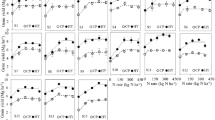
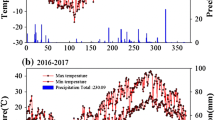
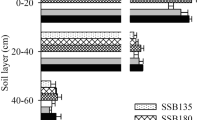
Abstract
During the first 35 years of the Green Revolution, Chinese grain production doubled, greatly reducing food shortage, but at a high environmental cost. In 2005, China alone accounted for around 38% of the global N fertilizer consumption, but the average on-farm N recovery efficiency for the intensive wheat–maize system was only 16–18%. Current on-farm N use efficiency (NUE) is much lower than in research trials or on-farm in other parts of the world, which is attributed to the overuse of chemical N fertilizer, ignorance of the contribution of N from the environment and the soil, poor synchrony between crop N demand and N supply, failure to bring crop yield potential into full play, and an inability to effectively inhibit N losses. Based on such analyses, some measures to drastically improve NUE in China are suggested, such as managing various N sources to limit the total applied N, spatially and temporally matching rhizospheric N supply with N demand in high-yielding crops, reducing N losses, and simultaneously achieving high-yield and high NUE. Maximizing crop yields using a minimum of N inputs requires an integrated, interdisciplinary cooperation and major scientific and practical breakthroughs involving plant nutrition, soil science, agronomy, and breeding.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayoub, M., A. Mackenzie, and D.L. Smith. 1995. Evaluation of N fertilizer rate, timing and wheat cultivars on soil residual nitrates. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science 175: 87–97.
Burns, I.G. 1980. Influence of the spatial distribution of nitrate on the uptake of N by plants: A review and a model for rooting depth. Journal of Soil Science 31: 155–173.
Cassman, K.G., A. Dobermann, and D.T. Walters. 2002. Agroecosystems, nitrogen use efficiency, and nitrogen management. Ambio 31: 132–140.
Chen, X.P. 2003. Optimization of the N fertilizer management of a winter wheat/summer maize rotation system in the North China Plain. PhD Thesis, University of Hohenheim, Stuttgart, Germany.
Chen, G.P., G.H. Yang, M. Zhao, and J.R. Zhao. 2008. Studies on maize small area super-high yield trails and cultivation technique. Journal of Maize Science 16: 1–4. (in Chinese).
Chen, X.P., F.S. Zhang, and V. Römheld. 2006. Synchronizing N supply from soil and fertilizer and N demand of winter wheat by an improved Nmin method. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 74: 91–98.
China Agricultural Yearbook. 1999. Editorial Committee of China Agricultural Yearbook, 587–605. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House. (in Chinese).
Cui, Z.L. 2005. Optimization of the nitrogen fertilizer management for a winter wheat–summer maize rotation system in the North China Plain—From field to regional scale. PhD Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China (in Chinese with English summary).
Cui, Z.L., X.P. Chen, F.S. Zhang, Y.X. Miao, and J.L. Li. 2008a. On-farm evaluation of the improved soil Nmin-based nitrogen management for summer wheat in North China Plain. Agronomy Journal 100: 517–525.
Cui, Z.L., Y.X. Miao, F.S. Zhang, and X.P. Chen. 2008b. Soil nitrate-N levels required for high yield maize production in the North China Plain. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 82: 187–196.
Cui, Z.L., F.S. Zhang, X.P. Chen, Miao, and J.L. Li. 2008c. On-farm evaluation of an in-season nitrogen management strategy based on soil Nmin test. Field Crops Research 105: 48–55.
Cui, Z.L., F.S. Zhang, Y.X. Miao, and X.P. Chen. 2008d. On-farm evaluation of winter wheat yield response to residual soil nitrate-N in North China Plain. Agronomy Journal 100: 1527–1534.
Davies, D.B., and R. Sylvester-Bradley. 1995. The contribution of fertilizer nitrogen to leachable nitrogen in the UK: A review. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 68: 399–406.
Dinnes, D.L., D.L. Karlen, D.B. Jaynes, T.C. Kaspar, J.L. Hatfield, T.S. Colvin, and C.A. Cambardella. 2002. Nitrogen management strategies to reduce nitrate leaching in tile-drained midwestern soils. Agronomy Journal 94: 153–171.
Dobermann, A. 2005. Nitrogen use efficiency state of the art. Paper of the IFA international workshop on enhanced efficiency fertilizers. Frankfurt, Germany.
Dobermann, A., and K.G. Cassman. 2005. Cereal area and nitrogen use efficiency are drivers of future nitrogen fertilizer consumption. Science in China Series C: Life Sciences 48: 745–758.
Drinkwater, L.E., and S.S. Snapp. 2007. Nutrients in agroecosystems: Rethinking the management paradigm. Advances in Agronomy 92: 163–186.
Fang, Q.X., Q. Yu, E.L. Wang, Y.H. Chen, G.L. Zhang, and J. Wang. 2006. Soil nitrate accumulation, leaching and crop nitrogen use as influenced by fertilization and irrigation in an intensive wheat–maize double cropping system in the North China Plain. Plant and Soil 284: 335–350.
FAOSTAT. 2002. FAO Statistical Databases. Agriculture Data. http://apps.fao.org/page/collections?subset=agriculture.
FAOSTAT. 2006. FAO Statistical Databases. Agriculture Data. http://apps.fao.org/page/collections?subset=agriculture.
Flowers, M., W. Randall, H. Ronnie, O. Deanna, and C. Carl. 2004. In-season optimization and site-specific nitrogen management for soft red winter wheat. Agronomy Journal 96: 124–134.
Galloway, J.N., and E.B. Cowling. 2002. Reactive nitrogen and the world: 200 years of change. Ambio 31: 64–71.
Hofman, G. 1999. Nutrient management legislation in European countries. NUMALEC Report. Concerted action, Fair6-CT98-4215.
Ju, X.T., C.L. Kou, F.S. Zhang, and P. Christie. 2006. Nitrogen balance and groundwater nitrate contamination: Comparison among three intensive cropping systems on the North China Plain. Environmental Pollution 143: 117–125.
Ju, X.T., X.J. Liu, F.S. Zhang, and M. Roelcke. 2004. Nitrogen fertilization, soil nitrate accumulation, and policy recommendations in several agricultural regions of China. Ambio 33: 300–305.
Ju, X.T., G.X. Xing, X.P. Chen, and X.B. Zhang. 2009. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 106: 3041–3046.
Ladha, J.K., H. Pathak, T.J. Krupnik, J. Six, and C. Kessel. 2005. Efficiency of fertilizer nitrogen in cereal production: Retrospects and prospects. Advances in Agronomy 87: 86–156.
Li, G.T., B.G. Li, and D.L. Chen. 2002a. Method for measurement of ammonia volatilization from large area field by Bowen Ratio System. Journal of China Agricultural University 6: 56–62. (in Chinese with English abstract.).
Li, G.T., B.G. Li, and D.L. Chen. 2002b. Ammonia volatilization from large field planted with winter wheat and summer maize. Acta Agriculture Boreall-sinica 17: 76–81. (in Chinese with English abstract.).
Li, J.M., S. Inanaga, Z.H. Li, and A.E. Eneji. 2005. Optimizing irrigation scheduling for winter wheat in the North China Plain. Agricultural Water Management 75: 8–23.
Liu, X.J., X.T. Ju, and Y. Zhang. 2006. Nitrogen deposition in agroecosystems in the Beijing area. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 113: 370–377.
Liu, H.B., Z.H. Li, and Y.G. Zhang. 2004. Characteristics of nitrate distribution and accumulation in soil profiles under main agro-land use types in Beijing. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 37: 692–698. (in Chinese with English abstract.).
Lopez-Bellido, L., R.J. Lopez-Bellido, and R. Redondo. 2005. Nitrogen efficiency in wheat under rainfed Mediterranean conditions as affected by split nitrogen application. Field Crops Research 94: 86–97.
Ma, W.Q. 1999. Current status and evaluation of crop fertilization in Shandong province. PhD Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China (in Chinese with English summary).
Ma, W.Q., D.R. Mao, and F.S. Zhang. 1999. Current status and evaluation of crop fertilization in Shandong province. Chinese Journal of Soil Science 30: 217–220. (in Chinese with English summary).
Novoa, R., and R.S. Loomis. 1981. Nitrogen and plant production. Plant and Soil 58: 177–204.
Pan, J.R. 2001. Fate of fertilizer nitrogen in winter wheat-summer maize rotation system at North China Plain. PhD Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China (in Chinese with English summary).
Peng, S., and G.S. Khush. 2003. Four decades of breeding for varietals improvement of irrigated lowland rice in the international rice research institute. Plant Production Science 6: 157–164.
Roth, G.W., and R.H. Fox. 1990. Soil nitrate accumulation following nitrogen fertilized corn in Pennsylvania. Journal of Environment Quality 9: 243–248.
Russelle, M.P., E.J. Deibert, R.D. Hauck, M. Stevanovic, and R.A. Olson. 1981. Effects of water and nitrogen management on yield and 15N-depleted fertilizer use efficiency of irrigated corn. Soil Science Society of America Journal 45: 553–558.
Sanchez, C.A., and A.M. Blackmer. 1988. Recovery of anhydrous ammonia derived nitrogen-15 during three years of corn production in Iowa. Agronomy Journal 80: 102–108.
Schleef, K.H., and W. Kleihanss. 1994. Mineral balance in agriculture in EU. Brounchweig, Germany: Institute of farm economics, Federal Agricultural Research Centre.
Shan, Y.S. 2001. Theory of high-yield wheat cultivation techniques. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese).
Shanahana, J.F., N.R. Kitchenb, and W.R. Raunc. 2007. Responsive in-season nitrogen management for cereals. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture Archive 61: 51–62.
Shearman, V.J., R. Sylvester-Bradley, R.K. Scott, and M.J. Foulkes. 2005. Physiological processes associated with wheat yield progress in the UK. Crop Science 45: 175–185.
Smil, V. 2001. Enriching the earth, 338. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press.
Sogbedji, J.M., H.M. Van Es, and C.L. Yang. 2000. Nitrate leaching and nitrogen budget as affected by maize nitrogen rate and soil type. Journal of Environment Quality 29: 1813–1820.
Su, F., X.Q. Ding, Z.L. Gao, B.X. Huang, X.P. Chen, F.S. Zhang, K. Martin, and V. Römheld. 2007. Ammonia volatilization from nitrogen fertilization of winter wheat-summer maize rotation system in the North China Plain. China Environmental Science 27: 409–413. (in Chinese with English abstract.).
Sun, H.Y., C.M. Liu, X.Y. Zhang, Y.J. Shen, and Y.Q. Zhang. 2006. Effects of irrigation on water balance, yield and WUE of winter wheat in the North China Plain. Agricultural Water Management 85: 211–218.
Tilman, D., K.G. Cassman, P.A. Matson, R. Naylor, and S. Polasky. 2002. Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 418: 671–678.
Tong, T.A., O. Emteryd, and S.L. Zhang. 2004. Evaluation of over-application of nitrogen fertilizer in China’s Shanxi province. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 37: 1239–1244. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, J.Q. 2007. Analysis and evaluation of yield increase of fertilization and nutrient utilization efficiency for major cereal crops in China. PhD Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China (in Chinese with English summary).
Wang, H., L. Zhang, W.R. Dawes, and C. Liu. 2001. Improving water use efficiency of irrigated crops in the North China Plain—Measurements and modeling. Agricultural Water Management 48: 151–167.
Welch, L.F., D.L. Mulvaney, M.G. Oldham, L.V. Boone, and J.W. Pendleton. 1971. Corn yields with fall, spring, and sidedress nitrogen. Agronomy Journal 63: 119–123.
Yuan, F.M., Z.M. Chen, Z.H. Yao, C.S. Zhou, G.M. Fu, Y.L. Song, and X.P. Li. 1995. Transformation, accumulation and leaching loss of nitrate-N in surface layer of an Fluvo-Aquic soil. Acta Pedologica Sinica 32: 388–399. (in Chinese with English abstract.).
Zhang, S.L., G.X. Cai, X.Z. Wang, Y.H. Xu, Z.L. Zhu, and J.R. Freney. 1992. Loss of urea-nitrogen applied to maize grown on a calcareous fluvo-aquic soil in North China Plain. Pedosphere 2: 171–178.
Zhang, Y.M., C.S. Hu, and X.X. Dong. 2005. Ammonia volatilization from wheat-maize rotation field in the piedmont of Taihang. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science 11: 417–419. (in Chinese with English abstract.).
Zhang, F.S., X.R. Wang, X.T. Ju, W.Q. Ma, Q.J. Wang, and C.L. Kou. 2002. Spatial and temporal variation of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, and fertilization recommendation. In Integrated nutrient management, ed. F.S. Zhang, and R.F. Jiang, 79–87. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press. (in Chinese).
Zhang, F.S., J.Q. Wang, W.F. Zhang, Z.L. Cui, W.Q. Ma, X.P. Chen, and R.F. Jiang. 2008. Nutrient use efficiencies of major cereal crops in china and measures for improvement. Acta Pedologica Sinica 45: 915–924. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao, J.R. 1997. The investigation and analysis of N application and yield in Beijing suburb. Beijing Agricultural Science 15: 36–38. (in Chinese).
Zhao, R.F. 2006. The sustainability evaluation of the optimized management of water and nitrogen resources for winter wheat-summer maize rotation system. PhD Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China (in Chinese with English summary).
Zhao, R.F., X.P. Chen, and F.S. Zhang. 2006. Fertilization and nitrogen balance in a wheat–maize rotation system in North China. Agronomy Journal 98: 938–945.
Zhu, Z.L. 1998. The present situation of nitrogen fertilizer use, and the problems and strategies in China. In Fertilizer problems in sustainable development of agriculture in China, ed. Q.K. Li, Z.L. Zhu, and T.R. Yu, 38–51. Nanchang: Jiangxi Science and Technology Publishers. (in Chinese).
Zhu, Z.L., and D.L. Chen. 2002. Nitrogen fertilizer use in China–Contributions to food production, impacts on the environment and best management strategies. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 63: 117–127.
Zhu, Z.L., and Q.X. Wen. 1992. Soil nitrogen in Chinese. Nanjing: Jiangsu Science and technique publisher. (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Z., Chen, X. & Zhang, F. Current Nitrogen Management Status and Measures to Improve the Intensive Wheat–Maize System in China. AMBIO 39, 376–384 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-010-0076-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-010-0076-6