Abstract
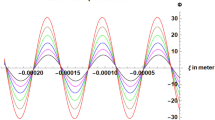
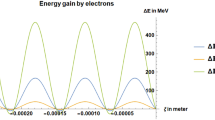
Laser wakefield acceleration (LWFA) is one of the prominent energy efficient techniques to generate high potential gradient (\(\sim\)GeV/m) to accelerate electrons. The phenomenon of LWFA depends on several parameters of plasma as well as laser beam like frequency of the laser pulse, the amplitude of the laser electric field, the shape of the laser pulse, density of plasma etc. These parameters can be adjusted to optimize the energy gain of electrons. In the present paper, the wakefield excitation by both positive and negative chirped laser pulse in an under-dense plasma is investigated. Effect of laser pulse length on LWFA is also investigated. For this purpose, the 1D model of laser wakefield acceleration is revisited to obtain analytical expressions for the longitudinal wakefield generated behind the laser pulse. Curves are plotted to compare and discuss the effect of pulse length and chirp (both positive and negative). The results show that the positive chirp enhances while the negative chirp diminishes the LWFA. Also, the wakefield generated by a laser pulse is maximal when the pulse length is close to the plasma wavelength. These results could be very useful as a starting point for optimization studies for a real LWFA experiment which is energy efficient.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
E. Everhart, P. Lorrain, The Cockcroft-Walton Voltage Multiplying Circuit. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 24(3), 221–226 (1953)
S.E. Hunt, The development and application of the Van de Graaff accelerator. Phys. Educ. 2(3), 140–145 (1967)
D.A. Bromley, The development of electrostatic accelerators. Nucl. Inst. Methods 122, 1–34 (1974)
M.S. Livingston, High Energy Accelerators: Standard Cyclotron. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Sci. 1(1), 157–167 (1952)
D.W. Kerst, A 20-Million Electron-Volt Betatron or Induction Accelerator. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 13(9), 387–394 (1942)
E.M. McMillan, A history of the synchrotron. Phys. Today 37(2), 31–37 (1984)
S.G. Lukishova, A. Valentin, Fabrikant: negative absorption, his 1951 patent application for amplification of electromagnetic radiation (ultraviolet, visible, infrared and radio spectral regions) and his experiments. J. Eur. Optic. Soc. 5 (2010)
J. Hecht, Short history of laser development. Optic. Eng. 49(9), 091002 (2010)
R.H. Pantell, Particle acceleration with lasers. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A. 393(1–3), 1–5 (1997)
T. Tajima, J.M. Dawson, Laser Electron Accelerator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 43(4), 267–270 (1979)
V.I. Berezhiani, I.G. Murusidze, Interaction of highly relativistic short laser pulses with plasmas and nonlinear wake-field generation. Phys. Scr. 45(2), 87–90 (1992)
H.K. Malik, S. Kumar, Y. Nishida, Electron acceleration by laser produced wakefield: Pulse shape effect. Optics Communications 280(2), 417–423 (2007)
S. Kumar, M. Yoon, Electron acceleration by a chirped circularly polarized laser pulse in vacuum in the presence of a planar magnetic wiggler. Phys. Scr. 77(2), 025404 (2008)
A. Pukhov, I. Kostyukov, Control of laser-wakefield acceleration by the plasma-density profile. Phys. Rev. E. 77(2) (2008)
H.R. Askari, A. Shahidani, Influence of properties of the Gaussian laser pulse and magnetic field on the electron acceleration in laser–plasma interactions. Opt. Laser Technol. 45, 613–619 (2013)
B.S. Xie, A. Aimidula, J.S. Niu, J. Liu, M.Y. Yu, Electron acceleration in the wakefield of asymmetric laser pulses. Laser Part. Beams 27(01), 27 (2009)
X. Zhang, B. Shen, L. Ji, W. Wang, J. Xu, Y. Yu, L. Yi, X. Wang, N. Hafz, V. Kulagin, Effect of pulse profile and chirp on a laser wakefield generation. Phys. Plasmas 19(5), 053103 (2012)
J.P. Palastro, J.L. Shaw, P. Franke, D. Ramsey, T.T. Simpson, D.H. Froula, Dephasing less Laser Wakefield Acceleration. Phys. Rev Lett. 124 (2020)
K. Gopal, D.N. Gupta, H. Suk, Pulse-length effect on laser wakefield acceleration of electrons by skewed laser pulses. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 49(3), 1152–1158 (2021)
V. Sharma, S. Kumar, To study the effect of laser frequency chirp on trapped electrons in laser wakefield acceleration. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2267, 012097 (2022)
M. Abedi-Varaki, N. Kant, Magnetic field-assisted wake-field generation and electron acceleration by Gaussian and super-Gaussian laser pulses in plasma. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2150604 (2022)
V. Sharma, S. Kumar, N. Kant, V. Thakur, Enhanced laser wakefield by beating of two co-propagating Gaussian laser pulses. J. Opt. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01250-6
R.T. White, H.E. Yabai, B.J. Orr, M. Kono, K.G.H. Baldwin, Control of frequency chirp in nanosecond-pulsed laser spectroscopy. J. Optic. Soc. Am. B. 21, 9 (2004)
V. Sharma, S. Kumar, N. Kant, V. Thakur, Excitation of the Laser wakefield by asymmetric chirped laser pulse in under dense plasma. J. Opt. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01326-3
P. Sprangle, E. Esarey, A. Ting, G. Joyce, laser wakefield acceleration and relativistic optical guiding. Appl. Phys. Lett. 53, 2146 (1988)
P. Jha, A. Saroch, N.K. Verma, Wakefield generation via two color laser pulses. Phys. Plasmas 20, 053102 (2013)
E. Esarey, C.B. Schroeder, W.P. Leemans, Physics of laser-driven plasma-based electron accelerators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1229 (2009)
H.T. Kim, V.B. Pathak, K.H. Pae, A. Lifschitz, F. Sylla, J.H. Shin, C. Hojbota, S.K. Lee, J.H. Sung, H.W. Lee, E. Guillaume, C. Thaury, K. Nakajima, J. Vieira, L.O. Silva, V. Malka, C.H. Nam, Stable multi-GeV electron accelerator driven by waveform-controlled PW laser pulses. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–8 (2017)
J. Shin, H.T. Kim, V.B. Pathak, C. Hojbota, S.K. Lee, J.H. Sung, H.W. Lee, J.W. Yoon, C. Jeon, K. Nakajima, F. Sylla, A. Lifschitz, E. Guillaume, C. Thaury, V. Malka, C.H. Nam, Quasi-monoenergetic multi-GeV electron acceleration by optimizing the spatial and spectral phases of PW laser pulses. Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 60, 064007 (2018)
A. Grigoriadis, G. Andrianaki, M. Tatarakis, E.P. Benis, N.A. Papadogiannis, The role of laser chirp in relativistic electron acceleration using multi-electron gas targets. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 65, 044001 (2023)
A. Grigoriadis, G. Andrianaki, I. Tazes, V. Dimitriou, M. Tatarakis, E.P. Benis, N.A. Papadogiannis, Efficient plasma electron accelerator driven by linearly chirped multi-10-TW laser pulses. Sci. Rep. 13, 2918 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This research work was carried out with the support of Lovely Professional University, Phagwara, India.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Vivek Sharma: derivation, methodology, analytical modeling and graph plotting; Sandeep Kumar: numerical analysis; Niti Kant: numerical analysis and result discussion; Vishal Thakur: supervision, reviewing, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, V., Kumar, S., Kant, N. et al. Effect of Frequency Chirp and Pulse Length on Laser Wakefield Excitation in Under-Dense Plasma. Braz J Phys 53, 157 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-023-01370-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-023-01370-1