Abstract
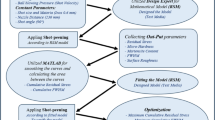
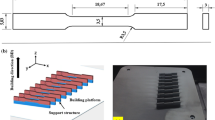
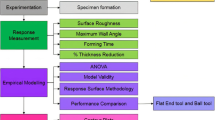
Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) technique of additive manufacturing has been proven to be the best technology for printing metallic components with higher density and better mechanical properties. However, due to higher surface roughness of the as-built metallic components, post-processing through shot blasting is the most recommended method for improving surface finish. In the present work, the optimum shot blasting conditions were explored for achieving desired surface roughness for the DMLS printed AlSi10Mg aluminum alloy plates. Three input parameters (viz., time, pressure and grit size) selected at three levels were used to formulate the design matrix. Consequently, 30 real-time shot blasting experiments were performed, and the results obtained as surface roughness were used to develop the quadratic model using response surface methodology. Further, the prediction effectiveness was verified using analysis of variance. The experimental results revealed that the effect of blasting pressure on the surface roughness was found to be positive and most significant (41.89%), followed by the negative influence of time of shot blasting (29.29%) and grit size of shots (23.71%). The predicted values of surface roughness (maximum and minimum) obtained at optimum set of process parameters were found to be in agreement (± 6%) with the experimentally measured data. The variations in surface roughness were further validated through scanning electron microscopy. The proposed mathematical model is effective, precise and promising for the prediction of surface roughness in the shot-blasted surfaces of additively manufactured aluminum alloys.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D.: Additive manufacturing (3D printing): a review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. (Internet) 143(December 2017), 172–196 (2018)
Deckers, J.; Shahzad, K.; Vleugels, J.; Kruth, J.P.: Isostatic pressing assisted indirect selective laser sintering of alumina components. Rapid Prototyp. J. 18(5), 409–419 (2012)
Simchi, A.; Petzoldt, F.; Pohl, H.: On the development of direct metal laser sintering for rapid tooling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 141(3), 319–328 (2003)
Brock, L.; Ogunsanya, I.; Asgari, H.; Patel, S.; Vlasea, M.: Relative performance of additively manufactured and cast aluminum alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. (Internet) 30(1), 760–782 (2021)
Gibson I.; Rosen D.; Stucker B.: Powder bed fusion processes. In Additive Manufacturing Technologies: 3D printing, rapid prototyping, and direct digital manufacturing. Springer, New York, NY, pp 107–145 (2015)
Calignano, F.; Manfredi, D.; Ambrosio, E.P.; Iuliano, L.; Fino, P.: Influence of process parameters on surface roughness of aluminum parts produced by DMLS. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 67(9–12), 2743–2751 (2013)
Mohammadi, M.; Asgari, H.: Achieving low surface roughness AlSi10Mg_200C parts using direct metal laser sintering. Addit. Manuf. (Internet) 20, 23–32 (2018)
Krishnan, M.; Atzeni, E.; Canali, R.; Calignano, F.; Manfredi, D.; Ambrosio, E.P., et al.: On the effect of process parameters on properties of AlSi10Mg parts produced by DMLS. Rapid Prototyp. J. 20(6), 449–458 (2014)
Bacchewar, P.B.; Singhal, S.K.; Pandey, P.M.: Statistical modelling and optimization of surface roughness in the selective laser sintering process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 221(1), 35–52 (2007)
Löber, L.; Flache, C.; Petters, R.; Kühn, U.; Eckert, J.: Comparison of different post processing technologies for SLM generated 316l steel parts. Rapid Prototyp. J. 19(3), 173–179 (2013)
Teng, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Li, L.; Jiang, L.: Study on magnetic abrasive finishing of AlSi10Mg alloy prepared by selective laser melting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 105(5–6), 2513–2521 (2019)
Sagbas, B.: Post-processing effects on surface properties of direct metal laser sintered AlSi10Mg parts. Met. Mater. Int. (Internet) 2019, 0123456789 (2019)
AlMangour, B.; Yang, J.M.: Improving the surface quality and mechanical properties by shot-peening of 17–4 stainless steel fabricated by additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. (Internet) 110, 914–924 (2016)
Sugavaneswaran, M.; Jebaraj, A.V.; Kumar, M.D.B.; Lokesh, K.; Rajan, A.J.: Enhancement of surface characteristics of direct metal laser sintered stainless steel 316L by shot peening. Surf. Interfaces (Internet) 12, 31–40 (2018)
Slătineanu, L.; Potârniche, S.; Coteaţă, M.; Grigoraş, I.; Gherman, L.; Negoescu, F.: Surface roughness at aluminium parts sand blasting. Proc. Manuf. Syst. 6(2), 4–9 (2011)
Varacalle, D.J.; Guillen, D.P.; Deason, D.M.; Rhodaberger, W.; Sampson, E.: Effect of grit-blasting on substrate roughness and coating adhesion. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 15(3), 348–355 (2006)
Maamoun, A.; Elbestawi, M.; Veldhuis, S.: Influence of shot peening on AlSi10Mg parts fabricated by additive manufacturing. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2(3), 40 (2018)
Poorna, C.K.; Vashista, M.; Sabiruddin, K.; Paul, S.; Bandyopadhyay, P.P.: Effects of grit blasting on surface properties of steel substrates. Mater. Des. (Internet) 30(8), 2895–2902 (2009)
Mohammadi, Z.; Ziaei-Moayyed, A.A.; Mesgar, A.S.M.: Grit blasting of Ti–6Al–4V alloy: optimization and its effect on adhesion strength of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 194(1–3), 15–23 (2007)
Unal, O.: Optimization of shot peening parameters by response surface methodology. Surf. Coat. Technol. (Internet) 305, 99–109 (2016)
Gaitonde, V.N.; Manjaiah, M.; Maradi, S.; Karnik, S.R.; Petkar, P.M.; Davim, J.P.: Multiresponse optimization in wire electric discharge machining (WEDM) of HCHCr steel by integrating response surface methodology (RSM) with differential evolution (DE) (Internet). Comput. Methods Prod. Eng. 2017, 199–221 (2017)
Çelik, E.; Demirkiran, A.Ş; Avci, E.: Effect of grit blasting of substrate on the corrosion behaviour of plasma-sprayed Al2O3 coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 116–119, 1061–1064 (1999)
Wang, H.Y.; Zhu, R.F.; Lu, Y.P.; Xiao, G.Y.; He, K.; Yuan, Y.F.: Effect of sandblasting intensity on microstructures and properties of pure titanium micro-arc oxidation coatings in an optimized composite technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. (Internet) 292, 204–212 (2014)
Asl, S.K.; Sohi, M.H.: Effect of grit-blasting parameters on the surface roughness and adhesion strength of sprayed coating. Surf. Interface Anal. 42(6–7), 551–554 (2010)
Haj, M.J.R.; Spelt, J.K.; Papini, M.: Surface roughness and erosion rate of abrasive jet micro-machined channels: experiments and analytical model. Wear (Internet) 303(1–2), 138–145 (2013)
Ahmed, A.A.; Mhaede, M.; Basha, M.; Wollmann, M.; Wagner, L.: The effect of shot peening parameters and hydroxyapatite coating on surface properties and corrosion behavior of medical grade AISI 316L stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. (Internet). 280, 347–358 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minhas, N., Thakur, A., Mehlwal, S. et al. Multi-variable Optimization of the Shot Blasting of Additively Manufactured AlSi10Mg Plates for Surface Roughness Using Response Surface Methodology. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 11671–11685 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05654-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05654-z