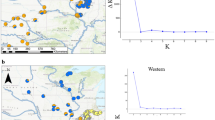
Abstract
The worldwide decline of pollinators is an emerging threat and is a matter both for ecological and economic concerns. Population genetics can be used to correlate bumblebee decline with genetic parameters. In order to do so, historical data are needed. We used eight microsatellite loci to genotype pinned museum specimens of the declining bumblebee Bombus veteranus. Bumblebee samples were collected spanning a period of three decades (1895–1923). We detected low genetic diversity and inbreeding in the samples collected during the respective time periods. Inbreeding was also confirmed by the occurrence of sterile diploid males. Based on the data obtained, we speculate that low genetic diversity and inbreeding did not directly result in the collapse of B. veteranus in Belgium. However, inbreeding might still play an indirect role in the decline of bumblebee populations because of the appearance of diploid males and because a low H E might reduce the capacity to react to the drivers of bumblebee decline.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, C.N.K., Ramakrishnan, U., Chan, Y.L., Hadly, E.A. (2005) Serial SimCoal: a population genetic model for data from multiple populations and points in time. Bioinformatics 21, 1733–1734
Ashley, M.V., Berger-Wolf, T.Y., Caballero, I.C., Chaovalitwongse, W., Dasgupta, B., et al. (2008) Full siblings reconstruction in wild populations from microsatellite genetic markers. Nova, Hauppauge. Computational Biology: New Research
Ashley, M.V., Caballero, I.C., Chaovalitwongse, W., Dasgupta, B., Govindan, P., Sheikh, S.I., Berger-Wolf, T.Y. (2009) KINALYZER, a computer program for reconstructing sibling groups. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 9, 1127–1131
Blacquière, T., Smagghe, G., Van Gestel, C.A.M., Mommaerts, V. (2012) Neonicotinoids in bees: a review on concentrations, side-effects and risk-assessment. Ecotoxicoly 21, 973–992
Callen, D.F., Thompson, A.D., Shen, Y., Phillips, H.A., Richards, R.I., Mulley, J.C., Sutherland, G.R. (1993) Incidence and origin of “null” alleles in the (AC)n microsatellite markers. Am. J. Hum. Genet 52, 922–927
Cameron, S.A., Lozier, J.D., Strange, J.P., Koch, J.B., Cordes, N., Solter, L.F., Griswold, T.L. (2011) Patterns of widespread decline in North American bumble bees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 18, 662–667
Chapuis, M.-P., Estoup, A. (2007) Microsatellite null alleles and estimation of population differentiation. Mol. Biol. Evol 24, 621–631
Chapuis, M.-P., Lecoq, M., Michalakis, Y., Loiseau, A., Sword, G.A., Piry, S., Estoup, A. (2008) Do outbreaks affect genetic population structure? A worldwide survey in Locusta migratoria, a pest plagued by microsatellite null alleles. Mol. Ecol 17, 3640–3653
Chybicki, I.J., Burczyk, J. (2009) Simultaneous estimation of null alleles and inbreeding coefficients. J. Hered 100, 106–113
Connop, S., Hill, T., Steer, J., Shaw, P. (2010) The role of dietary breadth in national bumblebee (Bombus) declines: simple correlation? Biol. Conserv 143, 2739–2746
Cook, J.M., Crozier, R.H. (1995) Sex determination and population biology in the Hymenoptera. Trends Ecol. Evol 10, 281–286
Crawford, N.G. (2010) SMOGD: software for the measurement of genetic diversity. Mol. Ecol. Resour 10, 556–557
Duchateau, M.J., Hishiba, H., Velthuis, H.H.W. (1994) Diploid males in the bumble bee Bombus terrestris. Entomol. Exp. Appl 71, 263–269
El Mousadik, A., Petit, R.J. (1996) Chloroplast DNA phylogeography of the argan tree of Morocco. Mol. Ecol 5, 547–555
Estoup, A., Solignac, M., Harry, M., Cornuet, J.-M. (1993) Characterization of (GT)n and (CT)n microsatellites in two insect species Apis mellifera and Bombus terrestris. Nucleic. Acid. Res 21, 1427–1431
Excoffier, L., Novembre, J., Schneider, S. (2000) SimCoal: a general coalescent program for simulation of molecular data in interconnected populations with arbitrary demography. J. Hered 91, 506–509
Frankham, R. (2005) Genetics and extinction. Biol. Conserv 126, 131–140
Garza, J.C., Williamson, E. (2001) Detection of reduction in population size using data from microsatellite DNA. Mol. Ecol 10, 305–318
Gerloff, C.U., Schmid-Hempel, P. (2005) Inbreeding depression and family variation in a social insect, Bombus terrestris (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Oikos 111, 67–80
Goudet, J. (2001) Fstat: a program to estimate and test gene diversities and fixation indices (version 2.9.3). Updated from Goudet, J. (1995): Fstat (version 1.2): a computer program to calculate F-statistics. J. Hered 86, 485–486
Goulson, D., Osborne, J.L. (2010) Foraging economics. Bumblebees: behaviour, ecology and conservation (ed. by D. Goulson), p. 96. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK
Goulson, D., Lye, G.C., Darvill, B. (2008) Decline and conservation of bumble bees. Annu. Rev. Entomol 53, 191–208
Guinand, B., Scribner, K.T. (2003) Evaluation of methodology for detection of genetic bottlenecks: inferences from temporally replicated lake trout populations. C. R. Biol 326(Supplement 1), 61–67
Hines, H.M., Hendrix, S.D. (2005) Bumble bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae) diversity and abundance in tallgrass prairie patches: effects of local and landscape floral resources. Environ. Entomol. 34, 1477–1484
Jost, L. (2008) G(ST) and its relatives do not measure differentiation. Mol. Ecol. 17, 4015–4026
Keller, L.F., Waller, D.M. (2002) Inbreeding effects in wild populations. Trends Ecol. Evol. 17, 230–241
Klein, A.-M., Vaissière, B.E., Cane, J.H., Steffan-Dewenter, I., Cunningham, S.A., et al. (2007) Importance of pollinators in changing landscapes for world crops. Proc. R. Soc. B. 274, 303–313
Kremen, C., Williams, N.M., Aizen, M.A., Gemmill-Herren, B., Le Buhn, G., et al. (2007) Pollination and other ecosystem services produced by mobile organisms: a conceptual framework for the effects of land-use change. Ecol. Lett 10, 299–314
Lozier, J.D., Cameron, S.A. (2009) Comparative genetic analyses of historical and contemporary collections highlight contrasting demographic histories for the bumblebees Bombus pensylvanicus and B. impatiens in Illinois. Mol. Ecol 18, 1875–1886
Meeus, I., Brown, M.J.F., de Graaf, D.C., Smagghe, G. (2011) Effects of invasive parasites on bumble bee declines. Conserv. Biol 25, 662–671
Nei, M. (1978) Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 89, 583–590
Packer, L., Owen, R. (2001) Population genetic aspects of pollinator decline. Conserv. Ecol 5, 4
Pauly, A., Rasmont, P. (2010) Les bourdons de la Belgique. Website Atlas Hymenoptera, Gembloux Agro-Biotech, Université de Mons, Gembloux, Mons. http://www.zoologie.umh.ac.be/hymenoptera/page.asp?id=160. Accessed 10 January, 2012.
Peakall, R., Smouse, F. (2006) GENALEX 6: Genetic Analysis in Excel. Population Genetic Software for Teaching and Research. Australian National University, Canberra, Australia
Rasmont, P., Iserbyt, I. (2010) Atlas of the European Bees: genus Bombus. STEP Project, Atlas Hymenoptera, Mons, Gembloux. http://www.zoologie.umh.ac.be//hymenoptera/page.asp?ID=169. Accessed 25 December, 2011.
Rasmont, P., Mersch, P. (1988) Premiere estimation de la dérive faunique chez les bourdons de la Belgique (Hymenoptera, Apidae). Ann. Soc. Royal Zool. Bel 118, 141–147
Rasmont, P., Leclercq, J., Jacob-Remacle, A., Pauly, A., Gaspar, C. (1993) The faunistic drift of Apoidea in Belgium. pp. 65-87, in Bruneau, E., Bees for pollination, Commission of the European Communities, Brussels, 237 pp.
Rasmont, P., Pauly, A., Terzo, M., Patiny, S., Michez, D., Iserbyt, S., Barbier, Y., Haubruge, E. (2005) The survey of wild bees (Hymenoptera, Apoidea) in Belgium and France. FAO, Roma, 18 pp.
Reber Funk, C., Schmidt-Hempel, R., Schmid-Hempel, P. (2006) Microsatellite loci for Bombus spp. Mol. Ecol. Notes 6, 83–86
Schmid-Hempel, P., Schmid-Hempel, R., Brunner, P.C., Seeman, O.D., Allen, G.R. (2007) Invasion success of the bumblebee, Bombus terrestris, despite a drastic genetic bottleneck. Heredity 99, 414–422
Söderman, G. (1999) Diversity of pollinator communities in Eastern Fennoskandia and Eastern Baltics. Results from pilot monitoring with yellow traps in 1997–1998. The Finnish Environment 355, Finnish Environment Institute, Helsinki.
Sorati, M., Newman, M., Hovman, A.A. (1996) Inbreeding and incompatibility in Trichogramma brassicae: evidence and implications for quality control. Entomol. Exp. Appl 78, 283–290
Strange, J.P., Knoblett, J., Griswold, T. (2009) DNA amplification from pin-mounted bumble bees (Bombus) in a museum collection: effects of fragment size and specimen age on successful PCR. Apidologie 40, 134–139
Stroot, P., Depiereux (1989) Proposition d'une méthodologie pour établir des listes rouges d'invertébrés menacé. Biol. Conserv 48, 163–179
Thompson, H.M. (2001) Assessing the exposure and toxicity of pesticides to bumblebees (Bombus sp.). Apidologie 32, 305–321
Van Oosterhout, C., Hutchinson, W.F., Wills, D.P.M., Shipley, P. (2004) MICROCHECKER: software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors. Mol. Ecol. Notes 4, 535–538
Voveikov, G.S. (1953) Estestvennaya smena samok vo cem’ya shchmelej (Hym. Bomb.). Russkoe entomol obozrenie 33, 174–184
Wandeler, P., Hoeck, P.E.A., Keller, L.F. (2007) Back to the future: museum specimens in population genetics. Trends Ecol. Evol 22, 634–642
Wang, J.L. (2004) Sibship reconstruction from genetic data with typing errors. Genetics 166, 1963–1979
Whitehorn, P.R., Tinsley, M.C., Brown, M.J.F., Darvill, B., Goulson, D. (2009) Impacts of inbreeding on bumblebee colony fitness under field conditions. BMC Evol. Biol 9, 152
Williams, P.H. (1982) The distribution and decline of British bumble bees (Bombus Latr.). J. Apic. Res 21, 236–245
Zayed, A. (2009) Bee genetics and conservation. Apidologie 40, 237–262
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Special Research Fund of Ghent University, the Fund for Scientific Research-Flanders (FWO-Vlaanderen), and the Fonds de la Recherche Scientifique–Fonds de la Recherche Fondamentale Collective (FNRS-FRFC) (FRFC convention no. 2.4618.12).
Bombus veteranus : l’analyse de microsatellites de cette espèce à partir d’échantillons d’un museum révèle une consanguinité avant leur régression.
Microsatellites / ADN ancien / collections muséographiques / diversité génétique / déclin des bourdons
Mikrosatelliten-Analyse von Museumsproben verrät das Auftreten von Inzucht bereits vor dem Rückgang von Bombus veteranus.
Mikrosatelliten / ancient DNA / Museumssammlungen / geneRückgang von Hummeln / Rückgang von Hummeln
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Bombus veteranus : l’analyse de microsatellites de cette espèce à partir d’échantillons d’un museum révèle une consanguinité avant leur régression.
Microsatellites/ADN ancien/collections muséographiques/diversité génétique/déclin des bourdons
Mikrosatelliten-Analyse von Museumsproben verrät das Auftreten von Inzucht bereits vor dem Rückgang von Bombus veteranus.
Mikrosatelliten/ancient DNA/Museumssammlungen/geneRückgang von Hummeln/Rückgang von Hummeln
Manuscript editor: Marina Meixner
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maebe, K., Meeus, I., Maharramov, J. et al. Microsatellite analysis in museum samples reveals inbreeding before the regression of Bombus veteranus . Apidologie 44, 188–197 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13592-012-0170-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13592-012-0170-9