Abstract
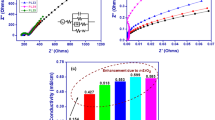
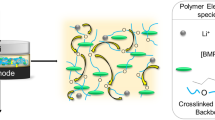
A kind of nanocomposite polymer electrolyte (NCPE) based on poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) was prepared by a solution casting technology, in which a room temperature ionic liquid, 1-ethyl-3-methyl-imidazolium tetrafluoroborate was used as plasticizer to improve the thermal stability. The obtained NCPE displayed a porous structure composed of many spherical polymer grains and its crystallinity decreased with the amount of SiO2 nanoparticles. Effect of SiO2 nanoparticles on its electrochemical properties was studied by impedance spectroscopy, linear sweep voltammetry and cyclic voltammetry. When the NCPE is filled with 2 % of SiO2 nanoparticles, it has a room temperature ionic conductivity of 4.7 × 10−4 S cm−1, and exhibits a high decomposition temperature up to 289 °C. The Li/LiFePO4 cells using this NCPE as separator show a good rate capability and a satisfied cycling performance. The results confirmed the feasibility of the as-prepared NCPE in rechargeable lithium batteries.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chakrabarti M.H., Hajimolana S.A., Mjalli F.S., Saleem M., Mustafa I.: Redox flow battery for energy storage. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 38(4), 723–739 (2013)
Tarascon J.M.: Is lithium the new gold?. Nat. Chem. 2(6), 680 (2010)
Tarascon J.M., Armand M.: Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414(6861), 359–367 (2001)
Bhattacharyya R., Key B., Chen H.L., Best A.S., Hollenkamp A.F., Grey C.P.: In situ NMR observation of the formation of metallic lithium microstructures in lithium batteries. Nat. Mater. 9(6), 504–510 (2010)
Hassoun J., Scrosati B.: A high-performance polymer tin sulfur lithium ion battery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49(13), 2371–2374 (2010)
Sunarso J., Shekibi Y., Efthimiadis J., Jin L., Pringle J.M., Hollenkamp A.F., MacFarlane D.R., Forsyth M., Howlett P.C.: Optimising organic ionic plastic crystal electrolyte for all solid-state and higher than ambient temperature lithium batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 16(5), 1841–1848 (2012)
Lalia B.S., Yoshimoto N., Egashira M., Morita M.: A mixture of triethylphosphate and ethylene carbonate as a safe additive for ionic liquid-based electrolytes of lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 195(21), 7426–7431 (2010)
Sirisopanaporn C., Fernicola A., Scrosati B.: New, ionic liquid-based membranes for lithium battery application. J. Power Sources 186(2), 490–495 (2009)
Suo L., Hu Y.S., Li H., Armand M., Chen L.: A new class of solvent-in-salt electrolyte for high-energy rechargeable metallic lithium batteries. Nat. Commun. 4, 1481–1489 (2013)
Tatsumisago, M.; Nagao, M.; Hayashi, A.: Recent development of sulfide solid electrolytes and interfacial modification for all-solid-state rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. doi:10.1016/j.jascer.2013.03.005 (2013)
Bouchet, R.; Maria, S.; Meziane, R.; Aboulaich, A.; Lienafa, L.; Bonnet, J.P.; Phan, T.N. T.; Bertin, D.; Gigmes, D.; Devaux, D.; Denoyel, R.; Armand, M.: Single-ion BAB triblock copolymers as highly efficient electrolytes for lithium-metal batteries. Nat. Mater. doi:10.1038/nmat3602 (2013)
Wen J., Yu Y., Chen C.: A review on lithium-ion batteries safety issues: existing problems and possible solutions. Mater. Express 2(3), 197–212 (2012)
Tang C., Hackenberg K., Fu Q., Ajayan P.M., Ardebili H.: High ion conducting polymer nanocomposite electrolytes using hybrid nanofillers. Nano Lett. 12(3), 1152–1156 (2012)
Schaefer J.L., Lu Y., Moganty S.S., Agarwal P., Jayaprakash N., Archer L.A.: Electrolytes for high-energy lithium batteries. Appl. Nanosci. 2(2), 91–109 (2012)
Tan G., Wu F., Li L., Liu Y., Chen R.: Magnetron sputtering preparation of nitrogen-incorporated lithium–aluminum–titanium phosphate based thin film electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 116(5), 3817–3826 (2012)
Lewandowski A., Świderska-Mocek A.: Ionic liquids as electrolytes for Li-ion batteries—an overview of electrochemical studies. J. Power Sources. 194(2), 601–609 (2009)
Hapiot P., Lagrost C.: Electrochemical reactivity in room-temperature ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 108(7), 2238–2264 (2008)
Armand M., Endres F., MacFarlane D.R., Ohno H., Scrosati B.: Ionic-liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future. Nat. Mater. 8(8), 621–629 (2009)
Li Z.H., Zhang P., Zhang H.P., Wu Y.P., Zhou X.D.: A lotus root-like porous nanocomposite polymer electrolyte. Electrochem. Commun. 10(5), 791–794 (2008)
Rosenberg Y., Siegmann A., Narkis M., Shkolnik S.: The sol/gel contribution to the behavior of γ-irradiated poly (vinylidene fluoride). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 43(3), 535–541 (1991)
Liu Y., Lee J.Y., Hong L.: In situ preparation of poly(ethylene oxide)–SiO2 composite polymer electrolytes. J. Power Sources. 129(2), 303–311 (2004)
He X.M., Shi Q., Zhou X., Wan C.R., Jiang C.Y.: In situ composite of nano SiO2–P(VDF-HFP) porous polymer electrolytes for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta. 51(6), 1069–1075 (2005)
Zhang J., Han H., Wu S., Xu S., Yang Y., Zhou C., Zhao X.: Conductive carbon nanoparticles hybrid PEO/P(VDF-HFP)/SiO2 nanocomposite polymer electrolyte type dye sensitized solar cells. Solid State Ionics. 178(29), 1595–1601 (2007)
Wang H.L., Liu X.T., Yu S.M., Shi T.J., Jiang S.T.: Preparation of P(AN-MMA)/SiO2 hybrid solid electrolytes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 114(3), 1365–1369 (2009)
Khan S.A., Baker G.L., Colson S.: Composite polymer electrolytes using fumed silica fillers: Rheology and ionic conductivity. Chem. Mater. 6(12), 2359–2363 (1994)
Aravindan V., Vickraman P.: Lithium fluoroalkylphosphate based novel composite polymer electrolytes (NCPE) incorporated with nanosized SiO2 filler. Mater. Chem. Phys. 115(1), 251–257 (2009)
Li Z.H., Jiang J., Lei G.T., Gao D.S.: Gel polymer electrolyte prepared by in situ polymerization of MMA monomers in room temperature ionic liquid. Polym. Adv. Technol. 17(7–8), 604–607 (2006)
Ratner M.A., Shriver D.F.: Ion transport in solvent-free polymers. Chem. Rev. 88(1), 109–124 (1988)
Singh T.J., Bhat S.V.: Morphology and conductivity studies of a new solid polymer electrolyte: (PEG) x LiClO4. Bull. Mater. Sci. 26(7), 707–714 (2003)
Markevich E., Baranchugov V., Aurbach D.: On the possibility of using ionic liquids as electrolyte solutions for rechargeable 5 V Li ion batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 8(8), 1331–1334 (2006)
Cheruvally G., Kim J.K., Choi J.W., Ahn J.H., Shin Y.J., Manuel J., Raghavan P., Kim K.W., Ahn H.J., Choi D.S.: Electrospun polymer membrane activated with room temperature ionic liquid: novel polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. J. Power Sources. 172(2), 863–869 (2007)
Raghavan P., Zhao X.H., Manuel J., Chauhan G.S., Ahn J.H., Ryu H.S., Ahn H.J., Kim K.W., Nah C.: Electrochemical performance of electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene)-based nanocomposite polymer electrolytes incorporating ceramic fillers and room temperature ionic liquid. Electrochim. Acta. 55(4), 1347–1354 (2010)
Umebayashi Y., Hamano H., Seki S., Minofar B., Fujii K., Hayamizu K., Tsuzuki S., Kameda Y., Kohara S., Watanabe M.: Liquid structure of and Li+ ion solvation in bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide based ionic liquids composed of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium and N-methyl-N-propylpyrrolidinium cations. J. Phys. Chem. B. 115(42), 12179–12191 (2011)
Zhou Q., Fitzgerald K., Boyle P.D., Henderson W.A.: Phase behavior and crystalline phases of ionic liquid-lithium salt mixtures with 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium salts. Chem. Mater. 22(3), 1203–1208 (2009)
Monteiro M.J., Bazito F.F.C., Siqueira L.J.A., Ribeiro M.C.C., Torresi R.M.: Transport coefficients, Raman spectroscopy, and computer simulation of lithium salt solutions in an ionic liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B. 112(7), 2102–2109 (2008)
Kim J.K., Cheruvally G., Li X., Ahn J.H., Kim K.W., Ahn H.J.: Preparation and electrochemical characterization of electrospun, microporous membrane-based composite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. J. Power Sources. 178(2), 815–820 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Q.C., Liu, H.Y., Xia, Q.L. et al. A Nanocomposite Polymer Electrolyte with High-Temperature Stability for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 6651–6657 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1180-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1180-x