Abstract
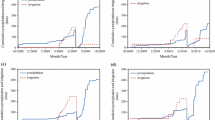
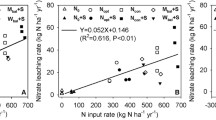
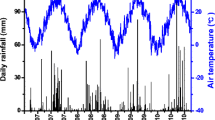
There is a growing concern about excessive nitrogen (N) and water use in agricultural systems in North China due to the reduced resource use efficiency and increased groundwater pollution. A two-year experiment with two soil moisture by four N treatments was conducted to investigate the effects of N application rates and soil moisture on soil N dynamics, crop yield, N uptake and use efficiency in an intensive wheat–maize double cropping system (wheat–maize rotation) in the North China Plain. Under the experimental conditions, crop yield of both wheat and maize did␣not␣increase significantly at N rates above 200 kg N ha−1. Nitrogen application rates affected little on ammonium-N (NH4-N) content in the 0–100 cm soil profiles. Excess nitrate-N (NO3-N), ranging from 221 kg N ha−1 to 620 kg N ha−1, accumulated in the 0–100 cm soil profile at the end of second rotation in the treatments with N rates of 200 kg N ha−1 and 300 kg N ha−1. In general, maize crop has higher N use efficiency than wheat crop. Higher NO3-N leaching occurred in maize season than in wheat season due to more water leakage caused by the concentrated summer rainfall. The results of this study indicate that the optimum N rate may be much lower than that used in many areas in the North China Plain given the high level of N already in the soil, and there is great potential for reducing N inputs to increase N use efficiency and to mitigate N leaching into the groundwater. Avoiding excess water leakage through controlled irrigation and matching N application to crop N demand is the key to reduce NO3-N leaching and maintain crop yield. Such management requires knowledge of crop water and N demand and soil N dynamics as they change with variable climate temporally and spatially. Simulation modeling can capture those interactions and is considered as a powerful tool to assist in␣the␣future optimization of N and irrigation managements.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BM:
-
Above ground biomass
- GY:
-
Grain yield
- IEN:
-
Internal N use efficiency
- P E :
-
Physiological efficiency
- PFP:
-
Partial factor productivity of applied N
- R F :
-
Apparent recovery fraction
References
InstitutionalAuthorNameAnonymous (2001) China agricultural yearbook Agricultural Publishing House Beijing
JM Bremner (1996) Nitrogen-total DL Sparks AL Page CT Johnston ME Summ (Eds) Methods of soil analysis part 3. Chemical methods SSSA Book Ser. No. 5. SSSA Madison 1058–1121
KG Cassman A Dobermann DT Walters (2002) ArticleTitleAgroecosystems, nitrogen-use efficiency, and nitrogen management Ambio 31 IssueID2 132–140 Occurrence Handle12078002
RF Follett JA Delgado (2002) ArticleTitleNitrogen fate and transport in agricultural systems J Soil Water Conserv 57 402–408
XT Ju XJ Liu FS Zhang M Roelcke (2004) ArticleTitleNitrogen fertilization, soil nitrate accumulation, and policy recommendations in several agricultural regions of China Ambio 33 278–283
XT Ju XJ Liu GY Zou ZH Wang FS Zhang (2002) ArticleTitleEvaluation of nitrogen loss way in winter wheat and summer maize rotation system Scientia Agric Sinica 35 1493–1499 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXltVehu7o%3D
Liu XH, Mu ZG (eds) (1993) Cropping systems in Huanghuaihai region. In: Cropping systems in China. Agricultural Press of China, Beijing, pp 388–407
XJ Liu XT Ju FS Zhang (2001) ArticleTitleEffect of urea application as basal fertilizer on inorganic nitrogen in soil profile J China Agric Univ 7 63–68
XJ Liu XT Ju FS Zhang JR Pan P Christie (2003) ArticleTitleNitrogen dynamics and budgets in a winter wheat–maize cropping system in the North China Plain Field Crops Res 83 111–124 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-4290(03)00068-6
HB Madsen CR Jensen T Boysen (1986) ArticleTitleA comparison of the thermocouple psychrometer and the pressure plate methods for determination of soil water characteristic curves J Soil Sci 37 357–362
DK Markus JP McKinnon AF Buccafuri (1985) ArticleTitleAutomated analysis of nitrite, nitrate and ammonium nitrogen in soils Soil Sci Soc Am J 49 1208–1215 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXlvFGnsr0%3D Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1985.03615995004900050028x
DT Parker WEE Larson (1962) ArticleTitleNitrification as affected by temperature and moisture content of mulched soil Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 26 238–242 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF3sXkvVGmsbs%3D Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1962.03615995002600030015x
S Peng FV Garcia RC Laza AL Sanico RM Visperas KG Cassman (1996) ArticleTitleIncreased N-use efficiency using a chlorophyll meter on high yielding irrigated rice Field Crops Res 47 243–252 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0378-4290(96)00018-4
M Roelcke Y Han ZC Cai J Richter (2002) ArticleTitleNitrogen mineralization in paddy soils of the Chinese Taihu Region under aerobic conditions Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 63 255–266 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XovVCmurk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1021115218531
M Roelcke Y Han KH Schleef JG Zhu G Liu ZC Cai J Richter (2004) ArticleTitleRecent trends and recommendations for nitrogen fertilization in intensive agriculture in eastern China Pedosphere 14 449–460
InstitutionalAuthorNameSAS Institute (1996) SAS user’s guide SAS Institute Cary, NC
GX Xing ZL Zhu (2000) ArticleTitleAn assessment of N loss from agricultural fields to the environment in China Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 57 67–73 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1009717603427
JC Yeomans JM Bremner (1988) ArticleTitleA rapid and precise method for routine determination of organic carbon in soil Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 19 1467–1476 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXlt1Oru7w%3D Occurrence Handle10.1080/00103628809368027
SL Zhang GX Cai XZ Wang YH Xu ZL Zhu JR Freney (1992) ArticleTitleLosses of urea–nitrogen applied to maize grown on a calcareous fluvo-aquic soil of North China Plain Pedosphere 2 171–178 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXksVyntLo%3D
WL Zhang ZX Tian N Zhang XQ Li (1996) ArticleTitleNitrate pollution of groundwater in northern China Agric Ecosyst Environ 59 223–231 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XntFCnsLo%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0167-8809(96)01052-3
XH Zhao JR Guo DM Wei CW Wang Y Liu K Lin (1997) ArticleTitleInvestigation and analysis on current status of chemical fertilizer inputs and crop yields in agricultural field of Beijing Suburb J Beijing Agric Sci 15 36–38
ZL Zhu (1998) Soil nitrogen fertility and its management in China SM Shen (Eds) Soil fertility in China China Agriculture Publisher Beijing 160–211
ZL Zhu DL Chen (2002) ArticleTitleNitrogen fertilizer use in China – contributions to food production, impacts on the environment and best management strategies Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 63 117–127 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XovVCmtbg%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1021107026067
Zhu ZL, Wen QX (eds) (1992) Nitrogen in soil of China. Jiangsu Science and Technology Publishing House, Jiangsu, pp 213–228
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Section Editor: L. Wade
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Q., Yu, Q., Wang, E. et al. Soil nitrate accumulation, leaching and crop nitrogen use as influenced by fertilization and irrigation in an intensive wheat–maize double cropping system in the North China Plain. Plant Soil 284, 335–350 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-0055-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-0055-7