Abstract
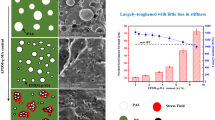
The toughening modification of PLA was successfully performed by incorporating modified natural rubber (MNR). The MNR was obtained from chemical modification of natural rubber (NR) in a latex system through a two-step procedure; hydrogenation followed by epoxidation reaction. Different amounts of NR and MNR were mixed with PLA by a physical melt-blending procedure. As a result, blending MNR (5% by weight) with PLA could efficiently strengthen fracture resistance (18.89 kJ/m2) and stretchability (113.79%), approximately fivefold and 16-fold, respectively, compared to the neat PLA (3.58 kJ/m2 impact strength and 7.08% elongation-at-break). In comparison, impact strength (7.21 kJ/m2) and elongation-at-break (8.64%) of NR/PLA were found at the same weight ratio. The high toughening efficiency of MNR for PLA could be explained by their good compatibility of the two phases. The impact-fractured surface of the blend showed fine rubber particles and stretched-rubber fibrils in the scanning electron microscope (SEM) image. Furthermore, the optical properties in terms of light transmission of the MNR/PLA blend displayed higher transparency (74.62%) than the unmodified NR/PLA blend (34.34%). The obtained results suggest that the developed MNR will offer a potential application as a high impact modifier for PLA.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others

References
D’Amato D, Korhonen J, Toppinen A (2019) Circular, green, and bio economy: how do companies in land-use intensive sectors align with sustainability concepts? Ecol Econ 158:116–133
D’Amato D, Droste N, Allen B, Kettunen M, Lähtinen K, Korhonen J, Leskinen P, Matthies BD, Toppinen A (2017) Green, circular, bio economy: a comparative analysis of sustainability avenues. J Clean Prod 168:716–734
Zinatloo-Ajabshir S, Heidari-Asil SA, Salavati-Niasari M (2021) Recyclable magnetic ZnCo2O4-based ceramic nanostructure materials fabricated by simple sonochemical route for effective sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of organic pollution. Ceram Int 47:8959–8972
Zinatloo-Ajabshir S, Heidari-Asil SA, Salavati-Niasari M (2021) Simple and eco-friendly synthesis of recoverable zinc cobalt oxide-based ceramic nanostructure as high-performance photocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic removal of organic contamination under solar light. Sep Purif Technol 267:118667
Taheri Qazvini N, Zinatloo S (2011) Synthesis and characterization of gelatin nanoparticles using CDI/NHS as a non-toxic cross-linking system. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 22:63–69
Zinatloo-Ajabshir S, Taheri Qazvini N (2014) Inverse miniemulsion method for synthesis of gelatin nanoparticles in presence of CDI/NHS as a non-toxic cross-linking system. J Nanostruct 4:267–275
Zinatloo-Ajabshir S, Mousavi-Kamazani M (2020) Effect of copper on improving the electrochemical storage of hydrogen in CeO2 nanostructure fabricated by a simple and surfactant-free sonochemical pathway. Ceram Int 46:26548–26556
Robaina M, Murillo K, Rocha E, Villar J (2020) Circular economy in plastic waste-efficiency analysis of European countries. Sci Total Environ 730:139038
Sverko Grdic Z, Krstinic Nizic M, Rudan E (2020) Circular economy concept in the context of economic development in EU countries. Sustainability 12:3060
Ding Y, Zhang C, Luo C, Chen Y, Zhou Y, Yao B, Dong L, Du X, Ji J (2021) Effect of talc and diatomite on compatible, morphological, and mechanical behavior of PLA/PBAT blends. E-Polymers 21:234–243
Diyana ZN, Jumaidin R, Selamat MZ, Ghazali I, Julmohammad N, Huda N, Ilyas RA (2021) Physical properties of thermoplastic starch derived from natural resources and its blends: a review. Polymers (Basel) 13:1396
Fekete I, Ronkay F, Lendvai L (2021) Highly toughened blends of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and natural rubber (NR) for FDM-based 3D printing applications: the effect of composition and infill pattern. Polym Test 99:107205
Naser AZ, Deiab I, Darras BM (2021) Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), green alternatives to petroleum-based plastics: a review. RSC Adv 11:17151–17196
Rezvani Ghomi E, Khosravi F, Saedi Ardahaei A, Dai Y, Neisiany RE, Foroughi F, Wu M, Das O, Ramakrishna S (2021) The life cycle assessment for polylactic acid (PLA) to make it a low-carbon material. Polymers (Basel) 13:1854
Zhou C, Li H, Zhang Y, Xue F, Huang S, Wen H, Li J, de Claville CJ, Yu D, Wu Z, Jiang S (2015) Deformation and structure evolution of glassy poly(lactic acid) below the glass transition temperature. Cryst Eng Comm 17:5651–5663
Oliaei E, Kaffashi B, Davoodi S (2016) Investigation of structure and mechanical properties of toughened poly(l-lactide)/thermoplastic poly(ester urethane) blends. J Appl Polym Sci 133:43104
Sun M, Huang S, Yu M, Han K (2021) Toughening modification of polylactic acid by thermoplastic silicone polyurethane elastomer. Polymers (Basel) 13:1953
Maroufkhani M, Katbab A, Liu W, Zhang J (2017) Polylactide (PLA) and acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) blends: the effect of ACN content on morphology, compatibility and mechanical properties. Polymer 115:37–44
Ferri JM, Garcia-Garcia D, Carbonell-Verdu A, Fenollar O, Balart R (2018) Poly(lactic acid) formulations with improved toughness by physical blending with thermoplastic starch. J Appl Polym Sci 135:45751
Trinh BM, Chang CC, Mekonnen TH (2021) Facile fabrication of thermoplastic starch/poly (lactic acid) multilayer films with superior gas and moisture barrier properties. Polymer 223:123679
Nazrin A, Sapuan SM, Zuhri MYM, Tawakkal ISMA, Ilyas RA (2021) Water barrier and mechanical properties of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch (TPS)/poly(lactic acid) (PLA) blend bionanocomposites. Nanotechnol Rev 10:431–442
Lerma-Canto A, Gomez-Caturla J, Herrero-Herrero M, Garcia-Garcia D, Fombuena V (2021) Development of polylactic acid thermoplastic starch formulations using maleinized hemp oil as biobased plasticizer. Polymers (Basel) 13:1392
Pyay S, Thanungkano W, Mungkalasiri J, Musikavong C (2019) A life cycle assessment of intermediate rubber products in Thailand from the product environmental footprint perspective. J Clean Prod 237:117632
Ayar M, Dalkiran A, Kale U, Nagy A, Karakoc TH (2021) Investigation of the substitutability of rubber compounds with environmentally friendly materials. Sustainability 13:5251
Smitthipong W, Suethao S, Shah D, Vollrath F (2016) Interesting green elastomeric composites: silk textile reinforced natural rubber. Polym Test 55:17–24
Bitinis N, Verdejo R, Cassagnau P, Lopez-Manchado MA (2011) Structure and properties of polylactide/natural rubber blends. Mater Chem Phys 129:823–831
Syed Mustafa SNI, Che Man SH, Baharulrazi N, Mohamad Z, Hassan A, Yusof NH (2020) Mechanical and thermal properties of polylactic acid/liquid epoxidized natural rubber blends. Chem Eng Trans 78:103–108
Klinkajorn J, Tanrattanakul V (2019) Compatibilization of poly(lactic acid)/epoxidized natural rubber blend with maleic anhydride. J Appl Polym Sci 137:48297
Phetphaisit CW, Wapanyakul W, Phinyocheep P (2019) Effect of modified rubber powder on the morphology and thermal and mechanical properties of blown poly(lactic acid)–hydroxyl epoxidized natural rubber films for flexible film packaging. J Appl Polym Sci 136:47503
Burkov A, Kraev A, Grishin M, Vesnin R, Fomin S, Iordanskii A (2021) Structural features and properties’ characterization of polylactic acid/natural rubber blends with epoxidized soybean oil. Polymers (Basel) 13:1101
Tessanan W, Chanthateyanonth R, Yamaguchi M, Phinyocheep P (2020) Improvement of mechanical and impact performance of poly(lactic acid) by renewable modified natural rubber. J Clean Prod 276:123800
Ikeda Y, Phinyocheep P, Kittipoom S, Ruancharoen J, Kokubo Y, Morita Y, Hijikata K, Kohjiya S (2008) Mechanical characteristics of hydrogenated natural rubber vulcanizates. Polym Adv Technol 19:1608–1615
Phinyocheep P, Phetphaisit CW, Derouet D, Campistron I, Brosse JC (2005) Chemical degradation of epoxidized natural rubber using periodic acid: preparation of epoxidized liquid natural rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 95:6–15
Samran J, Phinyocheep P, Daniel P, Kittipoom S (2005) Hydrogenation of unsaturated rubbers using diimide as a reducing agent. J Appl Polym Sci 95:16–27
Jaratrotkamjorn R, Khaokong C, Tanrattanakul V (2012) Toughness enhancement of poly(lactic acid) by melt blending with natural rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 124:5027–5036
Zhang C, Man C, Pan Y, Wang W, Jiang L, Dan Y (2011) Toughening of polylactide with natural rubber grafted with poly(butyl acrylate). Polym Int 60:1548–1555
Ji M, Yue D, Wu X, Zhao S, Sun S, Zhang L (2017) Structure and performance of hydrogenated natural rubber prepared by the latex method. Plast Rubber Compos 46:245–250
Jeerupun J, Wootthikanokkhan J, Phinyocheep P (2004) Effects of epoxidation content of ENR on morphology and mechanical properties of natural rubber blended PVC. Macromol Symp 216:281–292
Zhang C, Wang W, Huang Y, Pan Y, Jiang L, Dan Y, Luo Y, Peng Z (2013) Thermal, mechanical and rheological properties of polylactide toughened by expoxidized natural rubber. Mater Des 45:198–205
Rosli NA, Ahmad I, Anuar FH, Abdullah I (2016) Mechanical and thermal properties of natural rubber-modified poly(lactic acid) compatibilized with telechelic liquid natural rubber. Polym Test 54:196–202
Collyer AA (1994) Rubber toughened engineering plastics. Springer, Netherlands
Juntuek P, Ruksakulpiwat C, Chumsamrong P, Ruksakulpiwat Y (2012) Effect of glycidyl methacrylate-grafted natural rubber on physical properties of polylactic acid and natural rubber blends. J Appl Polym Sci 125:745–754
Zhao X, Hu H, Wang X, Yu X, Zhou W, Peng S (2020) Super tough poly(lactic acid) blends: a comprehensive review. RSC Adv 10:13316–13368
Pongtanayut K, Thongpin C, Santawitee O (2013) The effect of rubber on morphology, thermal properties and mechanical properties of PLA/NR and PLA/ENR blends. Energy Procedia 34:888–897
Wang Y, Chen K, Xu C, Chen Y (2015) Supertoughened biobased poly(lactic acid)–epoxidized natural rubber thermoplastic vulcanizates: fabrication, co-continuous phase structure, interfacial in situ compatibilization, and toughening mechanism. J Phys Chem B 119:12138–12146
Xu C, Yuan D, Fu L, Chen Y (2014) Physical blend of PLA/NR with co-continuous phase structure: preparation, rheology property, mechanical properties and morphology. Polym Test 37:94–101
Hoseini M, Haghtalab A, Famili MHN (2017) Rheology and morphology study of immiscible linear low-density polyethylene/poly(lactic acid) blends filled with nanosilica particles. J Appl Polym Sci 134:45526
Tomić NZ (2020) Introduction. In: Ajitha AR, Thomas S (eds) Compatibilization of polymer blends, 1st edn. Elsevier, Netherlands
Miao M, Wei C, Wang Y, Qian Y (2018) Effect of compatibilizer on the interface bonding of graphene oxide/polypropylene composite fibers. Polymers (Basel) 10:1283
Taraghi I, Paszkiewicz S, Irska I, Pypeć K, Piesowicz E (2020) The role of interfacial interactions on the functional properties of ethylene–propylene copolymer containing SiO2 nanoparticles. Polymers (Basel) 12:2308
Auras R, Harte B, Selke S (2004) An overview of polylactides as packaging materials. Macromol Biosci 4:835–864
Pluta M, Bojda J, Piorkowska E, Murariu M, Bonnaud L, Dubois P (2017) The effect of halloysite nanotubes and N, N′-ethylenebis (stearamide) on morphology and properties of polylactide nanocomposites with crystalline matrix. Polym Test 64:83–91
Mathlouthi M (1994) Food packaging and preservation. Springer, USA
Zhao L-L, Su J-J, Han J, Zhang B, Ou L (2017) Optimizing the balance between stiffness and flexibility by tuning the compatibility of a poly(lactic acid)/ethylene copolymer. RSC Adv 7:23065–23072
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Science Achievement Scholarship of Thailand (SAST) for Wasan Tessanan. Partial support from IRPC Public Company Limited is also appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tessanan, W., Phinyocheep, P. Toughening modification of poly(lactic acid) using modified natural rubber. Iran Polym J 31, 455–469 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-021-01000-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-021-01000-0