Abstract
Purpose
Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) are anti-neoplastic agents that are known to affect the growth of different cancer types, but their underlying mechanisms are still incompletely understood. Here, we compared the effects of two HDACi, i.e., Trichostatin A (TSA) and Valproic Acid (VPA), on the induction of cell death and autophagy in pancreatic cancer-derived cells that exhibit a high metastatic capacity and carry KRAS/p53 double mutations.
Methods
Cell viability and proliferation tests were carried out using Trypan blue dye exclusion, MTT and BrdU assays. FACS analyses were carried out to assess cell cycle progression, apoptosis, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and mitochondrial depolarization, while Western blot and immunoprecipitation analyses were employed to detect proteins involved in apoptosis and autophagy.
Results
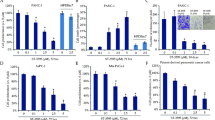
We found that both VPA and TSA can induce apoptosis in Panc1 and PaCa44 pancreatic cancer-derived cells by triggering mitochondrial membrane depolarization, Cytochrome c release and Caspase 3 activation, although VPA was more effective than TSA, especially in Panc1 cells. As underlying molecular events, we found that ERK1/2 was de-phosphorylated and that the c-Myc and mutant p53 protein levels were reduced after VPA and, to a lesser extent, after TSA treatment. Up-regulation of p21 and Puma was also observed, concomitantly with mutant p53 degradation. In addition, we found that in both cell lines VPA increased the pro-apoptotic Bim level, reduced the anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 level and increased ROS production and autophagy, while TSA was able to induce these effects only in PaCA44 cells.
Conclusions
From our results we conclude that both VPA and TSA can induce pancreatic cancer cell apoptosis and autophagy. VPA appears have a stronger and broader cytotoxic effect than TSA and, thus, may represent a better choice for anti-pancreatic cancer therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Siegel, E. Ward, O. Brawley, A. Jemal, Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin 61, 212–236 (2011)
M. Giulietti, G. Occhipinti, G. Principato, F. Piva, Weighted gene co-expression network analysis reveals key genes involved in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma development. Cell Oncol 39, 379–388 (2016)
X. Shi, S. Liu, J. Kleeff, H. Friess, M.W. Buchler, Acquired resistance of pancreatic cancer cells towards 5-fluorouracil and gemcitabine is associated with altered expression of apoptosis-regulating genes. Oncology 62, 354–362 (2002)
H.H. Wong, N.R. Lemoine, Pancreatic cancer: molecular pathogenesis and new therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 6, 412–422 (2009)
H. Lehrmann, L.L. Pritchard, A. Harel-Bellan, Histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases in the control of cell proliferation and differentiation. Adv Cancer Res 86, 41–65 (2002)
C. Das, T.K. Kundu, Transcriptional regulation by the acetylation of nonhistone proteins in humans -- a new target for therapeutics. IUBMB Life 57, 137–149 (2005)
S. Spange, T. Wagner, T. Heinzel, O.H. Kramer, Acetylation of non-histone proteins modulates cellular signalling at multiple levels. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41, 185–198 (2009)
P.A. Jones, S.B. Baylin, The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 3, 415–428 (2002)
S. Minucci, P.G. Pelicci, Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6, 38–51 (2006)
N. Carey, N.B. La Thangue, Histone deacetylase inhibitors: gathering pace. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6, 369–375 (2006)
P.A. Marks, W.S. Xu, Histone deacetylase inhibitors: potential in cancer therapy. J Cell Biochem 107, 600–608 (2009)
C. Cortes, S.C. Kozma, A. Tauler, S. Ambrosio, MYCN concurrence with SAHA-induced cell death in human neuroblastoma cells. Cell Oncol 38, 341–352 (2015)
B. Jang, J.A. Shin, Y.S. Kim, J.Y. Kim, H.K. Yi, I.S. Park, N.P. Cho, S.D. Cho, Growth-suppressive effect of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) on human oral cancer cells. Cell Oncol 39, 79–87 (2016)
Z. Chen, Y. Yang, B. Liu, B. Wang, M. Sun, L. Zhang, B. Chen, H. You, M. Zhou, Promotion of metastasis-associated Gene expression in survived PANC-1 cells following trichostatin a treatment. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem 15, 1317–1325 (2015)
J. Jones, W. Bentas, R.A. Blaheta, J. Makarevic, L. Hudak, S. Wedel, M. Probst, D. Jonas, E. Juengel, Modulation of adhesion and growth of colon and pancreatic cancer cells by the histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid. Int J Mol Med 22, 293–299 (2008)
S. Schuler, P. Fritsche, S. Diersch, A. Arlt, R.M. Schmid, D. Saur, G. Schneider, HDAC2 attenuates TRAIL-induced apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer 9, 80 (2010)
J.E. Bolden, M.J. Peart, R.W. Johnstone, Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5, 769–784 (2006)
M. Ouaissi, U. Giger, I. Sielezneff, N. Pirro, B. Sastre, A. Ouaissi, Rationale for possible targeting of histone deacetylase signaling in cancer diseases with a special reference to pancreatic cancer. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011, 315939 (2011)
J.K. Brunelle, A. Letai, Control of mitochondrial apoptosis by the Bcl-2 family. J Cell Sci 122, 437–441 (2009)
G. Pistritto, D. Trisciuoglio, C. Ceci, A. Garufi, G. D'Orazi, Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: function and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic strategies. Aging (Albany NY) 8, 603–619 (2016)
F. Natoni, L. Diolordi, C. Santoni, M.S. Gilardini Montani, Sodium butyrate sensitises human pancreatic cancer cells to both the intrinsic and the extrinsic apoptotic pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta 1745, 318–329 (2005)
O.H. Kramer, P. Zhu, H.P. Ostendorff, M. Golebiewski, J. Tiefenbach, M.A. Peters, B. Brill, B. Groner, I. Bach, T. Heinzel, M. Gottlicher, The histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid selectively induces proteasomal degradation of HDAC2. EMBO J 22, 3411–3420 (2003)
M.G. Catalano, N. Fortunati, M. Pugliese, L. Costantino, R. Poli, O. Bosco, G. Boccuzzi, Valproic acid induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in poorly differentiated thyroid cancer cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90, 1383–1389 (2005)
M. Gottlicher, S. Minucci, P. Zhu, O.H. Kramer, A. Schimpf, S. Giavara, J.P. Sleeman, F. Lo Coco, C. Nervi, P.G. Pelicci, T. Heinzel, Valproic acid defines a novel class of HDAC inhibitors inducing differentiation of transformed cells. EMBO J 20, 6969–6978 (2001)
B.E. Schultz, S. Misialek, J. Wu, J. Tang, M.T. Conn, R. Tahilramani, L. Wong, Kinetics and comparative reactivity of human class I and class IIb histone deacetylases. Biochemistry 43, 11083–11091 (2004)
M.S. Gilardini Montani, A. Prodosmo, V. Stagni, D. Merli, L. Monteonofrio, V. Gatti, M.P. Gentileschi, D. Barila, S. Soddu, ATM-depletion in breast cancer cells confers sensitivity to PARP inhibition. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 32, 95 (2013)
M. Granato, B. Chiozzi, M.R. Filardi, L.V. Lotti, L. Di Renzo, A. Faggioni, M. Cirone, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor tyrphostin AG490 triggers both apoptosis and autophagy by reducing HSF1 and mcl-1 in PEL cells. Cancer Lett 366, 191–197 (2015)
L.A. Gillies, T. Kuwana, Apoptosis regulation at the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Cell Biochem 115, 632–640 (2014)
J. Han, L.A. Goldstein, B.R. Gastman, H. Rabinowich, Interrelated roles for mcl-1 and BIM in regulation of TRAIL-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. J Biol Chem 281, 10153–10163 (2006)
G.J. Griffiths, L. Dubrez, C.P. Morgan, N.A. Jones, J. Whitehouse, B.M. Corfe, C. Dive, J.A. Hickman, Cell damage-induced conformational changes of the pro-apoptotic protein Bak in vivo precede the onset of apoptosis. J Cell Biol 144, 903–914 (1999)
L. Lalier, P.F. Cartron, P. Juin, S. Nedelkina, S. Manon, B. Bechinger, F.M. Vallette, Bax activation and mitochondrial insertion during apoptosis. Apoptosis 12, 887–896 (2007)
I. Ischenko, O. Petrenko, M.J. Hayman, A MEK/PI3K/HDAC inhibitor combination therapy for KRAS mutant pancreatic cancer cells. Oncotarget 6, 15814–15827 (2015)
R. Sears, G. Leone, J. DeGregori, J.R. Nevins, Ras enhances Myc protein stability. Mol Cell 3, 169–179 (1999)
E. Hessmann, G. Schneider, V. Ellenrieder, J.T. Siveke, MYC in pancreatic cancer: novel mechanistic insights and their translation into therapeutic strategies. Oncogene 35, 1609–1618 (2016)
N. Angela, V. Carafa, M. Conte, F.P. Tambaro, C. Abbondanza, J.H. Martens, M. Nees, R. Benedetti, I. Pallavicini, S. Minucci, G. Garcia-Manero, F. Iovino, G. Lania, C. Ingenito, V. Belsito Petrizzi, H.G. Stunnenberg and L. Altucci, c-Myc modulation & acetylation is a key HDAC inhibitor target in cancer. Clin Cancer Res (2016)
P.S. Moore, B. Sipos, S. Orlandini, C. Sorio, F.X. Real, N.R. Lemoine, T. Gress, C. Bassi, G. Kloppel, H. Kalthoff, H. Ungefroren, M. Lohr, A. Scarpa, Genetic profile of 22 pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Analysis of K-ras, p53, p16 and DPC4/Smad4. Virchows Arch 439, 798–802 (2001)
R. Brosh, V. Rotter, When mutants gain new powers: news from the mutant p53 field. Nat Rev Cancer 9, 701–713 (2009)
P.A. Muller, K.H. Vousden, p53 mutations in cancer. Nat Cell Biol 15, 2–8 (2013)
C.J. Brown, C.F. Cheok, C.S. Verma, D.P. Lane, Reactivation of p53: from peptides to small molecules. Trends Pharmacol Sci 32, 53–62 (2011)
C. Fiorini, M. Cordani, C. Padroni, G. Blandino, S. Di Agostino, M. Donadelli, Mutant p53 stimulates chemoresistance of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells to gemcitabine. Biochim Biophys Acta 1853, 89–100 (2015)
C.M. Aliouat-Denis, N. Dendouga, I. Van den Wyngaert, H. Goehlmann, U. Steller, I. van de Weyer, N. Van Slycken, L. Andries, S. Kass, W. Luyten, M. Janicot, J.E. Vialard, p53-independent regulation of p21Waf1/Cip1 expression and senescence by Chk2. Mol Cancer Res 3, 627–634 (2005)
J.R. Jeffers, E. Parganas, Y. Lee, C. Yang, J. Wang, J. Brennan, K.H. MacLean, J. Han, T. Chittenden, J.N. Ihle, P.J. McKinnon, J.L. Cleveland, G.P. Zambetti, Puma is an essential mediator of p53-dependent and -independent apoptotic pathways. Cancer Cell 4, 321–328 (2003)
R. Scherz-Shouval, Z. Elazar, ROS, mitochondria and the regulation of autophagy. Trends Cell Biol 17, 422–427 (2007)
J.S. Ungerstedt, Y. Sowa, W.S. Xu, Y. Shao, M. Dokmanovic, G. Perez, L. Ngo, A. Holmgren, X. Jiang, P.A. Marks, Role of thioredoxin in the response of normal and transformed cells to histone deacetylase inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102, 673–678 (2005)
C. Fiorini, M. Cordani, G. Gotte, D. Picone, M. Donadelli, Onconase induces autophagy sensitizing pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine and activates Akt/mTOR pathway in a ROS-dependent manner. Biochim Biophys Acta 1853, 549–560 (2015)
R. Scherz-Shouval, Z. Elazar, Regulation of autophagy by ROS: physiology and pathology. Trends Biochem Sci 36, 30–38 (2011)
D.J. Klionsky, K. Abdelmohsen, A. Abe, et al., Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy 12, 1–222 (2016)
D. McConkey, Proteasome and HDAC: who's zooming who? Blood 116, 308–309 (2010)
M. Cirone, L. Di Renzo, L.V. Lotti, V. Conte, P. Trivedi, R. Santarelli, R. Gonnella, L. Frati, A. Faggioni, Primary effusion lymphoma cell death induced by bortezomib and AG 490 activates dendritic cells through CD91. PLoS One 7, e31732 (2012)
D. Cecconi, M. Donadelli, A. Scarpa, A. Milli, M. Palmieri, M. Hamdan, L.B. Areces, J. Rappsilber, P.G. Righetti, Proteomic analysis of pancreatic ductal carcinoma cells after combined treatment with gemcitabine and trichostatin a. J Proteome Res 4, 1909–1916 (2005)
A.R. Goloudina, O.N. Demidov, C. Garrido, Inhibition of HSP70: a challenging anti-cancer strategy. Cancer Lett 325, 117–124 (2012)
M. Granato, V. Lacconi, M. Peddis, L.V. Lotti, L. Di Renzo, R. Gonnella, R. Santarelli, P. Trivedi, L. Frati, G. D'Orazi, A. Faggioni, M. Cirone, HSP70 inhibition by 2-phenylethynesulfonamide induces lysosomal cathepsin D release and immunogenic cell death in primary effusion lymphoma. Cell Death Dis 4, e730 (2013)
A.C. West, R.W. Johnstone, New and emerging HDAC inhibitors for cancer treatment. J Clin Invest 124, 30–39 (2014)
K.J. Falkenberg, R.W. Johnstone, Histone deacetylases and their inhibitors in cancer, neurological diseases and immune disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13, 673–691 (2014)
J. Roche, P. Bertrand, Inside HDACs with more selective HDAC inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 121, 451–483 (2016)
C.V. Dang, MYC on the path to cancer. Cell 149, 22–35 (2012)
A. Parrales, T. Iwakuma, Targeting oncogenic mutant p53 for cancer therapy. Front Oncol 5, 288 (2015)
L. Weisz, M. Oren, V. Rotter, Transcription regulation by mutant p53. Oncogene 26, 2202–2211 (2007)
G. Bougeard, R. Sesboue, S. Baert-Desurmont, S. Vasseur, C. Martin, J. Tinat, L. Brugieres, A. Chompret, B.B. de Paillerets, D. Stoppa-Lyonnet, C. Bonaiti-Pellie, T. Frebourg, L.F.S.w.g. French, Molecular basis of the Li-Fraumeni syndrome: an update from the French LFS families. J Med Genet 45, 535–538 (2008)
Y. Zerdoumi, J. Aury-Landas, C. Bonaiti-Pellie, C. Derambure, R. Sesboue, M. Renaux-Petel, T. Frebourg, G. Bougeard, J.M. Flaman, Drastic effect of germline TP53 missense mutations in Li-Fraumeni patients. Hum Mutat 34, 453–461 (2013)
A. Garufi, D. Pucci, V. D'Orazi, M. Cirone, G. Bossi, M.L. Avantaggiati, G. D'Orazi, Degradation of mutant p53H175 protein by Zn(II) through autophagy. Cell Death Dis 5, e1271 (2014)
A. Garufi, V. D'Orazi, A. Crispini, G. D'Orazi, Zn(II)-curc targets p53 in thyroid cancer cells. Int J Oncol 47, 1241–1248 (2015)
A. Willis, E.J. Jung, T. Wakefield, X. Chen, Mutant p53 exerts a dominant negative effect by preventing wild-type p53 from binding to the promoter of its target genes. Oncogene 23, 2330–2338 (2004)
G. Filomeni, E. Desideri, S. Cardaci, G. Rotilio, M.R. Ciriolo, Under the ROS...thiol network is the principal suspect for autophagy commitment. Autophagy 6, 999–1005 (2010)
S. Fulda, D. Kogel, Cell death by autophagy: emerging molecular mechanisms and implications for cancer therapy. Oncogene 34, 5105–5113 (2015)
G. He, G. Chen, W. Chen, W. Zhang, J. Cao, Q. Ye, Lack of association of XRCC1 rs1799782 genetic polymorphism with risk of pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol 35, 4545–4550 (2014)
H. Rikiishi, Autophagic and apoptotic effects of HDAC inhibitors on cancer cells. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011, 830260 (2011)
N. Gammoh, D. Lam, C. Puente, I. Ganley, P.A. Marks, X. Jiang, Role of autophagy in histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced apoptotic and nonapoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109, 6561–6565 (2012)
J. Zhang, S. Ng, J. Wang, J. Zhou, S.H. Tan, N. Yang, Q. Lin, D. Xia, H.M. Shen, Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce autophagy through FOXO1-dependent pathways. Autophagy 11, 629–642 (2015)
G.M. Matthews, A. Newbold, R.W. Johnstone, Intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathway signaling as determinants of histone deacetylase inhibitor antitumor activity. Adv Cancer Res 116, 165–197 (2012)
S. Mukhopadhyay, P.K. Panda, N. Sinha, D.N. Das, S.K. Bhutia, Autophagy and apoptosis: where do they meet? Apoptosis 19, 555–566 (2014)
R. Santarelli, R. Gonnella, G. Di Giovenale, L. Cuomo, A. Capobianchi, M. Granato, G. Gentile, A. Faggioni, M. Cirone, STAT3 activation by KSHV correlates with IL-10, IL-6 and IL-23 release and an autophagic block in dendritic cells. Sci Rep 4, 4241 (2014)
M. Granato, R. Santarelli, L.V. Lotti, L. Di Renzo, R. Gonnella, A. Garufi, P. Trivedi, L. Frati, G. D'Orazi, A. Faggioni, M. Cirone, JNK and macroautophagy activation by bortezomib has a pro-survival effect in primary effusion lymphoma cells. PLoS One 8, e75965 (2013)
M. Granato, C. Rizzello, M.A. Romeo, S. Yadav, R. Santarelli, G. D'Orazi, A. Faggioni, M. Cirone, Concomitant reduction of c-Myc expression and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling by quercetin induces a strong cytotoxic effect against Burkitt's lymphoma. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 79, 393–400 (2016)
A. Garufi, G. Pistritto, M. Cirone, G. D'Orazi, Reactivation of mutant p53 by capsaicin, the major constituent of peppers. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 35, 136 (2016)
S.T. Nawrocki, J.S. Carew, M.S. Pino, R.A. Highshaw, R.H. Andtbacka, K. Dunner Jr., A. Pal, W.G. Bornmann, P.J. Chiao, P. Huang, H. Xiong, J.L. Abbruzzese, D.J. McConkey, Aggresome disruption: a novel strategy to enhance bortezomib-induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 66, 3773–3781 (2006)
Acknowledgements
We thank Sandro Valia for technical assistance and the ASI (Italian Space Agency) (2014-033-R.O.) for supporting the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilardini Montani, M., Granato, M., Santoni, C. et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors VPA and TSA induce apoptosis and autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Oncol. 40, 167–180 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-017-0314-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-017-0314-z