) on magnetic mesoporous titanium dioxide–graphene oxide core–shell microspheres. New J Chem 38:6008–6016
Ma W, Cai R, Lin Z (1998) Studies on adsorption properties of Chromium (VI) on the nanometer-size TiO2 powders surfaces using on-line flow-injection analysis. Chem J Chin Univ Chin 19:1566–1569
Marczenko Z, Balcerzak M, Kloczko E (2000) Separation, preconcentration and spectrophotometry in inorganic analysis. Elsevier Science, New York
Marques M, Salvador A, Morales-Rubio A, De la Guardia M (2000) Chromium speciation in liquid matrices: a survey of the literature. Fresenius J Anal Chem 367:601–613
Mattia GD et al (2004) Impairment of cell and plasma redox state in subjects professionally exposed to chromium. Am J Ind Med 46:120–125
Narin I, Kars A, Soylak M (2008) A novel solid phase extraction procedure on Amberlite XAD-1180 for speciation of Cr(III), Cr(VI) and total chromium in environmental and pharmaceutical samples. J Hazard Mater 150:453–458
Ozaki H, Sharma K, Saktaywin W (2002) Performance of an ultra-low-pressure reverse osmosis membrane (ULPROM) for separating heavy metal: effects of interference parameters. Desalination 144:287–294
Pyrzynska K (2010) Carbon nanostructures for separation, preconcentration and speciation of metal ions TrAC. Trends Anal Chem 29:718–727
Saadi R, Saadi Z, Fazaeli R, Fard NE (2015) Monolayer and multilayer adsorption isotherm models for sorption from aqueous media. Korean J Chem Eng 32:787–799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-015-0053-7
Shanker AK, Cervantes C, Loza-Tavera H, Avudainayagam S (2005) Chromium toxicity in plants. Environ Int 31:739–753
Simpson NJ (2000) Solid-phase extraction: principles, techniques, and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Singh S, Barick K, Bahadur D (2011) Surface engineered magnetic nanoparticles for removal of toxic metal ions and bacterial pathogens. J Hazard Mater 192:1539–1547
Vilensky MY, Berkowitz B, Warshawsky A (2002) In situ remediation of groundwater contaminated by heavy-and transition-metal ions by selective ion-exchange methods. Environ Sci Technol 36:1851–1855
Wang J, Jia B, Guo L, Lin Q (2005) The determination of chromium in feeds by flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Guang pu xue yu guang pu fen xi = Guang pu 25:1142
Weckhuysen BM, Wachs IE, Schoonheydt RA (1996) Surface chemistry and spectroscopy of chromium in inorganic oxides. Chem Rev 96:3327–3350
WooáLee J, BináKim S (2011) Enhanced Cr(VI) removal using iron nanoparticle decorated graphene. Nanoscale 3:3583–3585
Xing Y, Chen X, Wang D (2007) Electrically regenerated ion exchange for removal and recovery of Cr(VI) from wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 41:1439–1443
Yao H, Ding Q, Zhou H, Zhao Z, Liu G, Wang G (2016) An adsorption–reduction synergistic effect of mesoporous Fe/SiO2–NH2 hollow spheres for the removal of Cr (vi) ions. RSC Adv 6:27039–27046
Zhai Y, Se Duan, He Q, Yang X, Han Q (2010) Solid phase extraction and preconcentration of trace mercury(II) from aqueous solution using magnetic nanoparticles doped with 1,5-diphenylcarbazide. Microchim Acta 169:353–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0363-8
Acknowledgement
The authors wish to thank Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University for the Instrumental support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Q. Aguilar-Virgen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Assi, N., Aberoomand Azar, P., Saber Tehrani, M. et al. Selective solid-phase extraction using 1,5-diphenylcarbazide-modified magnetic nanoparticles for speciation of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 4739–4748 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1868-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1868-7