Abstract
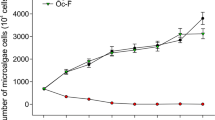
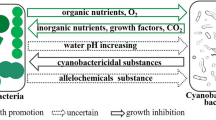
Application of algicidal bacteria is a promising and environmentally friendly way to control cyanobacterial blooms. Lytic effects of the algicidal bacteria on Microcystis aeruginosa have been observed, but the interactions between algicidal bacteria and the cyanobacteria are still elusive. An algicidal bacterium Bacillus sp. B50 isolated from Lake Donghu showed a highly lytic efficiency on M. aeruginosa NIES-843 through heat-resistant extracellular substances from strain B50. The cell density of strain B50 could be maintained at high levels during the lytic process in bacteria–Microcystis system with inoculation densities of 1.9 × 106 and 1.9 × 107 cfu/mL, resulting in the death of M. aeruginosa NIES-843. However, the population dynamics of strain B50 was a bell-shaped curve at low inoculation densities and no lytic effect could be observed. Results of physiological responses suggested that the lytic efficiency may be mediated through inhibition of metabolism and production of reactive oxygen species.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DM (1997) Turning back the harmful red tides. Nature 38:513–514
Aro EM, Virgin I, Andersson B (1993) Photoinhibition of photosystem II. Inactivation, protein damage and turnover. Biochim Biophys Acta 1143:113–134
Bustin SA (2000) Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J Mol Endocrinol 25:169–193
Carmichael WW (1995) Toxic Microcystis in the environment. In: Watanabe MF, Harada K, Carmichael WW, Fujiki H (eds) Toxic Microcystis. CRC Press, New York, pp 1–12
Fraleigh PC, Burnham JC (1988) Myxococcus predation on cyanobacterial nutrient effects. Limnol Oceanogr 33:476–483
Gamer J, Bujard H, Bukau B (1992) Physical interaction between heat shock proteins DnaK, DnaJ, and GrpE and the bacterial heat shock transcription factor σ32. Cell 69:833–842
Griffiths HR (2005) Chemical modifications of biomolecules by oxidants. Handb Environ Chem 2:33–62
Hong Y, Hu HY, Li FM (2008) Physiological and biochemical effects of allelochemical ethyl 2-methyl acetoacetate (EMA) on cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotox Environ Safe 71:527–534
Ichimura T (1979) Media for freshwater cyanobacteria. In: Nishizawa K, Chihara M (eds) Methods in phycology. Kyouritsu Shuppan, Tokyo, pp 295–296
Juttner F, Luthi H (2008) Topology and enhanced toxicity of bound microcystins in Microcystis PCC 7806. Toxicon 51:388–397
Kang YH, Kim JD, Kim BH, Kong DS, Han MS (2005) Isolation and characterization of a bio-agent antagonistic to diatom, Stephanodiscus hantzschii. J Appl Microbiol 98:1030–1038
Kennelly PJ, Potts M (1999) Life among the primitives: protein O-phosphatases in prokaryotes. Front Biosc 4:372–385
Kim B, Hwang S, Kim Y, Hwang S, Takamura N, Han M (2007) Effects of biological control agents on nuisance cyanobacterial and diatom blooms in freshwater systems. Microbes Environ 22:52–58
Kodani S, Akiko I, Mitsutani A, Murakami M (2002) Isolation and identification of the antialgal compound, harmane (1-methyl-β-carboline), produced by the algicidal bacterium, Pseudomonas sp. K44-1. J Appl Phycol 14:109–114
Kurmayer R, Kutzenberger T (2003) Application of real-time PCR for quantification of microcystin genotypes in a population of the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6723–6730
Latifi A, Ruiz M, Jeanjean R, Zhang CC (2007) PrxQ-A, a member of the peroxiredoxin Q family, plays a major role in defense against oxidative stress in the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC7120. Free Radic Bio Med 42:424–431
Lee YK, Ahn CY, Kim HS, Oh HM (2010) Cyanobactericidal effect of Rhodococcus sp. isolated from eutrophic lake on Microcystis sp. Biotechnol Lett 32:1673–1678
Lin S, Wu Z, Yu G, Zhu M, Yu B, Li R (2010) Genetic diversity and molecular phylogeny of Planktothrix (Oscillatoriales, cyanobacteria) strains from China. Harmful Algae 9:87–97
Manage PM, Kawabata Z, Nakano S (2000) Algicidal effect of the bacterium Alcaligenes denitrificans on Microcystis spp. Aquat Microb Ecol 22:111–117
Mayali X, Doucette GJ (2002) Microbial community interactions and population dynamics of an algicidal bacterium active against Karenia brevis (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 1:277–293
Mazouni K, Domain F, Cassier-Chauvat C, Chauvat F (2004) Molecular analysis of the key cytokinetic components of cyanobacteria: FtsZ, ZipN and MinCDE. Mol Microbiol 52:1145–1158
Mu RM, Fan ZQ, Pei HY, Yuan XL, Liu SX, Wang XR (2007) Isolation and algae-lysing characteristics of the algicidal bacterium B5. J Environ Sci (China) 19:1336–1340
Nübel U, Garcia-Pichel F, Muyzer G (1997) PCR primers to amplify 16S rRNA genes from cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3327–3332
Pan G, Zhang MM, Chen H, Zou H, Yan H (2006) Removal of cyanobacterial blooms in Taihu Lake using local soils I. Equilibrium and kinetic screening on the flocculation of Microcystis aeruginosa using commercially available clays and minerals. Environ Pollut 141:195–200
Pearson LA, Neilan BA (2008) The molecular genetics of cyanobacterial toxicity as a basis for monitoring water quality and public health risk. Curr Opin Biotech 19:281–288
Richards FA, Thompson TG (1952) The estimation and characterization of plankton populations by pigment analyses. II. A spectrophotometric method for the estimation of plankton pigments. J Marine Res 11:156–172
Shao J, Wu Z, Yu G, Pen X, Li R (2009) Allelopathic mechanism of pyrogallol to Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806 (cyanobacteria): from views of gene expression and antioxidant system. Chemosphere 75:924–928
Song L, Chen W, Peng L, Wan N, Gan N, Zhang X (2007) Distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in water columns: a systematic investigation into the environmental fate and the risks associated with microcystins in Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu. Water Res 41:2853–2864
Swarnamukhi PL, Sharma SK, Bajaj P, Surolia N, Surolia A, Suguna K (2006) Crystal structure of dimeric FabZ of Plasmodium falciparum reveals conformational switching to active hexamers by peptide flips. FEBS Lett 580:2653–2660
Tucker S, Pollard P (2005) Identification of cyanophage Ma-LBP and infection of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa from an Australian subtropical lake by the virus. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:629–635
Urbach E, Robertsin D, Chisholm S (1992) Multiple evolutionary origins of prochlorophytes within the cyanobacterial radiation. Nature 355:267–270
Vickerman MM, Brossard KA, Funk DB, Jesionowski AM, Gill SR (2007) Phylogenetic analysis of bacterial and archaeal species in symptomatic and asymptomatic endodontic infections. J Med Microbiol 56:110–118
Wang Q, Su M, Zhu W, Li X, Jia Y, Guo P, Chen Z, Jiang W, Tian X (2010) Growth inhibition of Microcystis aeruginosa by white-rot fungus Lopharia spadicea. Water Sci Technol 62:317–323
Welker M, von Döhren H (2006) Cyanobacterial peptides—nature’s own combinatorial biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 30:530–563
Yang CY, Zhou SW, Xia CH, Liu YD (2009) The effect of microcystin-RR on the growth and physiological characteristics of denitrifying bacteria. Chin J Environ Pollut Control 31:7–10
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21107024), Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (10JJ6045), and the Foundation of Furong Scholar project of Hunan Province. Professor Joe Lepo (University of West Florida) provided language assistance and useful suggestions in an early draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, J., Jiang, Y., Wang, Z. et al. Interactions between algicidal bacteria and the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa: lytic characteristics and physiological responses in the cyanobacteria. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 11, 469–476 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0205-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0205-4