Abstract
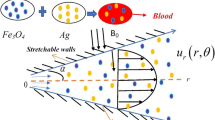
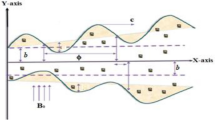
Hybrid nanofluids are used to enhance therapeutic effects and reduce the side effects in tumour therapy. These nanoparticles are transported nearest to the cancer’s tissues under the action of the peristaltic waves generated on the walls of the blood vessel. The motion of hybrid nanoparticles in non-uniform vertical channel having flexible boundaries is numerically elaborated in present study. Poisson equations are used on the basis of electro-osmotic theory to encounter the phenomena of applied electric field on the walls of the channel. Lubrication approach and Debye–Huckel linearization approximations are utilized to obtain the system of coupled ordinary differential equations from the basic conservation laws which are solved by using implicit finite difference scheme which is commonly known as Keller–Box method and MATLAB built in subroutine Bvp5c. The impact of electro-osmotic parameter on all features of flow of nanoparticles observed through several graphs and various tables. The current study is applicable and helpful in the design of micropumps and nanomedicine technologies.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Latham, T. W.: Fluid Motions in a Peristaltic Pump (Doctoral dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology)
Wang, Y.; Hayat, T.; Ali, N.; Oberlack, M.: Magnetohydrodynamic peristaltic motion of a Sisko fluid in a symmetric or asymmetric channel. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 387(2–3), 347–362 (2008)
Hayat, T.; Ali, N.; Asghar, S.; Siddiqui, A.M.: Exact peristaltic flow in tubes with an endoscope. Appl. Math. Comput. 182(1), 359–368 (2006)
Ali, N.; Abbasi, A.; Ahmad, I.: Channel flow of Ellis fluid due to peristalsis. AIP Adv. 5(9), 097214 (2015)
Ahmad, I.; Ali, N.; Abbas, A.; Aziz, W.; Hussain, M.; Ahmad, M.: Flow of a Burger’s fluid in a channel induced by peristaltic compliant walls. J. Appl. Math. 2014, 12 (2015)
Abbasi, A.; Farooq, W.; Ali, N.; Ahmad, I.: Simultaneous effects of Brownian motion, thermophoresis and curvature on peristaltic flow of an Oldroyd 4-constant fluid. J Nanofluids 8(4), 736–745 (2019)
Reuss, F.F.: Sur un nouvel effet de l’électricité galvanique. Mem. Soc. Imp. Nat. Mosc. 2, 327–337 (1809)
Dukhin, S.S.: Electrokinetic phenomena of the second kind and their applications. Adv. Coll. Interface Sci. 1(35), 173–196 (1991)
Casagrande, L.: Electro-osmotic stabilization of soils. J. Boston Soc. Eng. 39, 51–83 (1952)
Sadr, R.; Yoda, M.; Zheng, Z.; Conlisk, A.T.: An experimental study of electro-osmotic flow in rectangular microchannels. J. Fluid Mech. 506, 357–367 (2004)
Chakraborty, S.: Augmentation of peristaltic microflows through electro-osmotic mechanisms. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39(24), 5356 (2006)
Bandopadhyay, A.; Tripathi, D.; Chakraborty, S.: Electroosmosis-modulated peristaltic transport in microfluidic channels. Phys. Fluids 28(5), 052002 (2016)
Tripathi, D.; Bhushan, S.; Bég, O.A.: Analytical study of electro-osmosis modulated capillary peristaltic hemodynamics. J. Mech. Med. Biol 17(03), 1750052 (2017)
Tripathi, D.; Bhushan, S.; Bég, O.A.: Unsteady viscous flow driven by the combined effects of peristalsis and electro-osmosis. Alex. Eng. J. 57(3), 1349–1359 (2018)
Hussain, S.; Ali, N.; Ullah, K.: Peristaltic flow of Phan-Thien-Tanner fluid: effects of peripheral layer and electro-osmotic force. Rheol. Acta 58(9), 603–618 (2019)
Vajravelu, K.; Radhakrishnamacharya, G.; Radhakrishnamurty, V.: Peristaltic flow and heat transfer in a vertical porous annulus, with long wave approximation. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 42(5), 754–759 (2007)
Tang, G.; Yan, D.; Yang, C.; Gong, H.; Chai, J.C.; Lam, Y.C.: Assessment of Joule heating and its effects on electroosmotic flow and electrophoretic transport of solutes in microfluidic channels. Electrophoresis 27(3), 628–639 (2006)
Horiuchi, K.; Dutta, P.; Hossain, A.: Joule-heating effects in mixed electroosmotic and pressure-driven microflows under constant wall heat flux. J. Eng. Math. 54(2), 159 (2006)
Narla, V.K.; Tripathi, D.; Bég, O.A.: Analysis of entropy generation in biomimetic electroosmotic nanofluid pumping through a curved channel with joule dissipation. Therm. Sci. Eng. Progress 1(15), 100424 (2020)
Patel, D.J.; Mistri, P.A.; Prajapati, J.J.: Treatment of cancer by using nanoparticles as a drug delivery. Int. J. Drug Dev. Res. 4(1), 14–27 (2012)
McCarroll, J.; Teo, J.; Boyer, C.; Goldstein, D.; Kavallaris, M.; Phillips, P.: Potential applications of nanotechnology for the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer. Front Physiol 24(5), 2 (2014)
Purushotham, S.; Ramanujan, R.V.: Thermoresponsive magnetic composite nanomaterials for multimodal cancer therapy. Acta Biomater. 6(2), 502–510 (2010)
Abbasi, F.M.; Hayat, T.; Ahmad, B.: Peristalsis of silver-water nanofluid in the presence of Hall and Ohmic heating effects: applications in drug delivery. J. Mol. Liq. 1(207), 248–255 (2015)
Kothandapani, M.; Prakash, J.: The peristaltic transport of Carreau nanofluids under effect of a magnetic field in a tapered asymmetric channel: application of the cancer therapy. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 15(03), 1550030 (2015)
Zaman, A.; Ali, N.; Khan, A.A.: Computational biomedical simulations of hybrid nanoparticles on unsteady blood hemodynamics in a stenotic artery. Math. Comput. Simul. 1(169), 117–132 (2020)
Hayat, T.; Nadeem, S.: Heat transfer enhancement with Ag–CuO/water hybrid nanofluid. Results Phys. 7, 2317–2324 (2017)
Hayat, T.; Nadeem, S.; Khan, A.U.: Rotating flow of Ag–CuO/H2O hybrid nanofluid with radiation and partial slip boundary effects. Eur. Phys. J. E 41(6), 75 (2018)
Hayat, T.; Nadeem, S.; Khan, A.U.: Numerical analysis of Ag–CuO/water rotating hybrid nanofluid with heat generation and absorption. Can. J. Phys. 97(6), 644–650 (2019)
Nadeem, S.; Nadeem, A.; Khan, A.U.: Characteristics of three dimensional stagnation point flow of Hybrid nanofluid past a circular cylinder. Results Phys. 8, 829–835 (2018)
Nadeem, S.; Nadeem, A.: On both MHD and slip effect in micropolar hybrid nanofluid past a circular cylinder under stagnation point region. Can. J. Phys. 97(4), 392–399 (2019)
Abbas, N.; Malik, M.Y.; Nadeem, S.; Alarifi, I.M.: On extended version of Yamada-Ota and Xue models of hybrid nanofluid on moving needle. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135(2), 145 (2020)
Abbas, N.; Malik, M.Y.; Nadeem, S.: Transportation of magnetized micropolar hybrid nanomaterial fluid flow over a Riga curface surface. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 185, 105136 (2020)
Ghalambaz, M.; Doostani, A.; Izadpanahi, E.; Chamkha, A.J.: Conjugate natural convection flow of Ag–MgO/water hybrid nanofluid in a square cavity. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 139(3), 2321–2336 (2020)
Babazadeh, H.; Shah, Z.; Ullah, I.; Kumam, P.; Shafee, A.: Analysis of hybrid nanofluid behavior within a porous cavity including Lorentz forces and radiation impacts. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 1–9 (2020)
Tayebi, T.; Chamkha, A.J.: Entropy generation analysis due to MHD natural convection flow in a cavity occupied with hybrid nanofluid and equipped with a conducting hollow cylinder. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 139(3), 2165–2179 (2020)
Khan, M.I.; Hafeez, M.U.; Hayat, T.; Khan, M.I.; Alsaedi, A.: Magneto rotating flow of hybrid nanofluid with entropy generation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 183, 105093 (2020)
Khanafer, K.; Vafai, K.: The role of porous media in biomedical engineering as related to magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. Heat Mass Transf. 42(10), 939 (2006)
Nicholson, C.: Diffusion and related transport mechanisms in brain tissue. Rep. Prog. Phys. 64(7), 815 (2001)
Dash, R.K.; Mehta, K.N.; Jayaraman, G.: Casson fluid flow in a pipe filled with a homogeneous porous medium. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 34(10), 1145–1156 (1996)
Sharma, M.K.; Bansal, K.; Bansal, S.: Pulsatile unsteady flow of blood through porous medium in a stenotic artery under the influence of transverse magnetic field. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 24(3), 181–189 (2012)
Tripathi, D.; Bég, O.A.; Gupta, P.K.; Radhakrishnamacharya, G.; Mazumdar, J.: DTM simulation of peristaltic viscoelastic biofluid flow in asymmetric porous media: a digestive transport model. J. Bionic Eng. 12(4), 643–655 (2015)
Abbasi, F.M.; Hayat, T.; Ahmad, B.: Peristaltic transport of copper–water nanofluid saturating porous medium. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 67, 47–53 (2015)
Prakash, J.; Tripathi, D.; Bég, O.A.: Comparative study of hybrid nanofuids in microchannel slip fow induced by electroosmosis and peristalsis. Appl Nano Sci 2, 1–4 (2020)
Sun, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, R.; Duan, J.; Hu, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, J.; Xie, S.; Lu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, S.: Aluminum nanoparticles enhance anticancer immune response induced by tumor cell vaccine. Cancer Nanotechnol 1(1), 63 (2010)
Yesilot, S.; Aydin, C.: Silver nanoparticles; a new hope in cancer therapy? Eastern J. Med. 24(1), 111–116 (2019)
Devi, S.A.; Devi, S.S.: Numerical investigation of hydromagnetic hybrid Cu–Al2O3/water nanofluid flow over a permeable stretching sheet with suction. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 17(5), 249–257 (2016)
Ijaz, S.; Nadeem, S.: Biomedical theoretical investigation of blood mediated nanoparticles (Ag–Al2O3/blood) impact on hemodynamics of overlapped stenotic artery. J. Mol. Liq. 1(248), 809–821 (2017)
Prakash, J.; Siva, E. P.; Balaji, N.; Kothandapani, M.: Effect of peristaltic flow of a third grade fluid in a tapered asymmetric channel. In: Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2018 Apr (Vol. 1000, No. 1, p. 012165). IOP Publishing.
Mustafa, M.; Abbasbandy, S.; Hina, S.; Hayat, T.: Numerical investigation on mixed convective peristaltic flow of fourth grade fluid with Dufour and Soret effects. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 45(2), 308–316 (2014)
Mahmood, K.; Sajid, M.; Ali, N.: Nonorthogonal stagnation-point flow of a second-grade fluid past a lubricated surface. Z für Naturforschung A 71(3), 273–280 (2016)
Abbasi, A.; Riaz, I.; Farooq, W.; Ahmad, M.: Analysis of nonlinear thermal radiation and higher-order chemical reactions on the non-orthogonal stagnation point flow over a lubricated surface. Heat Transf. 49(2), 673–692 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbasi, A., Farooq, W. A Numerical Simulation for Transport of Hybrid Nanofluid. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 9249–9265 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04704-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04704-2