Abstract
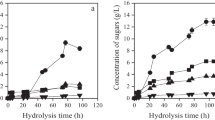
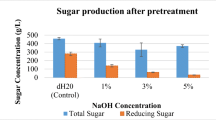
Five deep eutectic solvents (DES) were screened for their effectiveness in improving biosugar yield in Bambara groundnut haulm (BGH) for bioethanol production. Choline chloride-lactic acid (ChCl-LA) treatment provided the most promising result and was further optimised by investigating the effect of temperature and time on cellulose loss and enzymatic sugar yield. ChCl-LA pretreatment at 100 °C for 1 h was observed to be the best condition for hemicellulose (54.5%) and lignin (60.7%) removal along with optimum sugar recovery of 94.8%. The resulting hydrolysate was concentrated and fermented for 72 h with Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4743, and a maximum ethanol concentration of 11.57 g/L was achieved with an ethanol yield of 0.38 g/g sugar and productivity of 0.19 g/L/h. From the results obtained, it is evident that deep eutectic solvents are effective for breaking the recalcitrance in BGH due to their high delignification capacity. Furthermore, a recovery of the amorphous glucose and xylose in the BGH prior to DES pretreatment is vital to prevent sugar loss, thereby improving the biosugar yield for bioethanol production.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Muhammad I, Rafii MY, Ramlee SI et al (2020) Exploration of Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc), an underutilized crop, to aid global food security: varietal improvement, genetic diversity and processing. Agronomy 10:766. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10060766
Mayes S, Ho WK, Chai HH, Gao X, Kundy AC, Mateva KI, Zahrulakmal M, Hahiree MKIM, Kendabie P, Licea LCS, Massawe F, Mabhaudhi T, Modi AT, Berchie JN, Amoah S, Faloye B, Abberton M, Olaniyi O, Azam-Ali SN (2019) Bambara groundnut: an exemplar underutilised legume for resilience under climate change. Planta 250:803–820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-019-03191-6
Bhatia SK, Jagtap SS, Bedekar AA, Bhatia RK, Patel AK, Pant D, Rajesh Banu J, Rao CV, Kim YG, Yang YH (2020) Recent developments in pretreatment technologies on lignocellulosic biomass: effect of key parameters, technological improvements, and challenges. Bioresour Technol 300:122724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122724
Zdanowicz M, Wilpiszewska K, Spychaj T (2018) Deep eutectic solvents for polysaccharides processing: a review. Carbohydr Polym 200:361–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.07.078
Liu Y, Friesen JB, McAlpine JB et al (2018) Natural deep eutectic solvents: properties, applications, and perspectives. J Nat Prod 81:679–690. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00945
Loow YL, New EK, Yang GH, Ang LY, Foo LYW, Wu TY (2017) Potential use of deep eutectic solvents to facilitate lignocellulosic biomass utilization and conversion. Cellulose 24:3591–3618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1358-y
Pätzold M, Siebenhaller S, Kara S, Liese A, Syldatk C, Holtmann D (2019) Deep eutectic solvents as efficient solvents in biocatalysis. Trends Biotechnol 37:943–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2019.03.007
Xu GC, Ding JC, Han RZ et al (2016) Enhancing cellulose accessibility of corn stover by deep eutectic solvent pretreatment for butanol fermentation. Bioresour Technol 203:364–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.114976
Lin W, Xing S, Jin Y, Lu X, Huang C, Yong Q (2020) Insight into understanding the performance of deep eutectic solvent pretreatment on improving enzymatic digestibility of bamboo residues. Bioresour Technol 306:123163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123163
Isci A, Erdem GM, Bagder ES et al (2020) Effect of microwave-assisted deep eutectic solvent pretreatment on lignocellulosic structure and bioconversion of wheat straw. Cellulose 27:8949–8962. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03371-8
Gunny AAN, Arbain D, Nashef EM, Jamal P (2015) Applicability evaluation of deep eutectic solvents–cellulase system for lignocellulose hydrolysis. Bioresour Technol 181:297–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.057
Procentese A, Rehmann L (2018) Fermentable sugar production from a coffee processing by-product after deep eutectic solvent pretreatment. Bioresour Technol Rep 4:174–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2018.10.012
Liu Y, Zheng J, Xiao J, He X, Zhang K, Yuan S, Peng Z, Chen Z, Lin X (2019) Enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis and lignin extraction of wheat straw by triethylbenzyl ammonium chloride/lactic acid-based deep eutectic solvent pretreatment. ACS Omega 4:19829–19839. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b02709
Ren H, Chen C, Wang Q et al (2016) The properties of choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents and their performance in the dissolution of cellulose. BioResources 11:5435–5451
Smink D, Juan A, Schuur B, Kersten SR (2019) Understanding the role of choline chloride in deep eutectic solvents used for biomass delignification. Ind Eng Chem Res 58:16348–16357. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b03588
Xu F, Sun J, Wehrs M, Kim KH, Rau SS, Chan AM, Simmons BA, Mukhopadhyay A, Singh S (2018) Biocompatible choline-based deep eutectic solvents enable one-pot production of cellulosic ethanol. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:8914–8919. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b01271
Kothari N (2018) Integration of Clostridium thermocellum consolidated bioprocessing with thermochemical pretreatments for fuel ethanol production from switchgrass. Dissertation, UC Riverside
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60147a030
Xu F, Wang J, Dong M, Wang S, Xiao G, Li Q, Chen J, Li W, Hu W, Liu J (2019) Enhancing enzymatic hydrolysis yield of sweet sorghum straw polysaccharides by heavy ion beams irradiation pretreatment. Carbohydr Polym 222:114976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.114976
Sanusi IA, Faloye FD, Gueguim Kana EB (2019) Impact of various metallic oxide nanoparticles on ethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4743: screening, kinetic study and validation on potato waste. Catal Lett 149:2015–2031. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-019-02796-6
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R et al (2008) Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. Laboratory analytical procedure 1617:1–16
Sluiter J, Sluiter A (2010) Summative mass closure. Laboratory analytical procedure review and integration 2010:1–10
Dogan E, Dunaev T, Erguder TH, Demirer GN (2009) Performance of leaching bed reactor converting the organic fraction of municipal solid waste to organic acids and alcohols. Chemosphere 74:797–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.10.028
Tayeh HNA, Azaizeh H, Gerchman Y (2020) Circular economy in olive oil production–olive mill solid waste to ethanol and heavy metal sorbent using microwave pretreatment. Waste Manag 113:321–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.06.017
Kumar AK, Parikh BS, Pravakar M (2016) Natural deep eutectic solvent mediated pretreatment of rice straw: bioanalytical characterization of lignin extract and enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated biomass residue. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:9265–9275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4780-4
Smith EL, Abbott AP, Ryder KS (2014) Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their applications. Chem Rev 114:11060–11082. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr300162p
Bichot A, Delgenès JP, Méchin V, Carrère H, Bernet N, García-Bernet D (2018) Understanding biomass recalcitrance in grasses for their efficient utilization as biorefinery feedstock. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 17:707–748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-018-9485-y
Zhang CW, Xia SQ, Ma PS (2016) Facile pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass using deep eutectic solvents. Bioresour Technol 219:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.026
Tian D, Guo Y, Hu J, Yang G, Zhang J, Luo L, Xiao Y, Deng S, Deng O, Zhou W, Shen F (2020) Acidic deep eutectic solvents pretreatment for selective lignocellulosic biomass fractionation with enhanced cellulose reactivity. Int J Biol Macromol 142:288–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.100
Rudakiya DM, Gupte A (2019) Assessment of white rot fungus mediated hardwood degradation by FTIR spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. J Microbiol Methods 157:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2019.01.007
Chen Z, Wan C (2018) Ultrafast fractionation of lignocellulosic biomass by microwave-assisted deep eutectic solvent pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 250:532–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.11.066
Dong M, Wang S, Xu F, Wang J, Yang N, Li Q, Chen J, Li W (2019) Pretreatment of sweet sorghum straw and its enzymatic digestion: insight into the structural changes and visualization of hydrolysis process. Biotechnol Biofuels 12:276. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-019-1613-6
Xu FX, Zhang X, Zhang F, Jiang LQ, Zhao ZL, Li HB (2020) TG-FTIR for kinetic evaluation and evolved gas analysis of cellulose with different structures. Fuel 268:117365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117365
Chen Z, Reznicek WD, Wan C (2018) Deep eutectic solvent pretreatment enabling full utilization of switchgrass. Bioresour Technol 263:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.058
Chen YL, Zhang X, You TT, Xu F (2019) Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) for cellulose dissolution: a mini-review. Cellulose 26:205–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2130-7
Arumugam N, Biely P, Puchart V, Gerrano AS, de Mukherjee K, Singh S, Pillai S (2019) Xylan from bambara and cowpea biomass and their structural elucidation. Int J Biol Macromol 132:987–99327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.04.030
Lynd LR, Liang X, Biddy MJ, Allee A, Cai H, Foust T, Himmel ME, Laser MS, Wang M, Wyman CE (2017) Cellulosic ethanol: status and innovation. Curr Opin Biotechnol 45:202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2017.03.008
Lynam JG, Kumar N, Wong MJ (2017) Deep eutectic solvents’ ability to solubilize lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose; thermal stability; and density. Bioresour Technol 238:684–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.04.079
Ong VZ, Wu TY, Lee CBTL, Cheong NWR, Shak KPY (2019) Sequential ultrasonication and deep eutectic solvent pretreatment to remove lignin and recover xylose from oil palm fronds. Ultrason Sonochem 58:104598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.05.015
Tian D, Chandra RP, Lee JS, Lu C, Saddler JN (2017) A comparison of various lignin-extraction methods to enhance the accessibility and ease of enzymatic hydrolysis of the cellulosic component of steam-pretreated poplar. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:157. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0846-5
Procentese A, Johnson E, Orr V, Garruto Campanile A, Wood JA, Marzocchella A, Rehmann L (2015) Deep eutectic solvent pretreatment and subsequent saccharification of corncob. Bioresour Technol 192:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.05.053
Zulkefli S, Abdulmalek E, Rahman MBA (2017) Pretreatment of oil palm trunk in deep eutectic solvent and optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated oil palm trunk. Renew Energy 107:36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.01.037
Hou XD, Feng GJ, Ye M, Huang CM, Zhang Y (2017) Significantly enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of rice straw via a high-performance two-stage deep eutectic solvents synergistic pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 238:139–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.04.027
Procentese A, Raganati F, Olivieri G, Russo ME, Rehmann L, Marzocchella A (2017) Low-energy biomass pretreatment with deep eutectic solvents for bio-butanol production. Bioresour Technol 243:464–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.143
Liu X, Wei W, Wu S (2019) Synergism of organic acid and deep eutectic solvents pretreatment for the co-production of oligosaccharides and enhancing enzymatic saccharification. Bioresour Technol 290:121775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121775
Thi S, Lee KM (2019) Comparison of deep eutectic solvents (DES) on pretreatment of oil palm empty fruit bunch (OPEFB): cellulose digestibility, structural and morphology changes. Bioresour Technol 282:525–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.065
Tan YT, Ngoh GC, Chua ASM (2018) Evaluation of fractionation and delignification efficiencies of deep eutectic solvents on oil palm empty fruit bunch. Ind Crop Prod 123:271–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.06.091
DeMartini JD, Pattathil S, Miller JS et al (2013) Investigating plant cell wall components that affect biomass recalcitrance in poplar and switchgrass. Energy Environ Sci 6:898–909. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EE23801F
Silveira RL, Stoyanov SR, Gusarov S, Skaf MS, Kovalenko A (2013) Plant biomass recalcitrance: effect of hemicellulose composition on nanoscale forces that control cell wall strength. J Am Chem Soc 135:19048–19051. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja405634k
Yu Q, Zhang A, Wang W, Chen L, Bai R, Zhuang X, Wang Q, Wang Z, Yuan Z (2018) Deep eutectic solvents from hemicellulose-derived acids for the cellulosic ethanol refining of Akebia’ herbal residues. Bioresour Technol 247:705–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.159
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Prashant Bhagwat, Durban University of Technology, South Africa, for critically reviewing the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation (NRF) of South Africa (Thuthuka grants 93982 and 114227), and the ARC-DUT-UFS consortium supported. Opinions expressed and conclusions arrived at are those of the author and are not necessarily attributed to the funders.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Somiame Itseme Okuofu: methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft. Abe Shegro Gerrano: resources, writing—review and editing. Suren Singh: resources, writing—review and editing—co-supervision. Santhosh Pillai: conceptualisation, methodology, resources, writing—review and editing—supervision, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okuofu, S.I., Gerrano, A.S., Singh, S. et al. Deep eutectic solvent pretreatment of Bambara groundnut haulm for enhanced saccharification and bioethanol production. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 12, 3525–3533 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-01053-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-01053-w