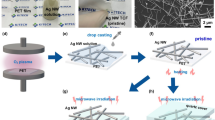
Abstract
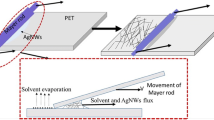
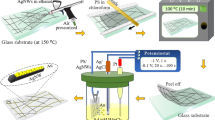
Though a percolated network of silver nanowires (AgNWs) has been considered the most promising flexible transparent electrode because of it high conductivity, high transmittance, and excellent flexibility, fabrication of AgNW-based transmission lines designed to conduct high frequency signals has been scarcely reported. The fabrication and performance of extremely thin (1.4 µm thick) and low lossy (smaller than − 17 dB for reflection coefficient corresponding to 2.5 GHz) transmission lines with unprecedented transparency (higher than 90% for the entire visible light spectrum) are demonstrated in this study. AgNWs deposited onto a 1.4 µm-thick polyethylene terephthalate (PET) sheet were irradiated by intense-pulsed-light to selectively raise their temperature. The intensive photon energy delivered to the AgNWs simultaneously caused the active diffusion of Ag atoms and plasmonic welding, resulting in large drops in resistivity without drastic changes in their physical shape or the optical transmittance of the films. Furthermore, absorption of heat also thermally activated the underlying polymer and causing it to react with the surface of the AgNWs—this results in enhanced adhesion between the AgNWs and the PET. Measurements and simulation of specially designed coplanar waveguide circuits revealed that the fabricated electrode could simultaneously provide excellent transmission characteristics and mechanical stability and transparency.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Webb, R.C., Bonifas, A.P., Behnaz, A., Zhang, Y., Yu, K.J., Cheng, H., Shi, M., Bian, Z., Liu, Z., Kim, Y.-S.: Ultrathin conformal devices for precise and continuous thermal characterization of human skin. Nat. Mater. 12, 938 (2013)
Lee, S., Reuveny, A., Reeder, J., Lee, S., Jin, H., Liu, Q., Yokota, T., Sekitani, T., Isoyama, T., Abe, Y., Suo, Z., Someya, T.: A transparent bending-insensitive pressure sensor. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 472 (2016)
Hwang, B.U., Lee, J.H., Trung, T.Q., Roh, E., Kim, D.I., Kim, S.W., Lee, N.E.: Transparent stretchable self-powered patchable sensor platform with ultrasensitive recognition of human activities. ACS Nano 9, 8801–8810 (2015)
Ho, M.D., Ling, Y., Yap, L.W., Wang, Y., Dong, D., Zhao, Y., Cheng, W.: Percolating network of ultrathin gold nanowires and silver nanowires toward “invisible” wearable sensors for detecting emotional expression and apexcardiogram. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27, 1700845 (2017)
Trung, T.Q., Ramasundaram, S., Hwang, B.U., Lee, N.E.: An all-elastomeric transparent and stretchable temperature sensor for body-attachable wearable electronics. Adv. Mater. 28, 502–509 (2016)
You, B., Kim, Y., Ju, B.K., Kim, J.W.: Highly stretchable and waterproof electroluminescence device based on superstable stretchable transparent electrode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 5486–5494 (2017)
Krantz, J., Stubhan, T., Richter, M., Spallek, S., Litzov, I., Matt, G.J., Spiecker, E., Brabec, C.J.: Spray-coated silver nanowires as top electrode layer in semitransparent P3HT:PCBM-based organic solar cell devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 1711–1717 (2013)
Wu, H., Kong, D., Ruan, Z., Hsu, P.-C., Wang, S., Yu, Z., Carney, T.J., Hu, L., Fan, S., Cui, Y.: A transparent electrode based on a metal nanotrough network. Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 421–425 (2013)
Pang, S., Hernandez, Y., Feng, X., Müllen, K.: Graphene as transparent electrode material for organic electronics. Adv. Mater. 23, 2779–2795 (2011)
Lee, S.M., Byeon, H.J., Lee, J.H., Baek, D.H., Lee, K.H., Hong, J.S., Lee, S.H.: Self-adhesive epidermal carbon nanotube electronics for tether-free long-term continuous recording of biosignals. Sci. Rep. 4, 6074 (2014)
Han, C.J., Park, B.-G., Oh, M.S., Jung, S.-B., Kim, J.-W.: Photo-induced fabrication of Ag nanowire circuitry for invisible, ultrathin, conformable pressure sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 9986–9994 (2017)
Song, L., Myers, A.C., Adams, J.J., Zhu, Y.: Stretchable and reversibly deformable radio frequency antennas based on silver nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 4248–4253 (2014)
Kaltenbrunner, M., White, M.S., Głowacki, E.D., Sekitani, T., Someya, T., Sariciftci, N.S., Bauer, S.: Ultrathin and lightweight organic solar cells with high flexibility. Nat. Commun. 3, 770 (2012)
White, M.S., Kaltenbrunner, M., Głowacki, E.D., Gutnichenko, K., Kettlgruber, G., Graz, I., Aazou, S., Ulbricht, C., Egbe, D.A.M., Miron, M.C., Major, Z., Scharber, M.C., Sekitani, T., Someya, T., Bauer, S., Sariciftci, N.S.: Ultrathin, highly flexible and stretchable PLEDs. Nat. Photonics 7, 811–816 (2013)
Reuveny, A., Lee, S., Yokota, T., Fuketa, H., Siket, C.M., Lee, S., Sekitani, T., Sakurai, T., Bauer, S., Someya, T.: High-frequency, conformable organic amplifiers. Adv. Mater. 28, 3298–3304 (2016)
Melzer, M., Kaltenbrunner, M., Makarov, D., Karnaushenko, D., Karnaushenko, D., Sekitani, T., Someya, T., Schmidt, O.G.: Imperceptible magnetoelectronics. Nat. Commun. 6, 6080 (2015)
Hayata, H., Okamoto, M., Takeoka, S., Iwase, E., Fujie, T., Iwata, H.: Printed high-frequency RF identification antenna on ultrathin polymer film by simple production process for soft-surface adhesive device. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 56, 05EC01 (2017)
Kaltenbrunner, M., Sekitan, T., Reeder, J., Yokota, T., Kuribara, K., Tokuhara, T., Drack, M., Schwödiauer, R., Graz, I., Bauer-Gogonea, S., Bauer, S., Someya, T.: An ultra-lightweight design for imperceptible plastic electronics. Nature 499, 458–463 (2013)
Elwi, T.A., Al-Rizzo, H.M., Rucker, D.G., Dervishi, E., Li, Z., Biris, A.S.: Multi-walled carbon nanotube-based RF antennas. Nanotechnology 21, 045301 (2010)
Huang, X., Leng, T., Zhu, M., Zhang, X., Chen, J., Chang, K., Aqeeli, M., Geim, A.K., Novoselov, K.S., Hu, Z.: Highly flexible and conductive printed graphene for wireless wearable communications applications. Sci. Rep. 5, 18298 (2016)
Komoda, N., Nogi, M., Suganuma, K., Kohno, K., Akiyama, Y., Otsuka, K.: Printed silver nanowire antennas with low signal loss at high-frequency radio. Nanoscale 4, 3148–3153 (2012)
Kim, Y., Ryu, T.I., Ok, K.-H., Kwak, M.-G., Park, S., Park, N.-G., Han, C.J., Kim, B.S., Ko, M.J., Son, H.J., Kim, J.-W.: Inverted layer-by-layer fabrication of an ultraflexible and transparent Ag nanowire/conductive polymer composite electrode for use in high-performance organic solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 4580–4589 (2015)
Ok, K.-H., Kim, J., Park, S.-R., Kim, Y., Lee, C.-J., Hong, S.-J., Kwak, M.-G., Kim, N., Han, C.J., Kim, J.-W.: Ultra-thin and smooth transparent electrode for flexible and leakage-free organic light-emitting diodes. Sci. Rep. 5, 9464 (2015)
Ni, H., Liu, J., Wang, Z., Yang, S.: A review on colorless and optically transparent polyimide films: chemistry, process and engineering applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 28, 16–27 (2015)
Jun, S., Han, C.J., Kim, Y., Ju, B.-K., Kim, J.-W.: A pressure-induced bending sensitive capacitor based on an elastomer-free, extremely thin transparent conductor. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 3221–3229 (2017)
Gotoh, K., Yasukawa, A., Kobayashi, Y.: Wettability characteristics of poly(ethylene terephthalate) films treated by atmospheric pressure plasma and ultraviolet excimer light. Polym. J. 43, 545–551 (2011)
Perez-Roldan, M.J., Debarnot, D., Poncin-Epaillard, F.: Processing of plasma-modified and polymer-grafted hydrophilic PET surfaces, and study of their aging and bioadhesive properties. RSC Adv. 4, 31409–31415 (2014)
Jun, S., Ju, B.-K., Kim, J.-W.: Ultra-facile fabrication of stretchable and transparent capacitive sensor employing photo-assisted patterning of silver nanowire networks. Adv. Mater. Technol. 1, 1600062 (2016)
Govorov, A.O., Richardson, H.H.: Generating heat with metal nanoparticles. Nanotoday 2, 30–38 (2007)
Garnett, E.C., Cai, W., Cha, J.J., Mahmood, F., Connor, S.T., Christoforo, M.G., Cui, Y., McGehee, M.D., Brongersma, M.L.: Self-limited plasmonic welding of silver nanowire junctions. Nat. Mater. 11, 241–249 (2012)
Song, C.H., Han, C.J., Ju, B.K., Kim, J.W.: Photoenhanced patterning of metal nanowire networks for fabrication of ultraflexible transparent devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8, 480–489 (2016)
Jiu, J., Nogi, M., Sugahara, T., Tokuno, T., Araki, T., Komoda, N., Suganuma, K., Uchida, H., Shinozaki, K.: Strongly adhesive and flexible transparent silver nanowire conductive films fabricated with a high-intensity pulsed light technique. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 23561–23567 (2012)
Jiu, J., Sugahara, T., Nogi, M., Araki, T., Suganuma, K., Uchida, H., Shinozaki, K.: High-intensity pulse light sintering of silver nanowire transparent films on polymer substrates: the effect of the thermal properties of substrates on the performance of silver films. Nanoscale 5, 11820–11828 (2013)
Pyo, K., Lee, D.H., Kim, Y., Kim, J.-W.: Extremely rapid and simple healing of a transparent conductor based on Ag nanowires and polyurethane with a Diels–Alder network. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 972–977 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant [number 2015R1A4A1042417] funded by the Korean government (MSIP). Further support was also provided by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, Republic of Korea [grant number N0002310] and the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology as “Characteristics of VO2 Nanoink and Intense Pulsed Light Low-Temperature Sintering for Flexible Smart Window Films Using Direct Printing Technology [kitech EO-17-0026]”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SW., Kim, KS., Park, M. et al. 1.4 µm-Thick Transparent Radio Frequency Transmission Lines Based on Instant Fusion of Polyethylene Terephthalate Through Surface of Ag Nanowires. Electron. Mater. Lett. 14, 599–609 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0069-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0069-3