Abstract
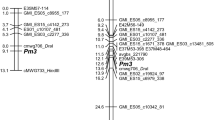
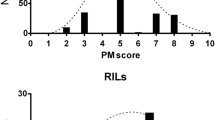
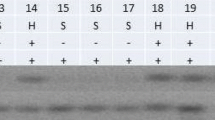
The genetics of resistance to powdery mildew caused by Blumeria graminis f. sp. avenae of four cultivated oats was studied using monosomic analysis. Cultivar ‘Bruno’ carries a gene (Pm6) that shows a recessive mode of inheritance and is located on chromosome 10D. Cultivar ‘Jumbo’ possesses a dominant resistance gene (Pm1) on chromosome 1C. In cultivar ‘Rollo’, in addition to the gene Pm3 on chromosome 17A, a second dominant resistance gene (Pm8) was identified and assigned to chromosome 4C. In breeding line APR 122, resistance was conditioned by a dominant resistance gene (Pm7) that was allocated to chromosome 13A. Genetic maps established for resistance genes Pm1, Pm6 and Pm7 employing amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) markers indicated that these genes are independent of each other, supporting the results from monosomic analysis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aslam M, Schwarzbach E (1980) An inoculation technique for quantitative studies of brown rust resistance in barley. J Phytopathol 99:87–91
Aung T, Thomas H (1978) The structure and breeding behaviour of a translocation involving the transfer of mildew resistance from Avena barbata Pott. into the cultivated oat. Euphytica 27:731–739
Aung T, Thomas H, Jones IT (1977) The transfer of the gene for mildew resistance from Avena barbata (4x) into the cultivated oat A. sativa by an induced translocation. Euphytica 26:623–632
Flor HH (1955) Host–parasite interaction in flax rust—its genetics and other implications. Phytopathology 45:680–685
Herrmann K, Roderick HW (1996) Characterisation of new oat germplasm for resistance to powdery mildew. Euphytica 89:405–410
Hoppe HD, Kummer M (1991) New productive hexaploid derivatives after introgression of Avena pilosa features. Vortr Pflanzenzüchtg 20:56–61
Hsam SLK, Zeller FJ (1998) Chromosomal location of genes for resistance to powdery mildew in cultivated oat (Avena sativa L.). 1. Gene Eg-3 in the cultivar ‘Mostyn’. Plant Breeding 117:177–178
Hsam SLK, Peters N, Paderina EV, Felsenstein F, Oppitz K, Zeller FJ (1997) Genetic studies of powdery mildew resistance in common oat (Avena sativa L.) I. Cultivars and breeding lines grown in Western Europe and North America. Euphytica 96:421–427
Hsam SLK, Paderina EV, Gordei S, Zeller FJ (1998) Genetic studies of powdery mildew resistance in cultivated oat (Avena sativa L.) II. Cultivars and breeding lines grown in Northern and Eastern Europe. Hereditas 129:227–230
Huang XQ, Zeller FJ, Hsam SLK, Wenzel G, Mohler V (2000) Chromosomal location of AFLP markers in common wheat utilizing nulli-tetrasomic stocks. Genome 43:298–305
Irigoyen ML, Linares C, Ferrer E, Fominaya A (2002) Fluorescence in situ hybridization mapping of Avena sativa L. cv. SunII and its monosomic lines using cloned repetitive DNA sequences. Genome 45:1230–1237
Jellen EN, Rooney WL, Phillips RL, Rines HW (1993) Characterization of the hexaploid oat Avena byzantina cv. Kanota monosomic series using C-banding and RFLPs. Genome 36:962–970
Jellen EN, Phillips RL, Rooney WL, Rines HW (1995) Molecular genetic identification of Avena chromosomes related to the group 1 chromosomes of the Triticeae. Genome 38:185–189
Jellen EN, Rines HW, Fox SL, Davis DW, Phillips RL, Gill BS (1997) Characterization of ‘Sun II’ oat monosomics through C-banding and identification of eight new ‘Sun II’ monosomics. Theor Appl Genet 95:1190–1195
Jones IT (1977) The effect on grain yield of adult plant resistance to mildew in oats. Ann Appl Biol 86:267–277
Jones IT (1982) A study of the host–pathogen relationships and inheritance of resistance to Erysiphe graminis avenae. Dissertation, University of Wales
Jones ET, Griffiths DJ (1952) Varietal resistance and susceptibility of oats to powdery mildew (Erysiphe graminis). Trans Brit Mycol Soc 35:71–80
Jones IT, Jones ERL (1979) Mildew of oats. UK Cereal Pathogen Virulence Survey, 1978 Annual Report, pp 59–63
Jones IT, Roderick HW, Clifford BC (1987) The integration of host resistance with fungicides in the control of oat powdery mildew. Ann Appl Biol 110:591–602
Kummer M (1984) Neue Resistenzquellen bei Echtem Mehltau für die Züchtung des Saathafers. Tag-Ber, Akad Landwirtsch-Wiss, Berlin 225:191–199
Lawes DA, Hayes JD (1965) The effect of mildew (Erysiphe graminis f. sp. avenae) on spring oat. Plant Pathol 14:125–128
Leath S, Bruckner PL, Wilson IP (1991) Reaction of winter oat germplasm to an epidemic of oat powdery mildew. Plant Dis 75:807–809
Leggett JM (1992) Classification and speciation in Avena. In: Marshall HG, Sorrells ME (eds) Oat science and technology. Agronomy Monograph 33. American Society of Agronomy and Crop Science Society of America, Madison, pp 29–52
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Mohler V, Zeller FJ, Hsam SLK (2012) Molecular mapping of powdery mildew resistance gene Eg-3 in cultivated oat (Avena sativa L. cv. ‘Rollo’). J Appl Genet 53:145–148
Morikawa T (1985) Identification of the 21 monosomic lines in Avena byzantina C. Koch cv. ‘Kanota’. Theor Appl Genet 70:271–278
Morikawa T (1995) Transfer of mildew resistance from the wild oat Avena prostrata into the cultivated oat. Bull Univ Osaka Prefect Ser B 47:1–10
Okoń S (2012) Identification of powdery mildew resistance genes in Polish common oat (Avena sativa L.) cultivars using host–pathogen tests. Acta Agrobot 65:63–68
Okoń S, Kowalczyk K (2012) Deriving isolates of powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis DC. f. sp. avenae Em. Marchal.) in common oat (Avena sativa L.) and using them to identify selected resistance genes. Acta Agrobot 65:155–160
Oliver RE, Tinker NA, Lazo GR, Chao S, Jellen EN, Carson ML, Rines HW, Obert DE, Lutz JD, Shackelford I, Korol AB, Wight CP, Gardner KM, Hattori J, Beattie AD, Bjørnstad Å, Bonman JM, Jannink JL, Sorrells ME, Brown-Guedira GL, Mitchell Fetch JW, Harrison SA, Howarth CJ, Ibrahim A, Kolb FL, McMullen MS, Murphy JP, Ohm HW, Rossnagel BG, Yan W, Miclaus KJ, Hiller J, Maughan PJ, Redman Hulse RR, Anderson JM, Islamovic E, Jackson EW (2013) SNP discovery and chromosome anchoring provide the first physically-anchored hexaploid oat map and reveal synteny with model species. PLoS One 8:e58068
Pohler W, Hoppe HD (1991) Avena macrostachya—a potential gene source for oat breeding. Vortr Pflanzenzüchtg 20:66–71
Rajhathy T (1963) A standard karyotype for Avena sativa. Can J Genet Cytol 5:127–132
Roderick HW, Jones ERL, Šebesta J (2000) Resistance to oat powdery mildew in Britain and Europe: a review. Ann Appl Biol 136:85–91
Rooney WL, Jellen EN, Phillips RL, Rines HW, Kianian SF (1994) Identification of homoeologous chromosomes in hexaploid oat (A. byzantina cv Kanota) using monosomics and RFLP analysis. Theor Appl Genet 89:329–335
Sánchez-Martín J, Rubiales D, Prats E (2011) Resistance to powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis f. sp. avenae) in oat seedlings and adult plants. Plant Pathol 60:846–856
Sanz MJ, Jellen EN, Loarce Y, Irigoyen ML, Ferrer E, Fominaya A (2010) A new chromosome nomenclature system for oat (Avena sativa L. and A. byzantina C. Koch) based on FISH analysis of monosomic lines. Theor Appl Genet 121:1541–1552
Schwarz G, Herz M, Huang XQ, Michalek W, Jahoor A, Wenzel G, Mohler V (2000) Application of fluorescence-based semi-automated AFLP analysis in barley and wheat. Theor Appl Genet 100:545–551
Schwarzbach E, Smith IM (1988) Erysiphe graminis DC. In: Smith IM, Dunez J, Lelliot RA, Phillips DH, Archer SA (eds) European handbook of plant diseases. Blackwell, Oxford
Sebesta J, Roderick HW, Chong J, Harder DE (1993) The oat line Pc54 as a source of resistance to crown rust, stem rust and powdery mildew in Europe. Euphytica 71:91–97
Singrün C, Hsam SLK, Hartl L, Zeller FJ, Mohler V (2003) Powdery mildew resistance gene Pm22 in cultivar Virest is a member of the complex Pm1 locus in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L. em Thell.). Theor Appl Genet 106:1420–1424
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap® 3.0 software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Yu J, Herrmann M (2006) Inheritance and mapping of a powdery mildew resistance gene introgressed from Avena macrostachya in cultivated oat. Theor Appl Genet 113:429–437
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), Bonn, for the financial support (Ze132/17-1).
Ethical standards
The authors declare that the experiments comply with the current laws of Germany.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 58 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsam, S.L.K., Mohler, V. & Zeller, F.J. The genetics of resistance to powdery mildew in cultivated oats (Avena sativa L.): current status of major genes. J Appl Genetics 55, 155–162 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-014-0196-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-014-0196-y