Abstract
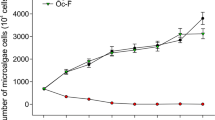
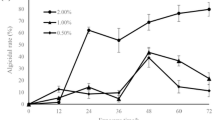
To biocontrol algal bloom, a novel algicidal bacterium, Enterobacter sp. NP23, was isolated. This strain has an effective algicidal activity against Chlorella vulgari, Microcystis aeruginosa, Scenedesmus, and Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Meanwhile, the growth factors were assayed to obtain a high cell density of strain NP23. As a result, three growth factors (i.e., KNO3 0.6 %, MnSO4·H2O 0.001 %, and K2HPO4 0.3 %) were determined as the critical roles in enhancing the cell density of 1013 CFU/mL. Moreover, algicidal activity assays revealed that strain NP23 exhibited high algicidal activities against M. aeruginosa and Scenedesmus. These results indicate that this wild-type strain would provide a new member for biocontrolling microalgal and cyanobacterial populations in eco-technology.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bährs, H., Menzel, R., Kubsch, G., Stösser, R., Putschew, A., Heinze, T., & Steinberg, C. E. (2012). Does quinone or phenol enrichment of humic substances alter the primary compound from a non-algicidal to an algicidal preparation? Chemosphere, 87, 1193–1200.
Cho, J. Y. (2012). Algicidal activity of marine Alteromonas sp. KNS-16 and isolation of active compounds. Bioscience Biotechnology Biochemical, 76, 1452–1458.
Choi, H.-J., Kim, B.-H., Kim, J.-D., & Han, M.-S. (2005). Streptomyces neyagawaensis as a control for the hazardous biomass of Microcystis aeruginosa (Cyanobacteria) in eutrophic freshwaters. Biology Control, 33, 335–343.
Doucette, G. J., McGovern, E. R., & Babinchak, J. A. (1999). Algicidal bacteria active against Gymnodinium breve (Dinophyceae). I. Bacterial isolation and characterization of killing activity. Journal of Phycology, 35, 1447–1457.
Kang, Y.-H., Kim, J.-D., Kim, B.-H., Kong, D. S., & Han, M.-S. (2005). Isolation and characterization of a bio-agent antagonistic to diatom, Stephanodiscus hantzschii. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 98, 1030–1038.
Kang, Y. K., Cho, S. Y., Kang, Y. H., Katano, T., Jin, E. S., Kong, D. S., & Han, S. M. (2008). Isolation, identification and characterization of algicidal bacteria against Stephanodiscus hantzschii and Peridinium bipes for the control of freshwater winter algal blooms. Journal of Applied Phycology, 20, 375–386.
Kim, J.-D., & Lee, C.-G. (2006). Antialgal effect of a novel polysaccharolytic Sinorhizobium kostiense AFK-13 on Anabaena flos-aquae causing water bloom. Journal of Microbiology Biotechnology, 16, 1613–1621.
Li, Z., Lin, S., Liu, X., Tan, J., Pan, J., & Yang, H. (2014). A freshwater bacterial strain, Shewanella sp. Lzh-2, isolated from Lake Taihu and its two algicidal active substances, hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione and 2,3-indolinedione. Applied Microbiology Biotechnology, 98, 4737–4748.
Liao, C.L., Liu, X.B., Shan, L.N. (2014). Study on optimization of liquid media and biosafety assessment for algae lysing bacterium NP23. Canadian Journal Microbiology. doi:10.1139/cjm-2014-0330.
Mayali, X., & Doucette, G. J. (2002). Microbial community interactions and population dynamics of an algicidal bacterium active against Karenia brevis (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae, 1, 277–293.
Mitsutani, A., Yamasaki, I., Kitaguchi, H., Kato, J., Ueno, S., & Ishida, Y. (2001). Analysis of algicidal proteins of a diatom-lytic marin bacterium Pseudoalteromnas sp. Strain A25 by two-dimensional electrophoresis. Phycologia, 40, 286–291.
Nakayama, N., Fujimoto, A., Kawami, H., Tomaru, Y., Hata, N., & Nagasaki, K. (2013). High interaction variability of the bivalve-killing dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama strains and their single-stranded RNA virus HcRNAV isolates. Microbes and Environments, 28, 112–119.
Paul, C., & Pohnert, G. (2011). Interactions of the algicidal bacterium Kordia algicida with diatoms: regulated protease excretion for specific algal lysis. PloS One, 6, e21032.
Symondson, W. O. C., Sundeland, K. D., & Greenstone, M. H. (2002). Can generalist predators be effective biocontrol agent? Annual Review of Entomology, 47, 561–594.
Thanongsak, C., Ampin, K., Charin, T., Noppol, L., Phisit, S., & Prasert, H. (2011). Optimization of cellulase-free xylanase production by thermophilic Streptomyces thermovulgaris TISTR1948 through Plackett-Burman and response surface methodological approaches. Bioscience Biotechnology Biochemical, 75, 531–537.
Yoon, H. K., Jung, S. W., & Joo, J. H. (2012). Use of immobilized algicidal bacteria to control natural freshwater diatom blooms. Hydrobiologia, 683, 151–162.
Zhang, C., Yi, Y. L., Hao, K., Liu, G. L., & Wang, G. X. (2013). Algicidal activity of Salvia miltiorrhiza bung on Microcystis aeruginosa—towards identification of algicidal substance and determination of inhibition mechanism. Chemosphere, 93, 997–1004.
Zhao, L., Chen, L., & Yin, P. (2014). Algicidal metabolites produced by Bacillus sp. strain B1 against Phaeocystis globosa. Journal of India Microbiology Biotechnology, 41, 593–9.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the Henan Key Science and Technology Research (Grant No. 122102310061 and Grant No. 112102310084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Chunli Liao and Xiaobo Liu are co-fist authors who have equal contributions to this study.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 104 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, C., Liu, X. High-Cell-Density Cultivation and Algicidal Activity Assays of a Novel Algicidal Bacterium to Control Algal Bloom Caused by Water Eutrophication. Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 2120 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2120-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2120-9