Abstract
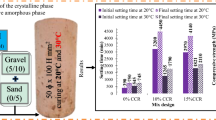
Conventional Portland cement concrete has been extensively used in the past century due to its superior performance compared to other building materials. Recognizing the environmental impact of cement composites and global pressure toward implementation of sustainable construction materials, geopolymer concrete has been introduced as a potential alternative to conventional cement concrete. This study investigates the properties of metakaolin-based geopolymer concrete by employing various mix design parameters based on locally sourced materials. The test results reported herein comprised 16 mixes divided into three groups to understand the influence of various parameters on the workability and compressive strength of the concrete and hence optimizing the mix proportions. The outcome of this research provided insights into the curing conditions, curing age, sodium hydroxide molarity, sodium silicate content, molar ratios of the mix, and aggregate water absorption effect on the geopolymer concrete behavior. A model is proposed for deciding the water to solids ratio based on the total aggregate percentage for workable geopolymer mixes. In order to produce MK-based geopolymer concrete for structural applications, thresholds are proposed for the three molar ratios, namely sodium oxide to silicon oxide, sodium oxide to aluminum oxide, and water to sodium oxide ratios.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar, P.; Pankar, C.; Manish, D.; Santhi, A.S.: Study of mechanical and microstructural properties of geopolymer concrete with GGBS and Metakaolin. Mater. Today Proc. 5(14), 28127–28135 (2018)
Heah, C.Y.; Kamarudin, H.; Mustafa Al Bakri, A.M.; Binhussain, M.; Luqman, M.; Khairul Nizar, I.; Ruzaidi, C.M.; Liew, Y.M.: Effect of curing profile on kaolin-based geopolymers. Phys. Proc. 22, 305–311 (2011)
Okoye, F.N.; Durgaprasad, J.; Singh, N.B.: Mechanical properties of alkali activated flyash/Kaolin based geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build Mater. 98, 685–691 (2015)
Aliabdo, A.A.; Abd Elmoaty, A.M.; Salem, H.A.: Effect of cement addition, solution resting time and curing characteristics on fly ash based geopolymer concrete performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 123, 581–593 (2016)
Nazari, A.; Bagheri, A.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Dao, M.; Mallawa, C.; Zannis, P.; Zumbo, S.: Thermal shock reactions of Ordinary Portland cement and geopolymer concrete: microstructural and mechanical investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 196, 492–498 (2019)
Kathirvel, P.; Kaliyaperumal, S.R.M.: Influence of recycled concrete aggregates on the flexural properties of reinforced alkali activated slag concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 102, 51–58 (2016)
He, J.; Jie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, G.: Synthesis and characterization of red mud and rice husk ash-based geopolymer composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 37, 108–118 (2013)
Zabihi, S.M.; Tavakoli, M.; Mohseni, E.: Engineering and microstructural properties of fiber-reinforced rice husk–ash based geopolymer concrete. J Mater. Civ. Eng. 30(8), 1–10 (2018)
Bondar, D.; Lynsdale, C.J.; Milestone, N.B.; Hassani, N.; Ramezanianpour, A.A.: Engineering properties of alkali-activated natural pozzolan concrete. ACI Mater. J. 108, 1–9 (2011)
Kantarcı, F.; Türkmen, İ.; Ekinci, E.: Optimization of production parameters of geopolymer mortar and concrete: a comprehensive experimental study. Constr. Build. Mater. 228, 1–17 (2019)
Sagoe-Crentsil, K.; Weng, L.: Dissolution processes, hydrolysis and condensation reactions during geopolymer synthesis: part II. High Si/Al ratio systems. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 3007–3014 (2007)
Weng, L.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K.: Dissolution processes, hydrolysis and condensation reactions during geopolymer synthesis: part I—Low Si/Al ratio systems. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 2997–3006 (2007)
Yao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Y.: Geopolymerization process of alkali–metakaolinite characterized by isothermal calorimetry. Thermochim Acta 493(1–2), 49–54 (2009)
Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.: Semi-empirical AM1 calculations on 6-memebered alumino-silicate rings model: implications for dissolution process of metakaoline in alkaline solutions. J Mater Sci 42(9), 3015–3023 (2007)
Yunsheng, Z.; Wei, S.; Zongjin, L.; Yantao, J.: Study of polycondensation process of metakaolin-based geopolymeric cement using semi-empirical AM1 calculations. Adv. Cem. Res. 21(2), 67–73 (2009)
Bing-hui, M.; Zhu, H.; Xue-min, C.; Yan, H.; Si-yu, G.: Effect of curing temperature on geopolymerization of metakaolin-based geopolymers. Appl. Clay Sci. 99, 144–148 (2014)
Muñiz-Villarreal, M.S.; Manzano-Ramírez, A.; Sampieri-Bulbarela, S.; Gasca-Tirado, J.R.; Reyes-Araiza, J.L.; Rubio-Ávalos, J.C.; Pérez-Bueno, J.J.; Apatiga, L.M.; Zaldivar-Cadena, A.; Amigó-Borrás, V.: The effect of temperature on the geopolymerization process of a metakaolin-based geopolymer. Mater. Lett. 65(6), 995–998 (2011)
Perera, D.S.; Uchida, O.; Vance, E.R.; Finnie, K.S.: Influence of curing schedule on the integrity of geopolymers. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 3099–3106 (2007)
Rovnaník, P.: Effect of curing temperature on the development of hard structure of metakaolin-based geopolymer. Constr. Build Mater. 24(7), 1176–1183 (2010)
Pires, E.F.C.; Azevedo, C.M.C.; Pimenta, A.R.; Silva, F.J.; Darwish, F.A.I.: Fracture properties of geopolymer concrete based on metakaolin, fly ash and rice rusk ash. Mater. Res. 20, 630–636 (2017)
Mohseni, E.: Assessment of Na2SiO3 to NaOH ratio impact on the performance of polypropylene fiber-reinforced geopolymer composites. Constr. Build Mater. 186, 904–911 (2018)
Alanazi, H.; Yang, M.; Zhang, D.; Gao, Z.: Early strength and durability of metakaolin-based geopolymer concrete. Magn. Concr. Res. 69(1), 46–54 (2017)
Pouhet, R.; Cyr, M.: Formulation and performance of flash metakaolin geopolymer concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 120, 150–160 (2016)
Xie, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Fang, C.; Zhang, B.; Liu, F.: Coupling effects of recycled aggregate and GGBS/metakaolin on physicochemical properties of geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 226, 345–359 (2019)
Standard, A. S. T. M.: ASTM C-143 Standard test method for slump of Portland cement concrete. ASTM International (1990)
Standard, A. S. T. M.: ASTM C39 Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. ASTM International (2015)
Albitar, M.; Visintin, P.; Ali, M.S.M.; Drechsler, M.: Assessing behaviour of fresh and hardened geopolymer concrete mixed with class-F fly ash. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 19, 1445–1455 (2015)
Hardjito, D.; Wallah, S.E.; Sumajouw, D.M.J.; Rangan, B.V.: On the development of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. Mater. J. 101, 467–472 (2004)
Nath, P.; Sarker, P.K.: Flexural strength and elastic modulus of ambient-cured blended low-calcium fly ash geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build Mater. 130, 22–31 (2017)
Aliabdo, A.A.; Abd Elmoaty, A.M.; Salem, H.A.: Effect of water addition, plasticizer and alkaline solution constitution on fly ash based geopolymer concrete performance. Constr. Build Mater. 121, 694–703 (2016)
Parveen, S.D.; Junaid, M.T.; Jindal, B.B.; Mehta, A.: Mechanical and microstructural properties of fly ash based geopolymer concrete incorporating alccofine at ambient curing. Constr. Build Mater. 180, 298–307 (2018)
Wang, H.; Li, H.; Yan, F.: Synthesis and mechanical properties of metakaolinite-based geopolymer. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 268(1–3), 1–6 (2005)
Sperberga, I.; Rundans, M.; Cimmers, A.; Krage, L.; Sidraba, I.: Mechanical properties of materials obtained via alkaline activation of illite-based clays of Latvia. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 602, 1–4 (2015)
Monita, O.; Nikraz, H.: Properties of fly ash geopolymer concrete designed by Taguchi method. Mater. Des. 36, 191–198 (2012)
Pan, Z.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Rangan, B.V.: Fracture properties of geopolymer paste and concrete. Magn. Concr. Res. 63(10), 763–771 (2011)
Rowles, M.R.; O'connor B, : Chemical optimisation of the compressive strength of aluminosilicate geopolymers synthesised by sodium silicate activation of metakaolinite. J. Mater. Chem. 13, 1161–1165 (2003)
Lahoti, M.; Narang, P.; Tan, K.H.; Yang, E.: Mix design factors and strength prediction of metakaolin-based geopolymer. Ceram. Int. 43(14), 11433–11441 (2017)
Acknowledgements
he authors are grateful to the Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University, for funding through Vice Deanship of Scientific Research Chairs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alghannam, M., Albidah, A., Abbas, H. et al. Influence of Critical Parameters of Mix Proportions on Properties of MK-Based Geopolymer Concrete. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 4399–4408 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04970-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04970-0