Abstract
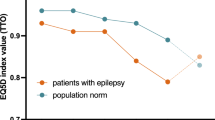
Epilepsy patients whose seizures cannot be controlled by treatment have a lower quality of life (QoL). The aim of the present study was to compare the potential factors affecting the QoL in patients who were seizure-free with medication or who had drug-resistant epilepsy. The study included 46 drug-resistant and 42 seizure-free epilepsy patients. The demographic and clinical features of the patients were investigated for their effects on patient QoL. The QoL was assessed by the QoL in Epilepsy Inventory-89 and depression was detected by the Beck Depression Inventory. The QoL was significantly lower in the drug-resistant patients than in the seizure-free epilepsy patients (p < 0.001). Depression, lower education level, and unemployment were associated with lower QoL scores (p < 0.001, p < 0.01, p < 0.001, respectively). After adjusting for lower education level and unemployment, depression remained as an independent factor affecting QoL (p < 0.05). In addition to their efforts to control and stop seizures, clinicians should remain aware of depression and treat it effectively to improve the QoL of drug-resistant epilepsy patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacoby A, Baker GA (2008) Quality-of-life trajectories in epilepsy: a review of the literature. Epilepsy Behav 12:557–571
Johnson EK, Jones JE, Seidenberg M, Hermann BP (2004) The relative impact of anxiety, depression, and clinical seizure features on health-related quality of life in epilepsy. Epilepsia 45:544–550
Şenol V, Soyuer F, Arman F, Öztürk A (2007) Influence of fatigue, depression, and demographic, socioeconomic, and clinical variables on quality of life of patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 10:96–104
Luoni C, Bisulli F, Canevini MP et al (2011) Determinants of health-related quality of life in pharmacoresistant epilepsy: results from a large multicenter study of consecutively enrolled patients using validated quantitative assessments. Epilepsia 52:2181–2191
Mehta S, Tyagi A, Tripathi R, Kumar M (2014) Study of inter-relationship of depression, seizure frequency and quality of life of people with epilepsy in India. Ment Illn 6:5169
Leidy NK, Elixhauser A, Vickrey B, Means E, Willian MK (1999) Seizure frequency and the health-related quality of life of adults with epilepsy. Neurology 53:162–166
Vickrey BG, Hays RD, Rausch R, Sutherling WW, Engel J, Brook RH (1994) Quality of life of epilepsy surgery patients as compared with outpatients with hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, and/or depressive symptoms. Epilepsia 35:597–607
Wiebe S, Rose K, Derry P, McLachlan R (1997) Outcome assessment in epilepsy: comparative responsiveness of quality of life and psychosocial instruments. Epilepsia 38:430–438
Baker GA, Hesdon B, Marson AG (2000) Quality-of-life and behavioral outcome measures in randomized controlled trials of antiepileptic drugs: a systematic review of methodology and reporting standards. Epilepsia 41:1357–1363
Taylor RS, Sander JW, Taylor RJ, Baker GA (2011) Predictors of health-related quality of life and costs in adults with epilepsy: a systematic review. Epilepsia 52:2168–2180
Rose KJ, Derry PA, Wiebe S, McLachian RS (1996) Determinants of health-related quality of life after temporal lobe epilepsy surgery. Qual Life Res 5:395–402
Spencer SS, Berg AT, Vickrey BG, Sperling MR, Bazil CW, Haut S, Langfitt JT, Walczak TS, Devinsky O (2007) Health-related quality of life over time since resective epilepsy surgery. Ann Neurol 62:327–334
Baker GA, Nashef L, van Hout BA (1997) Current issues in the management of epilepsy: the impact of frequent seizures on cost of illness, quality of life, and mortality. Epilepsia 38(Suppl 1):S1–S8
Gilliam FG, Fessler AJ, Baker G, Vahle V, Carter J, Attarian H (2004) Systematic screening allows reduction of adverse antiepileptic drug effects: a randomized trial. Neurology 62:23–27
Cramer JA, Brandenburg NA, Xu X, Vera-Llonch M, Oster G (2007) The impact of seizures and adverse effects on global health ratings. Epilepsy Behav 11:179–184
Tracy JI, Dechant V, Sperling MR, Cho R, Glosser D (2007) The association of mood with quality of life ratings in epilepsy. Neurology 68:1101–1107
Kwan P, Yu E, Leung H, Leon T, Mychaskiw MA (2009) Association of subjective anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbance with quality-of-life ratings in adults with epilepsy. Epilepsi. 50:1059–1066
Park S-P, Song H-S, Hwang Y-H, Lee H-W, Suh C-K, Kwon S-H (2010) Differential effects of seizure control and affective symptoms on quality of life in people with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 18:455–459
Devinsky O, Vickrey BG, Cramer J, Perrine K, Hermann B, Meador K, Hays RD (1995) Development of the quality of life in epilepsy inventory. Epilepsia 36:1089–1104
Kwan P, Brodie MJ (2000) Early identification of refractory epilepsy. N Engl J Med 342:314–319
Mallaoglu M, Durna ZEE (2001) Quality of life of patients with Epilepsy, epilepsy: assessment with the use of quality of life in Turkish, Inventory-89 (QOLIE-89). Epilepsia 7:73–80
Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbauch J (1961) An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 4:561–571
Hisli N (1989) Beck depresyon envanterinin universite ogrencileri icin gecerliligi ve guvenirligi. Psikol Derg 7:3–13
Stavem K, Loge JH, Kaasa S (2000) Health status of people with epilepsy compared with a general reference population. Epilepsia 41:85–90
Ulate-Campos A, Cean-Cabrera L, Petanas-Argemi J et al (2014) Vagus nerve stimulator implantation for epilepsy in a paediatric hospital: outcomes and effect on quality of life. Neurologia 30:465–471
Mikati MA, Ataya NF, El-ferezli JC, Baghdadi TS, Turkmani AH, Comair YG, Kansagra S, Najjar MW (2009) Quality of life after vagalnervestimulator insertion. Epileptic Disord 11:67–74
Dodrill CB, Morris GL (2001) Effects of vagal nerve stimulation on cognition and quality of life in epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 2:46–53
Gilliam FG, Santos J, Vahle V, Carter J, Brown K, Hecimovic H (2004) Depression in epilepsy: ignoring clinical expression of neuronal network dysfunction? Epilepsia 45(Suppl 2):28–33
Boylan LS, Flint LA, Labovitz DL, Jackson SC, Starner K, Devinsky O (2004) Depression but not seizure frequency predicts quality of life in treatment-resistant epilepsy. Neurology 62:258–261
Gilliam F, Kanner AM (2002) Treatment of depressive disorders in epilepsy patients. Epilepsy Behav 3:2–9
Gilliam F, Kuzniecky R, Faught E, Black L, Carpenter G, Schrodt R (1997) Patient-validated content of epilepsy-specific quality-of-life measurement. Epilepsia 38:233–236
Johnson EK, Jones JE, Seidenberg M, Hermann BP (2004) The relative impact of anxiety, depression, and clinical seizure features on health-related quality of life in epilepsy. Epilepsia 45:544–550
Szaflarski JP, Sangha KS, Lindsell CJ, Shutter LA (2010) Prospective, randomized, single-blinded comparative trial of intravenous levetiracetam versus phenytoin for seizure prophylaxis. Neurocrit Care 12:165–172
Hermann BP, Seidenberg M, Bell B (2000) Psychiatric comorbidity in chronic epilepsy: identification, consequences, and treatment of major depression. Epilepsia 41(Suppl 2):S31–S41
Jacobson AM, de Groot M, Samson JA (1997) The effects of psychiatric disorders and symptoms on quality of life in patients with type I and type II diabetes mellitus. Qual Life Res 6:11–20
Szaflarski M, Meckler JM, Privitera MD, Szaflarski JP (2006) Quality of life in medication-resistant epilepsy: the effects of patient’s age, age at seizure onset, and disease duration. Epilepsy Behav 8:547–551
Perucca P, Carter J, Vahle V, Gilliam FG (2009) Adverse antiepileptic drug effects: toward a clinically and neurobiologically relevant taxonomy. Neurology 72:1223–1229
Boylan LS, Devinsky O, Barry JJ, Ketter TA (2002) Psychiatric uses of antiepileptic treatments. Epilepsy Behav 3:54–59
Kwon O-Y, Park S-P (2011) What is the role of depressive symptoms among other predictors of quality of life in people with well-controlled epilepsy on monotherapy? Epilepsy Behav 20:528–532
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Ethical approval was received from the local ethics committee.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akdemir, V., Sut, N. & Guldiken, B. Factors affecting the quality of life in drug-resistant epilepsy patients. Acta Neurol Belg 116, 513–518 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-016-0622-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-016-0622-5