Abstract
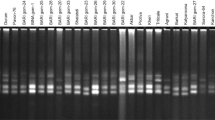
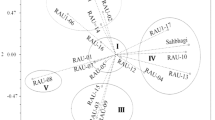
A set of 24 genotypes bred at different centres in India as well as in CIMMYT showing variability for drought tolerance were selected for molecular and morpho-physiological characterization. A set of 35 SSR markers, having genome-wide coverage, was chosen for genotyping the inbreds. These markers generated a total of 111 polymorphic alleles with an average of 3.17 alleles per locus. The minimum and maximum PIC value was 0.27 and 0.77 with a mean of 0.5. A total of 13 unique alleles were found in the 24 inbred lines. The coefficient of genetic dissimilarity ranged from 0.192 to 0.803. NJ-based tree suggested the presence of three major clusters of which, two of them had subgroups. Phenotyping of inbreds by morpho-physiological traits revealed that there was a positive relationship among root length, chlorophyll content, relative water content while anthesis-silking interval was negative relationship with all these traits. Genotyping data complemented by morpho-physiological parameters were used to identify a number of pair-wise combinations for the development of mapping population segregating for drought tolerance and potential heterotic pairs for the development of drought tolerant hybrids.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RWC:
-
Relative water content
- ASI:
-
Anthesis-silking interval
- RL:
-
Root length
- CC:
-
Chlorophyll content
- LAI:
-
Leaf area index
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait locus
References
Ajmone-Marsan P, Castiglioni P, Fusari F, Kuiper M, Motto M (1998) Genetic diversity and its relationship to hybrid performance in maize as revealed by RFLP and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 96:219–227
Barata C, Carena MJ (2006) Classification of North Dakota maize inbred lines into heterotic groups based on molecular and testcross data. Euphytica 151:339–349
Beck DL, Vasal SK, Crossa J (1991) Heterosis and combining ability among subtropical and temperate intermediate-maturity maize germplasm. Crop Sci 31:68–73
Chin ECL, Senior ML, Shu H, Smith JSC (1996) Maize simple repetitive DNA sequences: abundance and allele variation. Genome 39:866–873
Dickson Ng’uni, Mulatu Geleta, Tomas Bryngelsson (2011) Genetic diversity in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) accessions of Zambia as revealed by simple sequence repeats (SSR) 148:52–62.
Dubreuil P, Charcosset A (1999) Relationships among maize inbred lines and populations from European and North-American origins as estimated using RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 99:473–480
Dubreuil P, Dufour P, Krejci E, Causse M, de Vienne D, Gallais A, Charcosset A (1996) Organization of RFLP diversity among inbred lines of maize representing the most significant heterotic groups. Crop Sci 36:790–799
Enoki H, Sato H, Koinuma K (2002) SSR analysis of genetic diversity among maize inbred lines adapted to cold regions of Japan. Theor Appl Genet 104:1270–1277
GENSTAT 14 Committee. 2011. GENSTAT 6 reference manual. Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK.
Chenyang H, Wang L, Ge H, Dong Y, Zhang X (2011) Genetic diversity and linkage disequilibrium in Chinese Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) revealed by SSR markers. PLoS ONE 6(2):e17279
Gethi JG, Labate JA, Lamkey KR, Smith ME, Kresovich S (2002) SSR variation in important US maize inbred lines. Crop Sci 42:951–957
Goodman MM, Bird RM (1977) The races of maize IV: tentative grouping of 219 Latin American races. Econ Bot 31:204–221
Heckenberger M, Melchinger AE, Ziegle JS, Joe LK, Hauser JD, Hutton M, Bohn M (2002) Variation of DNA fingerprints among accessions within maize inbred lines with regard to the identification of essentially derived varieties. I. Genetic and technical sources of variation in SSR data. Mol Breed 10:181–191
Jiang H-F, Ren X-P, Zhang X-J, Huang J-Q, Lei Y, Yan L-Y, Liao B-S, Upadhyaya HD, Holbrook CC (2010) Comparison of genetic diversity based on SSR markers between peanut mini core collections from China and ICRISAT. Acta Agron Sin 36:1084–1091
Le Clerc V, Bazante F, Baril C, Guiard J, Zhang D (2005) Assessing temporal changes in genetic diversity of maize varieties using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 110:294–302
Legesse BW, Myburg AA, Pixley KV, Botha AM (2007) Genetic diversity of African maize inbred lines revealed by SSR markers. Hereditas 144:10–7
Liu K, Muse SV (2005) PowerMarker: integrated analysis environment for genetic marker data. Bioinformatics 21:2128–2129
Liu ZW, Biyashev R, Saghai-Maroof M (1996) Development of simple sequence repeats DNA markers and their integration into a barley linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 93:869–876
Liu K, Goodman M, Muse S et al (2003) Genetic structure and diversity among maize inbred lines as inferred from DNA microsatellites. Genetics 165:2117–2128
Lu H, Bernardo R (2001) Molecular marker diversity among current and historical maize inbreds. Theor Appl Genet 103:613–617
Matsuoka Y, Mitchell SE, Kresovich S (2002) Microsatellites in Zea -variability, patterns of mutations and use for evolutionary studies. Theor Appl Genet 104:436–450
Melchinger AE, Gumber RK (1998) Overview of heterosis and heterotic groups in agronomic crops. In: Lamkey KR, Staub JE (eds) Concepts and breeding of heterosis in crop plants. CSSA, Madison, pp 29–44
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Perrier X, Flori A, Bonnot F (2003) Data analysis methods. In: Hamon P, Seguin M, Perrier X, Glaszmann JC (eds) Genetic diversity of cultivated tropical plants. Science Publishers Montpellier, Enfield, pp 43–76
Pinto LR, Vieira MLC, de Souza CL et al (2003) Genetic diversity assessed by microsatellites in tropical maize population submitted to high-density reciprocal recurrent selection. Euphytica 134:277–286
Reif JC, Melchinger AE, Xia XC, Warburton ML et al (2003) Use of SSRs for establishing heterotic groups in subtropical maize. Theor Appl Genet 107:947–957
Ron Parra J, Hallauer AR (1997) Utilization of exotic maize germplasm. Plant Breed Rev 14:165–187
Saker MM, Youssef SS, Abdallah NA, Bashandy HS et al (2005) Genetic analysis of some Egyptian rice genotypes using RAPD, SSR and AFLP. Afr J Biotechnol 4:882–890
Schug MD, Hutter CM, Wetterstr KA et al (1998) The mutation rate of di, tri and tetra-nucleotide repeats in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol 15:1751–1760
Semagn K, Bjørnstad A, Ndjiondjop MN (2006) Principles, requirements and prospects of genetic mapping in plants. African J Biotech 5:2569–2587
Senior ML, Chin ECL, Lee M et al (1996) Simple sequences repeat markers developed from maize sequences found in the GENEBANK database: map construction. Crop Sci 36:1676–1683
Senior ML, Murphy JP, Goodman MM et al (1998) Utility of SSRs for determining genetic similarities and relationships in maize using agarose gel system. Crop Sci 38:1088–1098
Sharon EM, Kresovich S, Jester CA, Hernandez CJ, Szewc-McFadden AK (1997) Application of multiplex PCR and fluorescence-based, semi-automated allele sizing technology for genotyping plant genetic resources. Crop Sci 37:617–624
Singh NN, Venkatesh S, Sekhar JC, Zaidi PH (2005) Stresses on maize in the tropics - progress and challenges. In: Stresses on maize in tropics. Directorate of Maize Research, New Delhi, India
Smart RE, Bingham GE (1974) Rapid estimates of relative water content. Plant Physiol 53:258–260
Smith JSC, Smith OS (1992) Fingerprinting crop varieties. Adv Agron 47:85–140
Smith JSC, Chin ECL, Shu H, Smith OS, Wall SJ, Senior ML, Mitchell SE, Kresovich S, Ziegle J (1997) An evaluation of the utility of SSR loci as molecular markers in maize (Zea mays L.): comparisons with data from RFLPs and pedigree. Theor Appl Genet 95:163–173
Souza SGH, Carpentieri-Pípolo V, Ruas CF, Carvalho VP et al (2008) Comparative analysis of genetic diversity among the maize inbred lines (Zea mays L.) obtained by RAPD and SSR markers. Braz Arch Biol Technol 51:183–192
Tautz D (1989) Hypervariablity of simple sequences as a general source of polymorphic DNA markers. Nucleic Acids Res 17:6463–6471
Tóth G, Gáspári Z, Jurka J (2000) Microsatellites in different eukaryotic genomes: survey and analysis. Genome Res 10:967–981
Van Inghelandt D, Melchinger AE, Lebreton C, Stich B (2010) Population structure and genetic diversity in a commercial maize breeding program assessed with SSR and SNP markers. Theor Appl Genet 120:1289–1299
Vaz Patto MC, Satovic Z, Pego S et al (2004) Assessing the genetic diversity of Portuguese maize germplasm using microsatellite markers. Euphytica 137:63–72
Vigouroux Y, McMullen M, Hittinger CT, Houchins K, Schulz L, Kresovich S, Matsuoka Y, Doebley J (2002) Identifying genes of agronomic importance in maize by screening microsatellites for evidence of selection during domestication. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:9650–9655
Warburton ML, Xianchun X, Crossa J et al (2002) Genetic characterization of CIMMYT inbred maize lines and open pollinated populations using large scale fingerprinting methods. Crop Sci 42:1832–1840
Warburton ML, Reif JC, Frisch M, Bohn M, Bedoya C, Xia XC, Crossa J, Franco J, Hoisington D, Pixley K, Taba S, Melchinger AE (2008) Genetic diversity in CIMMYT non-temperate maize germplasm: landraces, open pollinated varieties, and inbred lines. Crop Sci 48:617–624
Acknowledgement
The authors sincerely acknowledge the National Agricultural Innovation Project (NAIP) for their financial support to carry out this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nepolean, T., Singh, I., Hossain, F. et al. Molecular characterization and assessment of genetic diversity of inbred lines showing variability for drought tolerance in maize. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 22, 71–79 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-012-0112-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-012-0112-7