Abstract
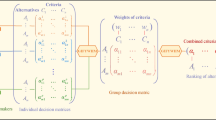
Technique for order preference by similarity to an ideal solution (TOPSIS) is an effective technique to solve multi-criteria decision-making problem. It aims to select the alternative, which has the “shortest distance” from positive ideal solution (PIS) and the “farthest distance” from negative ideal solution (NIS). Nevertheless, much literature has demonstrated that the solution calculated by TOPSIS only is the compromise of PIS and NIS, and it is of great restriction in dealing with the practical problems which have diverse demands and properties. Therefore, in the presented model, an optimism coefficient is defined to expand the physical meaning of the standard TOPSIS. Decision-makers (DMs) can describe their attitudes toward risk and profit by changing the value of optimism coefficient. Furthermore, intuitionistic fuzzy number is introduced to measure the evaluations (linguistic values) of DMs to alternatives under diverse criteria. Intuitionistic fuzzy weighted averaging operator is used for fusing the judgments of all DMs. Finally, a conclusion can be safely obtained that the proposed model is stable and validity from the illustrative examples and sensitivity analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Debnath, A.; Majumder, M.; Pal, M.: Potential of fuzzy-ELECTRE MCDM in evaluation of cyanobacterial toxins removal methods. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41(10), 3931–3944 (2016)
Jang, W.; Hong, H.U.; Han, S.H.; Baek, S.W.: Optimal supply vendor selection model for LNG plant projects using fuzzy-TOPSIS theory. J. Manag. Eng. 33(2), 04016035 (2017)
Peng, Y.; Wang, G.; Kou, G.; Shi, Y.: An empirical study of classification algorithm evaluation for financial risk prediction. Appl. Soft Comput. 11(2), 2906–2915 (2011)
Quader, M.A.; Ahmed, S.: A hybrid fuzzy mcdm approach to identify critical factors and co 2 capture technology for sustainable iron and steel manufacturing. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41(11), 1–20 (2016)
Rudnik, K.; Kacprzak, D.: Fuzzy TOPSIS method with ordered fuzzy numbers for flow control in a manufacturing system. Appl. Soft Comput. 52, 1020–1041 (2017)
Toklu, M.C.; Erdem, M.B.; Taskin, H.: A fuzzy sequential model for realization of strategic planning in manufacturing firms. Comput. Ind. Eng. 102, 512–519 (2016)
Arasteh, A.; Aliahmadi, A.: A multi-stage multi criteria model for portfolio management. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(5), 4269–4283 (2014)
Sadoddin, A.; Sheikh, V.; Mostafazadeh, R.; Halili, M.G.: Analysis of vegetation-based management scenarios using mcdm in the ramian watershed, golestan, iran. Int. J. Plant Prod. 4(1), 1735–6814 (2010)
Lin, K.P.; Hung, K.C.: An efficient fuzzy weighted average algorithm for the military uav selecting under group decision-making. Knowl. Based Syst. 24(6), 877–889 (2011)
Opricovic, S.; Tzeng, G.H.: Compromise solution by mcdm methods: a comparative analysis of vikor and topsis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 156(2), 445–455 (2004)
Yu, P.L.: A class of solutions for group decision problems. Manag. Sci. 19(8), 936–946 (1973)
Zeleny, M.: Multiple Criteria Decision Making. Springer, New York (1980)
Tong, L.I.; Chen, C.C.; Wang, C.H.: Optimization of multi-response processes using the vikor method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 31(11), 1049–1057 (2007)
Opricovic, S.; Tzeng, G.H.: Extended vikor method in comparison with outranking methods. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 178(2), 514–529 (2007)
Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.: Improved vikor algorithm based on ahp and shannon entropy in the selection of thermal power enterprise’s coal suppliers. In: International Conference on Information Management, Innovation Management and Industrial Engineering, pp. 129–133 (2009)
Sanayei, A.; Mousavi, S.F.; Yazdankhah, A.: Group decision making process for supplier selection with vikor under fuzzy environment. Expert Syst. Appl. 37(1), 24–30 (2010)
Devi, K.: Extension of vikor method in intuitionistic fuzzy environment for robot selection. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(11), 14163–14168 (2011)
Yang, Y.P.O.; Shieh, H.M.; Tzeng, G.H.: A vikor technique based on dematel and anp for information security risk control assessment. Inf. Sci. 232(5), 482–500 (2013)
Huang, K.W.; Huang, J.H.; Tzeng, G.H.: New hybrid multiple attribute decision-making model for improving competence sets: enhancing a companys core competitiveness. Sustainability 8(2), 175 (2016)
Hwang, C.L.; Yoon, K.: Multiple Attribute Decision Making, vol. 186. Computer Science University of Southampton UK Her, Southampton (1995)
Tsaur, S.H.; Chang, T.Y.; Yena, C.H.: The evaluation of airline service quality by fuzzy mcdm. Tour. Manag. 23(2), 107–115 (2002)
Jahanshahloo, G.R.; Lotfi, F.H.; Izadikhah, M.: An algorithmic method to extend topsis for decision-making problems with interval data. Appl. Math. Comput. 175(2), 1375–1384 (2006)
Chu, T.: Facility location selection using fuzzy topsis under gropu decision. Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzziness Knowl. Based Syst. 10(6), 687–701 (2012)
Chu, T.C.: Selecting plant location via a fuzzy topsis approach. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 20(20), 859–864 (2002)
Triantaphyllou, E.; Lin, C.T.: Development and evaluation of five fuzzy multiattribute decision-making methods. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 14(4), 281–310 (1996)
Jiang, W.; Xie, C.; Luo, Y.; Tang, Y.: Ranking z-numbers with an improved ranking method for generalized fuzzy numbers. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 32(3), 1931–1943 (2017). doi:10.3233/JIFS-16139
Kuo, T.: A modified TOPSIS with a different ranking index. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 260(1), 152–160 (2017)
Yaakob, A.M.; Serguieva, A.; Gegov, A.: FN-TOPSIS: fuzzy networks for ranking traded equities. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 25(2, SI), 315–332 (2017)
Walczak, D.; Rutkowska, A.: Project rankings for participatory budget based on the fuzzy TOPSIS method. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 260(2), 706–714 (2017)
Hu, J.; Du, Y.; Mo, H.; Wei, D.; Deng, Y.: A modified weighted topsis to identify influential nodes in complex networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 444, 73–85 (2016)
Kang, B.; Hu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, D.: A new methodology of multicriteria decision-making in supplier selection based on Z-numbers. Math. Probl. Eng. (2016). doi:10.1155/2016/8475987
Zhang, X.; Deng, Y.; Chan, F.T.S.; Adamatzky, A.; Mahadevan, S.: Supplier selection based on evidence theory and analytic network process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 230(3), 562–573 (2016). doi:10.1177/0954405414551105
Lu, C.; You, J.X.; Liu, H.C.; Li, P.: Health-care waste treatment technology selection using the interval 2-tuple induced topsis method. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 13(6), 562 (2016)
Afsordegan, A.; Snchez, M.; Agell, N.; Zahedi, S.; Cremades, L.V.: Decision making under uncertainty using a qualitative topsis method for selecting sustainable energy alternatives. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13(6), 1–14 (2016)
Mo, H.; Deng, Y.: A new aggregating operator in linguistic decision making based on d numbers. Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzziness Knowl. Based Syst. 24(6), 831–846 (2016)
Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, F.; Deng, X.; Deng, Y.: A novel method to use fuzzy soft sets in decision making based on ambiguity measure and Dempster–Shafer theory of evidence: an application in medical diagnosis. Artif. Intell. Med. 69, 1–11 (2016)
Zhou, X.; Shi, Y.; Deng, X.; Deng, Y.: D-DEMATEL: a new method to identify critical success factors in emergency management. Saf. Sci. 91, 93–104 (2017)
Deng, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, J.: Zero-sum matrix game with payoffs of Dempster–Shafer belief structures and its applications on sensors. Sensors 17(4), 922 (2017). doi:10.3390/s17040922
Fei, L.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, F.; Chen, L.; Deng, Y.: A modified TOPSIS method based on D numbers and its applications in human resources Selection. Math. Probl. Eng. (2016). doi:10.1155/2016/6145196
Wang, N.; Liu, F.; Wei, D.: A modified combination rule for D numbers theory. Math. Probl. Eng. (2016). doi:10.1155/2016/3596517
Zhou, X.; Deng, X.; Deng, Y.; Mahadevan, S.: Dependence assessment in human reliability analysis based on d numbers and ahp. Nucl. Eng. Des. 313, 243–252 (2017)
Deng, X.; Xiao, F.; Deng, Y.: An improved distance-based total uncertainty measure in belief function theory. Appl. Intell. (2017, in press). doi:10.1007/s10489-016-0870-3
Jiang, W.; Zhan, J.: A modified combination rule in generalized evidence theory. Appl. Intell. 46(3), 630–640 (2017). doi:10.1007/s10489-016-0851-6
Wang, J.; Xiao, F.; Deng, X.; Fei, L.; Deng, Y.: Weighted evidence combination based on distance of evidence and entropy function. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 12(7) (2016). doi:10.1177/155014773218784
Bazzazi, A.A.; Osanloo, M.; Karimi, B.: Deriving preference order of open pit mines equipment through madm methods: application of modified vikor method. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(3), 2550–2556 (2011)
Sayadi, M.K.; Heydari, M.; Shahanaghi, K.: Extension of vikor method for decision making problem with interval numbers. Appl. Math. Model. 33(5), 2257–2262 (2009)
Atanassov, K.T.: Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 20(1), 87–96 (1986)
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8(3), 338–353 (1965)
Xu, Z.: Intuitionistic fuzzy aggregation operators. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 14(6), 1179–1187 (2008)
Xu, Z.; Yager, R.R.: Some geometric aggregation operators based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 35(4), 417–433 (2006)
Xu, Z.; Cai, X.: Dynamic intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute decision making. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 48(1), 246–262 (2008)
Boran, F.E.; Genc, S.; Kurt, M.; Akay, D.: A multi-criteria intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making for supplier selection with TOPSIS method. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(8), 11363–11368 (2009)
Jiang, W.; Xie, C.; Zhuang, M.; Shou, Y.; Tang, Y.: Sensor data fusion with z-numbers and its application in fault diagnosis. Sensors 16(9), 1509 (2016)
Jiang, W.; Xie, C.; Zhuang, M.; Tang, Y.: Failure mode and effects analysis based on a novel fuzzy evidential method. Appl. Soft Comput. 57, 672–683 (2017)
Yang, J.; Huang, H.Z.; He, L.P.; Zhu, S.P.; Wen, D.: Risk evaluation in failure mode and effects analysis of aircraft turbine rotor blades using Dempster–Shafer evidence theory under uncertainty. Eng. Fail. Anal. 18(8), 2084–2092 (2011)
Guo, S.; Zhao, H.; Yan, J.: Optimal site selection of electric vehicle charging station by using fuzzy topsis based on sustainability perspective. Appl. Energy 158, 390–402 (2015)
Liu, H.C.; You, J.X.; Shan, M.M.; Shao, L.N.: Failure mode and effects analysis using intuitionistic fuzzy hybrid topsis approach. Soft Comput. 19(4), 1085–1098 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The work was partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61671384), Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (Program No. 2016JM6018), Aviation Science Foundation (Program No. 20165553036), the Fund of Shanghai Aerospace Science and Technology SAST(Program No. SAST2016083), the Seed Foundation of Innovation and Creation for Graduate Students in Northwestern Polytechnical University (Program No. Z2017142).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Jiang, W. Extension of TOPSIS Method and its Application in Investment. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 693–705 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2736-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2736-3