Abstract
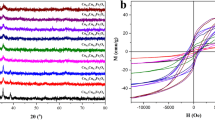
Well-dispersed magnetite nanoparticles of different sizes between 15 and 43 nm were synthesized by an electrochemical method in a controlled manner by simply changing the synthesis temperature. These nanoparticles were used as a reusable adsorbent to remove Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. The recovery efficiency was found to be highly dependent on environmental parameters, such as temperature and pH. In addition, it was demonstrated that the initial concentrations of both Cr(VI) and magnetite nanoparticles strongly influence the removal capability of these nanomaterials. Remarkably, the nanoparticle size has a key role on the Cr(VI) adsorption efficiency, which gradually increases as the diameter decreases due to the augmentation of the surface area. The low aggregation in the case of small particles that results from the low magnetization saturation values also contributes to the enhancement of the surface area available for Cr(VI) adsorption. In contrast, nanoparticles with larger sizes are more easily manipulated by a magnet, and the efficiency is largely maintained after five cycles. The adsorption process fits the Langmuir isotherm model well, and the reaction was found to follow a pseudo-second-order rate.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal D, Goyal M, Bansal RC (1999) Adsorption of chromium by activated carbon from aqueous solution. Carbon 37:1989–1997. doi:10.1016/S0008-6223(99)00072-X
Andrés-Vergés M, Morales MP, Veintemillas-Verdaguer S, Palomares FJ, Serna CJ (2011) Core/shell magnetite/bismuth oxide nanocrystals with tunable size, colloidal, and magnetic properties. Chem Mater 24:319–324. doi:10.1021/cm202949q
Benefield LD, Judkins JF, Weand BL (1982) Process chemistry for water and wastewater treatment. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Boddu VM, Abburi K, Talbott JL, Smith ED (2003) Removal of hexavalent chromium from wastewater using a new composite chitosan biosorbent. Environ Sci Technol 37:4449–4456
Burks T et al (2014) Studies on the adsorption of chromium(VI) onto 3-mercaptopropionic acid coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 425:36–43. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2014.03.025
Cabrera L, Gutierrez S, Menendez N, Morales MP, Herrasti P (2008) Magnetite nanoparticles: electrochemical synthesis and characterization. Electrochim Acta 53:3436–3441. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2007.12.006
Chastain J, King RC, Moulder JF (1992) Handbook of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: a reference book of standard spectra for identification and interpretation of XPS data. [s.n.], Physical electronics. Eden Prairie, Perkin-Elmer
Chowdhury SR, Yanful EK, Pratt AR (2012) Chemical states in XPS and Raman analysis during removal of Cr(VI) from contaminated water by mixed maghemite–magnetite nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 235–236:246–256. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.07.054
Crane RA, Dickinson M, Popescu IC, Scott TB (2011) Magnetite and zero-valent iron nanoparticles for the remediation of uranium contaminated environmental water. Water Res 45:2931–2942
Dula T, Siraj K, Kitte SA (2014) Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using chemically activated carbon prepared from locally available waste of bamboo (Oxytenanthera abyssinica). ISRN Environ Chem 2014:9. doi:10.1155/2014/438245
Faghihian H, Bowman RS (2005) Adsorption of chromate by clinoptilolite exchanged with various metal cations. Water Res 39:1099–1104. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2004.12.010
Gupta K, Chen K (1978) Arsenic removal by adsorption. J Water Pollut Control Fed 50:493
Hu J, Lo IMC, Chen G (2004) Removal of Cr(VI) by magnetite nanoparticle. Water Sci Technol 50:139–146
Hu J, Chen G, Lo I (2006) Selective removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewater using maghemite nanoparticle: performance and mechanisms. J Environ Eng 132:709–715. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2006)132:7(709)
Hu J, Lo IMC, Chen G (2007) Comparative study of various magnetic nanoparticles for Cr(VI) removal. Sep Purif Technol 56:249–256
Khezami L, Capart R (2005) Removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution by activated carbons: kinetic and equilibrium studies. J Hazard Mater 123:223–231
Leyva Ramos R, Juarez Martinez A, Guerrero Coronado RM (1994) Adsorption of chromium(VI) from aqueous solutions on activated carbon. Water Sci Technol 30:191–197
Liu Y et al (2012) Synthesis of high saturation magnetization superparamagnetic Fe3O4 hollow microspheres for swift chromium removal. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:4913–4920. doi:10.1021/am301239u
Mazario E, Morales MP, Galindo R, Herrasti P, Menendez N (2012) Influence of the temperature in the electrochemical synthesis of cobalt ferrites nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 536(Supplement 1):S222–S225. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.10.073
Mor S, Ravindra K, Bishnoi NR (2007) Adsorption of chromium from aqueous solution by activated alumina and activated charcoal. Bioresour Technol 98:954–957. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2006.03.018
Patterson RR, Fendorf S, Fendorf M (1997) Reduction of hexavalent chromium by amorphous iron sulfide. Environ Sci Technol 31:2039–2044. doi:10.1021/es960836v
Roisnel T, Rodriguez-Carvajal J (2000) WinPLOTR: a windows tool for powder diffraction patterns analysis. In: Materials science forum, proceedings of the seventh European powder diffraction conference (EPDIC 7), Barcelona (Spain), pp 118–123
Sanchez-Garcia JA et al (2009) Production of nanohole/nanodot patterns on Si(001) by ion beam sputtering with simultaneous metal incorporation. J Phys Condens Matter 21:0953–8984
Selvi K, Pattabhi S, Kadirvelu K (2001) Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by adsorption onto activated carbon. Bioresour Technol 80:87–89. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00068-2
Shahriari T, Nabi Bidhendi G, Mehrdadi N, Torabian A (2014) Effective parameters for the adsorption of chromium(III) onto iron oxide magnetic nanoparticle. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:349–356. doi:10.1007/s13762-013-0315-z
Sharma YC, Srivastava V (2010) Comparative studies of removal of Cr(VI) and Ni(II) from aqueous solutions by magnetic nanoparticles. J Chem Eng Data 56:819–825. doi:10.1021/je100428z
Singh A, Prasad SM (2015) Remediation of heavy metal contaminated ecosystem: an overview on technology advancement. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:353–366. doi:10.1007/s13762-014-0542-y
Singh DB, Gupta GS, Prasad G, Rupainwar DC (1993) The use of hematite for chromium(VI) removal. J Environ Sci Health Part A Environ Sci Eng Toxicol 28:1813–1826. doi:10.1080/10934529309375979
Vunain E, Mishra AK, Krause RW (2013) Fabrication, characterization and application of polymer nanocomposites for arsenic(III) removal from water. J Inorg Organomet Polym 23:293–305. doi:10.1007/s10904-012-9775-8
Yuan P et al (2009) Montmorillonite-supported magnetite nanoparticles for the removal of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 166:821–829
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (MAT2012-37109-C02-02, MAT2013-47878-C2-1-R and CSD2008-00023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez, L.J., Muñoz-Bonilla, A., Mazario, E. et al. Adsorption of chromium(VI) onto electrochemically obtained magnetite nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 4017–4024 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0832-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0832-z