Abstract
Carbon nanotube field-effect transistor (CNT-FET) based sensor devices are widely used in sensing applications of biomolecules in high sensitivity. In addition, covalent functionalization process can increase the interaction between the CNTs and biological molecules. In this article, we present the effect of boronic acid functionalization on the electrical properties of the CNT-FET due to boronic acid and its derivatives have been widely used for the glucose recognition. For this purpose, CNT-FET transistors were fabricated on SiO2/Si substrates utilising high purity semiconducting nanotubes as the channel layer and functionalized with pyrene-1-boronic acid. It was found that boronic acid functionalization causes a variation in electrical parameters of CNT-FET transistors such as conductance, transconductance, threshold voltage, field effect mobility, resistance, hysteresis gap, and charge transfer of carriers per unit length. The results show that pyrene-1-boronic acid treatment was observed to have a significant beneficial effect on the electrical properties of the CNT-FET and pyrene-1-boronic acid functionalized CNT-FET sensor devices may have great potential for glucose sensing applications.
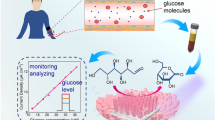
Graphical Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
IDF_Atlas_10th_Edition_2021.pdf - IDF Diabetes Atlas. https://www.diabetesatlas.org.
Williams, R., Karuranga, S., Malanda, B., Saeedi, P., Basit, A., Besançon, S., Colagiuri, S.: Global and regional estimates and projections of diabetes-related health expenditure: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 162, 108072 (2020)
Chakraborty, P., Dhar, S., Deka, N., Debnath, K., S. P.: Mondal Non-enzymatic salivary glucose detection using porous CuO nanostructures. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 302, 127134 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127134
Coyle, V.E., Kandjani, A.E., Field, M.R., Hartley, P., Chen, M., Sabri, Y.M., Bhargava, S.K.: Co3O4 needles on Au honeycomb as a non-invasive electrochemical biosensor for glucose in saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 141, 111479 (2019)
Yang, M., Ma, C., Ding, S., Zhu, Y., Shi, G., Zhu, A.: Rational design of stimuli-responsive polymers modified nanopores for selective and sensitive determination of salivary glucose. Anal. Chem. 91(21), 14029–14035 (2019)
Diouf, A., Bouchikhi, B., El Bari, N.: A nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer and its application in measuring saliva glucose. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 98, 1196–1209 (2019)
Toi, P.T., Trung, T.Q., Dang, T.M.L., Bae, C.W., Lee, N.E.: Highly electrocatalytic, durable, and stretchable nanohybrid fiber for on-body sweat glucose detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(11), 10707–10717 (2019)
Wang, Y., Wang, X., Lu, W., Yuan, Q., Zheng, Y., Yao, B.A.: thin film polyethylene terephthalate (PET) electrochemical sensor for detection of glucose in sweat. Talanta 198, 86–92 (2019)
Cao, Q., Liang, B., Tu, T., Wei, J., Fang, L., Ye, X.: Three-dimensional paper-based microfluidic electrochemical integrated devices (3D-PMED) for wearable electrochemical glucose detection. RSC Adv. 9(10), 5674–5681 (2019)
Bruen, D., Delaney, C., Florea, L., Diamond, D.: Glucose sensing for diabetes monitoring: recent developments. Sensors 17(8), 1866 (2017)
Allen, B.L., Kichambare, P.D., Star, A.: Carbon nanotube field-effect-transistor-based biosensors. Adv. Mater. 19(11), 1439–1451 (2007)
Ahmad, M., Anguita, J.V., Stolojan, V., Corless, T., Chen, J.S., Carey, J.D., Silva, S.R.P.: High quality carbon nanotubes on conductive substrates grown at low temperatures. Adv. Func. Mater. 25(28), 4419–4429 (2015)
Choi, W.B., Cheong, B.H., Kim, J.J., Chu, J., Bae, E.: Selective growth of carbon nanotubes for nanoscale transistors. Adv. Func. Mater. 13(1), 80–84 (2003)
Hong, S., Myung, S.: A flexible approach to mobility. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2(4), 207–208 (2007)
Tans, S.J., Verschueren, A.R., Dekker, C.: Room-temperature transistor based on a single carbon nanotube. Nature 393(6680), 49–52 (1998)
Martel, R., Schmidt, T., Shea, H.R., Hertel, T., Avouris, P.: Single-and multi-wall carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73(17), 2447–2449 (1998)
Collins, P.G., Bradley, K., Ishigami, M., Zettl, D.A.: Extreme oxygen sensitivity of electronic properties of carbon nanotubes. Science 287(5459), 1801–1804 (2000)
Kong, J., Chapline, M.G., Dai, H.: Functionalized carbon nanotubes for molecular hydrogen sensors. Adv. Mater. 13(18), 1384–1386 (2001)
Star, A., Han, T.R., Gabriel, J.C.P., Bradley, K., Grüner, G.: Interaction of aromatic compounds with carbon nanotubes: correlation to the Hammett parameter of the substituent and measured carbon nanotube FET response. Nano Lett. 3(10), 1421–1423 (2003)
Someya, T., Small, J., Kim, P., Nuckolls, C., Yardley, J.T.: Alcohol vapor sensors based on single-walled carbon nanotube field effect transistors. Nano Lett. 3(7), 877–881 (2003)
Aikawa, S., Xiang, R., Einarsson, E., Chiashi, S., Shiomi, J., Nishikawa, E., Maruyama, S.: Facile fabrication of all-SWNT field-effect transistors. Nano Res. 4(6), 580–588 (2011)
Yoon, H., Ko, S., Jang, J.: Field-effect-transistor sensor based on enzyme-functionalized polypyrrole nanotubes for glucose detection. J. Phys. Chem. B 112(32), 9992–9997 (2008)
James, T.D., Sandanayake, K.S., Shinkai, S.: Saccharide sensing with molecular receptors based on boronic acid. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 35(17), 1910–1922 (1996)
Zhao, L., Huang, Q., Liu, Y., Wang, Q., Wang, L., Xiao, S., Ding, J.: Boronic acid as glucose-sensitive agent regulates drug delivery for diabetes treatment. Materials 10(2), 170 (2017)
Lee, J., Ko, S., Kwon, C.H., Lima, M.D., Baughman, R.H., Kim, S.J.: Carbon nanotube yarn-based glucose sensing artificial muscle. Small 12(15), 2085–2091 (2016)
Chen, J.S., Stolojan, V., Silva, S.R.P.: Towards type-selective carbon nanotube growth at low substrate temperature via photo-thermal chemical vapour deposition. Carbon 84, 409–418 (2015)
Dresselhaus, M.S., Dresselhaus, G., Jorio, A., Souza Filho, A.G., Pimenta, M.A., Saito, R.: Single nanotube Raman spectroscopy. Acc. Chem. Res. 35(12), 1070–1078 (2002)
Chen, G., Qiu, J., Xu, J., Fang, X.A., Liu, Y., Liu, S., Zhu, F.: A novel probe based on phenylboronic acid functionalized carbon nanotubes for ultrasensitive carbohydrate determination in biofluids and semi-solid biotissues. Chem. Sci. 7(2), 1487–1495 (2016)
Lerner, M.B., Kybert, N., Mendoza, R., Villechenon, R., Bonilla Lopez, M.A., Charlie Johnson, A.T.: Scalable, non-invasive glucose sensor based on boronic acid functionalized carbon nanotube transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102(18), 183113 (2013)
Norrild, J.C., Søtofte, I.: Design, synthesis, and structure of new potential electrochemically active boronic acid-based glucose sensors. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2(2), 303–311 (2002)
Williams, G.T., Kedge, J.L., Fossey, J.S.: Molecular boronic acid-based saccharide sensors. ACS sensors 6(4), 1508–1528 (2021)
Wang, W., Gao, X., Wang, B.: Boronic acid-based sensors. Curr. Org. Chem. 6(14), 1285–1317 (2002)
Chen, G., Qiu, J., Xu, J., Fang, X.A., Liu, Y., Liu, S., Zhu, F.: A novel probe based on phenylboronic acid functionalized carbon nanotubes for ultrasensitive carbohydrate determination in biofluids and semi-solid biotissues. Chem. Sci. 7(2), 1487–1495 (2016)
Allen, C.S., Liu, G., Chen, Y., Robertson, A.W., He, K., Porfyrakis, K., Warner, J.H.: Optically enhanced charge transfer between C 60 and single-wall carbon nanotubes in hybrid electronic devices. Nanoscale 6(1), 572–580 (2014)
Jorio, A., Souza Filho, A.G., Dresselhaus, G., Dresselhaus, M.S., Swan, A.K., Ünlü, M.S., Saito, R.: G-band resonant Raman study of 62 isolated single-wall carbon nanotubes. Phys.Rev. B 65(15), 155412 (2002)
Xuan, C.T., Thuy, N.T., Luyen, T.T., Huyen, T.T., Tuan, M.A.: Carbon nanotube field-effect transistor for DNA sensing. J. Electron. Mater. 46(6), 3507–3511 (2017)
Javey, A., Wang, Q., Kim, W., and Dai, H.: In: IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, pp. 1–4 (2004)
Tans, S.J., Verschueren, A.R.M., Dekker, C.: Room-temperature transistor based on a single carbon nanotube. Nat. 393(6680), 49–52 (1998)
Stefansson, S., Stefansson, L.A., Chung, S.W., Ko, K., Kwon, H.H., Ahn, S.N.: Evaluation of aromatic boronic acids as ligands for measuring diabetes markers on carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. J. Nanotechnol. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/371487
Kim, J.P., Lee, B.Y., Lee, J., Hong, S., Sim, S.J.: Enhancement of sensitivity and specificity by surface modification of carbon nanotubes in diagnosis of prostate cancer based on carbon nanotube field effect transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 24(11), 3372–3378 (2009)
Hill, A.V.: A new mathematical treatment of changes of ionic concentration in muscle and nerve under the action of electric currents, with a theory as to their mode of excitation. J. Physiol. 40(3), 190–224 (1910)
Lee, H., Song, C., Hong, Y.S., Kim, M.S., Cho, H.R., Kang, T., Kim, D.H.: Wearable/disposable sweat-based glucose monitoring device with multistage transdermal drug delivery module. Sci. Adv. 3(3), 1601314 (2017)
Acknowledgements
H. Altuntas gratefully acknowledges TUBITAK-BIDEB 2219 Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Altuntas, H., Snashall, K., Oke-Altuntas, F. et al. Effect of Pyrene-1 Boronic Acid Functionalization on the Electrical Characteristics of Carbon Nanotube Field-Effect Transistor. Electron. Mater. Lett. 19, 405–414 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-023-00415-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-023-00415-6