Abstract
Purpose
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is an aggressive type of cancer that exhibits a rapid progression. Previously LOX-1, which is a type II trans-membrane glycoprotein that is expressed in endothelial cells, has been found to be involved in the development of several types of cancer. As yet, however, the expression of LOX-1 and its functional consequences in PC have not been documented. The present study was aimed at investigating the prognostic relevance of LOX-1 expression in PC patients and at resolving its role in PC metastasis.
Methods
LOX-1 expression was assessed by immunohistochemistry on a tissue microarray containing samples from 98 PC patients. Kaplan-Meier analyses were performed to compare survival curves, whereas Cox regression analyses were performed to explore the independent prognostic value of LOX-1 expression on the overall survival (OS) of PC patients. Harrel’s concordance index was applied to calculate the predictive accuracy of established models. In addition, in vitro scratch wound healing and Transwell assays were used to assess the effect of LOX-1 expression silencing and over-expression on PC cell migration and invasion, whereas Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8) and Flow Cytometry (FCM) assays were used to assess its effects on PC cell proliferation and apoptosis.
Results
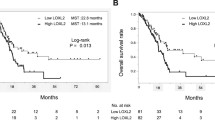
We found that LOX-1 is highly expressed in the PC tumor tissues tested and is related to the occurrence of lymph node metastases, higher TNM stages and a poor OS. We also found that LOX-1 expression may serve as an independent prognostic factor for the OS of PC patients. Our in vitro assays revealed that LOX-1 expression may promote the migration and invasion of PC cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). No effect on PC cell proliferation was noted.
Conclusions
From our data we conclude that a high LOX-1 expression in PC tissues is indicative for the occurrence of lymph node metastases, high TNM stages and a poor prognosis. LOX-1 may serve as an independent prognostic biomarker. Our in vitro assays additionally revealed that LOX-1 may enhance the migration and invasion of PC cells through EMT. LOX-1 may also serve as a novel therapeutic target.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.L. Siegel, K.D. Miller, A. Jemal, Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 66, 7–30 (2016)
K.E. Poruk, M.A. Firpo, D.G. Adler, S.J. Mulvihill, Screening for pancreatic cancer: why, how, and who? Ann. Surg. 257, 17–26 (2013)
A. Makohon-Moore, C.A. Iacobuzio-Donahue, Pancreatic cancer biology and genetics from an evolutionary perspective. Nat. Rev. Cancer 16, 553–565 (2016)
V. Taucher, H. Mangge, J. Haybaeck, Non-coding RNAs in pancreatic cancer: challenges and opportunities for clinical application. Cell. Oncol. 39, 295–318 (2016)
M. Giulietti, G. Occhipinti, G. Principato, F. Piva, Weighted gene co-expression network analysis reveals key genes involved in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma development. Cell. Oncol. 39, 379–388 (2016)
M.S. Gilardini Montani, M. Granato, C. Santoni, P. Del Porto, N. Merendino, G. D'Orazi, A. Faggioni, M. Cirone, Histone deacetylase inhibitors VPA and TSA induce apoptosis and autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell. Oncol. 40, 167–180 (2017)
S. Mitra, T. Goyal, J.L. Mehta, Oxidized LDL, LOX-1 and atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 25, 419–429 (2011)
T. Sawamura, N. Kume, T. Aoyama, H. Moriwaki, H. Hoshikawa, Y. Aiba, T. Tanaka, S. Miwa, Y. Katsura, T. Kita, T. Masaki, An endothelial receptor for oxidized low-density lipoprotein. Nature 386, 73–77 (1997)
R. Yoshimoto, Y. Fujita, A. Kakino, S. Iwamoto, T. Takaya, T. Sawamura, The discovery of LOX-1, its ligands and clinical significance. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 25, 379–391 (2011)
N. Inacio Pinto, J. Carnier, L.M. Oyama, J.P. Otoch, P.S. Alcantara, F. Tokeshi, C.M. Nascimento, Cancer as a Proinflammatory environment: metastasis and cachexia. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 791060 (2015)
L. Tao, J.Y. Park, J.D. Lambert, Differential prooxidative effects of the green tea polyphenol, (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, in normal and oral cancer cells are related to differences in sirtuin 3 signaling. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 59, 203–211 (2015)
L. Cominacini, A.F. Pasini, U. Garbin, A. Davoli, M.L. Tosetti, M. Campagnola, A. Rigoni, A.M. Pastorino, V. Lo Cascio, T. Sawamura, Oxidized low density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) binding to ox-LDL receptor-1 in endothelial cells induces the activation of NF-kappaB through an increased production of intracellular reactive oxygen species. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 12633–12638 (2000)
H. Yoshitomi, S. Kobayashi, M. Ohtsuka, F. Kimura, H. Shimizu, H. Yoshidome, M. Miyazaki, Specific expression of endoglin (CD105) in endothelial cells of intratumoral blood and lymphatic vessels in pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 37, 275–281 (2008)
H.A. Hirsch, D. Iliopoulos, A. Joshi, Y. Zhang, S.A. Jaeger, M. Bulyk, P.N. Tsichlis, X. Shirley Liu, K. Struhl, A transcriptional signature and common gene networks link cancer with lipid metabolism and diverse human diseases. Cancer Cell 17, 348–361 (2010)
M. Khaidakov, S. Mitra, B.Y. Kang, X. Wang, S. Kadlubar, G. Novelli, V. Raj, M. Winters, W.C. Carter, J.L. Mehta, Oxidized LDL receptor 1 (OLR1) as a possible link between obesity, dyslipidemia and cancer. PLoS One 6, e20277 (2011)
F. Wan, X. Qin, G. Zhang, X. Lu, Y. Zhu, H. Zhang, B. Dai, G. Shi, D. Ye, Oxidized low-density lipoprotein is associated with advanced-stage prostate cancer. Tumour Biol. 36, 3573–3582 (2015)
M. Murdocca, R. Mango, S. Pucci, S. Biocca, B. Testa, R. Capuano, R. Paolesse, M. Sanchez, A. Orlandi, C. di Natale, G. Novelli, F. Sangiuolo, The lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor-1: a new potential molecular target in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 7, 14765–14780 (2016)
L. Jiang, S. Jiang, Y. Lin, H. Yang, Z. Zhao, Z. Xie, Y. Lin, H. Long, Combination of body mass index and oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor 1 in prognosis prediction of patients with squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 6, 22072–22080 (2015)
L. Wang, J. Yin, X. Wang, M. Shao, F. Duan, W. Wu, P. Peng, J. Jin, Y. Tang, Y. Ruan, Y. Sun, J. Gu, C-type lectin-like receptor 2 suppresses AKT signaling and invasive activities of gastric cancer cells by blocking expression of phosphoinositide 3-kinase subunits. Gastroenterology 150, 1183–1195 (2016)
X.P. Chen, G.H. Du, Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1: protein, ligands, expression and pathophysiological significance. Chin. Med. J. 120, 421–426 (2007)
D. Li, K. Xie, R. Wolff, J.L. Abbruzzese, Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 363, 1049–1057 (2004)
Y. Delneste, G. Magistrelli, J. Gauchat, J. Haeuw, J. Aubry, K. Nakamura, N. Kawakami-Honda, L. Goetsch, T. Sawamura, J. Bonnefoy, P. Jeannin, Involvement of LOX-1 in dendritic cell-mediated antigen cross-presentation. Immunity 17, 353–362 (2002)
D.P. Ryan, T.S. Hong, N. Bardeesy, Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 371, 1039–1049 (2014)
Z. von Marschall, T. Cramer, M. Hocker, R. Burde, T. Plath, M. Schirner, R. Heidenreich, G. Breier, E.O. Riecken, B. Wiedenmann, S. Rosewicz, De novo expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human pancreatic cancer: evidence for an autocrine mitogenic loop. Gastroenterology 119, 1358–1372 (2000)
Y. Matsuo, P.M. Campbell, R.A. Brekken, B. Sung, M.M. Ouellette, J.B. Fleming, B.B. Aggarwal, C.J. Der, S. Guha, K-Ras promotes angiogenesis mediated by immortalized human pancreatic epithelial cells through mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. Mol. Cancer Res. 7, 799–808 (2009)
X.Z. Zou, Z.C. Gong, T. Liu, F. He, T.T. Zhu, D. Li, W.F. Zhang, J.L. Jiang, C.P. Hu, Involvement of epithelial-mesenchymal transition afforded by activation of LOX-1/TGF-beta1/KLF6 signaling pathway in diabetic pulmonary fibrosis. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 44, 70–77 (2017)
B.N. Smith, N.A. Bhowmick, Role of EMT in metastasis and therapy resistance. J. Clin. Med. 5, (2016)
K.J. Woollard, D.C. Phillips, H.R. Griffiths, Direct modulatory effect of C-reactive protein on primary human monocyte adhesion to human endothelial cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 130, 256–262 (2002)
T. Fu, J. Borensztajn, Macrophage uptake of low-density lipoprotein bound to aggregated C-reactive protein: possible mechanism of foam-cell formation in atherosclerotic lesions. Biochem. J. 366, 195–201 (2002)
L. Li, N. Roumeliotis, T. Sawamura, G. Renier, C-reactive protein enhances LOX-1 expression in human aortic endothelial cells: relevance of LOX-1 to C-reactive protein-induced endothelial dysfunction. Circ. Res. 95, 877–883 (2004)
X.Q. Zhao, M.W. Zhang, F. Wang, Y.X. Zhao, J.J. Li, X.P. Wang, P.L. Bu, J.M. Yang, X.L. Liu, M.X. Zhang, F. Gao, C. Zhang, Y. Zhang, CRP enhances soluble LOX-1 release from macrophages by activating TNF-alpha converting enzyme. J. Lipid Res. 52, 923–933 (2011)
O. Hofnagel, B. Luechtenborg, K. Stolle, S. Lorkowski, H. Eschert, G. Plenz, H. Robenek, Proinflammatory cytokines regulate LOX-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24, 1789–1795 (2004)
C. Li, G. Zhao, C. Che, J. Lin, N. Li, L. Hu, N. Jiang, Y. Liu, The role of LOX-1 in innate immunity to aspergillus fumigatus in corneal epithelial cells. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 56, 3593–3603 (2015)
H. Sawai, H. Funahashi, Y. Okada, Y. Matsuo, M. Sakamoto, M. Yamamoto, H. Takeyama, T. Manabe, Interleukin-1alpha enhances IL-8 secretion through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and reactive oxygen species signaling in human pancreatic cancer cells. Med. Sci. Monit. 11, BR343–BR350 (2005)
Y. Zhang, W. Yan, M.A. Collins, F. Bednar, S. Rakshit, B.R. Zetter, B.Z. Stanger, I. Chung, A.D. Rhim, M.P. di Magliano, Interleukin-6 is required for pancreatic cancer progression by promoting MAPK signaling activation and oxidative stress resistance. Cancer Res. 73, 6359–6374 (2013)
M.D. Barber, J.J. Powell, S.F. Lynch, K.C. Fearon, J.A. Ross, A polymorphism of the interleukin-1 beta gene influences survival in pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 83, 1443–1447 (2000)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Basic Research Program of China 973 Program (2012CB822104) and the National Natural Science Fund (31370808, 81572317, 31600648).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jie Zhang designed and carried out experiments, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript; Lei Zhang collected and analyzed clinical data; Can Li, Caiting Yang and Lili Li performed experiments; Shushu Song and Hao Wu analyzed data; Jianxin Gu contributed the materials and experimental equipment; Lan Wang and Fenglin Liu conceived the research idea and took responsibility for this part of the project.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Fig. S1
ROC analysis for CES score of LOX-1 IHC staining. a ROC curve analysis shows the optimal cut-off value of CES is 6 (CES6), and the area under the ROC curve is 0.825 (95% CI, 0.733–0.916, P < 0.001). CES > 6 indicates high expression of LOX-1, while CES ≤ 6 indicates LOX-1 low expression. b Representative images show high and low expression of CLEC2, respectively. Scale bar, 100 mm. (GIF 660 kb)
Supplementary Fig. S2
Survival analyses for PC patients in TNM I and TNM II-IV according to LOX-1 expression. Kaplan–Meier analyses of overall survival were performed in PC patients with early-stage cancer (TNM I) and advanced-stage cancer (TNM II-IV). (GIF 45 kb)
Supplementary Fig. S3
LOX-1 promotes migration of PC cells. Representative photographs of scratch wound-healing motility assays in AsPC-1 with LOX-1 overexpression or SW1990 cells with LOX-1 knock-down. (GIF 175 kb)
Supplementary Fig. S4
LOX-1 has a positive correlation with IL-6 cytokine. a Correlation analysis of levels of different cytokines in LOX-1 knock-down cells and control cells by Real-time PCR. (GIF 69 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 12 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Zhang, L., Li, C. et al. LOX-1 is a poor prognostic indicator and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in pancreatic cancer patients. Cell Oncol. 41, 73–84 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-017-0360-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-017-0360-6