Abstract
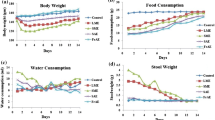
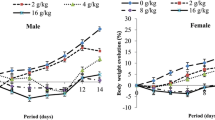
Streblus asper Lour (Family: Moraceae) is a medicinal plant wildly grows in most part of Asian countries. It has many traditional uses like leprosy, piles, diarrhoea, dysentery, elephantiasis, cancer etc. This present study was relates in terms of behavioural safety and toxicity studies of methanol and petroleum ether extracts of S. asper. Brine Shrimps lethality bioassay method was established for the present study and cytotoxicity was reported in terms of 50% lethality concentration (LC50). Different concentrations of drug solutions were added to the Brine Shrimps, surviving shrimps were counted after 24 h and 50% lethality concentration (LC50) were assessed. Acute toxicity was studied on Swiss albino mice after single dose. Sub-Chronic toxicity was performed for 28 days and assessed with biochemical and histopathological parameters. On cytotoxicity studies of brine shrimps it was found methanol extract of S. asper (MESA) was weakly toxic, may be due to the presence of cardiac glycosides and bioactive compounds, however petroleum ether extract of S. asper (PESA) was non toxic. But, in case of acute and sub-acute toxicity study both extracts were found to be non-toxic.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam M (1992) Medical ethnobotany of the Marma tribe of Bangladesh. Econ Bot 46:330–335. doi:10.1007/BF02866632
Barahona M, Sanchez-Fortun S (1999) Toxicity of carbamates to the brine shrimp Artemia salina and the effect of atropine, BW284c51, iso-OMPA and 2-PAM on carbaryl toxicity. Environ Pollut 104:469–476. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(98)00152-3
Bhandary M, Chandrashekar K, Kaveriappa K (1995) Medical ethnobotany of the siddis of Uttara Kannada district, Karnataka, India. J Ethnopharmacol 47:149–158
Cepleanu F, Hamburger M, Sordat B, Msonthi J, Gupta M, Saadou M, Hostettmann K (1994) Screening of tropical medicinal plants for molluscicidal, larvicidal, fungicidal and cytotoxic activities and brine shrimp toxicity. Pharm Biol 32:294–307
Chan K (2003) Some aspects of toxic contaminants in herbal medicines. Chemosphere 52:1361–1371
Deciga-Campos M, Rivero-Cruz I, Arriaga-Alba M, Castaneda-Corral G, Angeles-Lopez GE, Navarrete A, Mata R (2007) Acute toxicity and mutagenic activity of Mexican plants used in traditional medicine. Journal of ethnopharmacology 110:334–342
Fennell C, Lindsey K, McGaw L, Sparg S, Stafford G, Elgorashi E, Grace O, Van Staden J (2004) Assessing African medicinal plants for efficacy and safety: pharmacological screening and toxicology. J Ethnopharmacol 94:205–217
Fiebig M, Duh CY, Pezzuto JM, Kinghorn AD, Farnsworth NR (1985) Plant anticancer agents, XLI. Cardiac glycosides from Streblus asper. J Nat Prod 48:981–985
Gupta M, Monge A, Karikas G, Lopez de Cerain A, Solis P, De Leon E, Trujillo M, Suarez O, Wilson F, Montenegro G (1996) Screening of Panamanian medicinal plants for brine shrimp toxicity, crown gall tumor inhibition, cytotoxicity and DNA intercalation. Pharm Biol 34:19–27
Kostis JB, Turkevich D, Sharp J (1984) Association between leukocyte count and the presence and extent of coronary atherosclerosis as determined by coronary arteriography. Am J Cardiol 53:997–999
Lapornik B, Prosek M, Golc Wondra A (2005) Comparison of extracts prepared from plant by-products using different solvents and extraction time. J Food Eng 71:214–222
Malek D, Malley L, Slone T, Elliott G, Kennedy G, Mellert W, Deckardt K, Gembardt C, Hildebrand B, Murphy S (1997) Repeated dose toxicity study (28 days) in rats and mice with N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP). Drug Chem Toxicol 20:63–77
Meyer B, Ferrigni N, Putnam J, Jacobsen L, Nichols D, McLaughlin J (1982) Brine shrimp: a convenient general bioassay for active plant constituents. Planta Med 45:31–34
Michael A, Thompson C, Abramovitz M (1956) Artemia salina as a test organism for bioassay. Science 123:464
Mongelli E, Martino V, Coussio J, Ciccia G (1996) Screening of Argentine medicinal plants using the brine shrimp microwell cytotoxicity assay. Pharm Biol 34:249–254
Pelka M, Danzl C, Distler W, Petschelt A (2000) A new screening test for toxicity testing of dental materials. J Dent 28:341–345
Rastogi S, Kulshrestha DK, Rawat AKS (2006) Streblus asper Lour. (Shakhotaka): a review of its chemical, pharmacological and ethnomedicinal properties. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 3(2):217–222. doi:10.1093/ecam/nel018
Solis PN, Wright CW, Anderson MM, Gupta MP, Phillipson JD (1993) A microwell cytotoxicity assay using Artemia salina (brine shrimp). Planta Med 59:250–250
Acknowledgement
This work was fully funded by University Grants Commission (U.G.C), Grant number P-1\RS\115\2010, New Delhi, India. This funding had no role in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data or in the writing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R.B.S., Puratchikodi, A., Prasanna, A. et al. Pre clinical studies of Streblus asper Lour in terms of behavioural safety and toxicity. Orient Pharm Exp Med 11, 243–249 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-011-0040-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-011-0040-4