Abstract
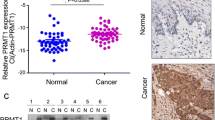
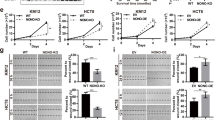
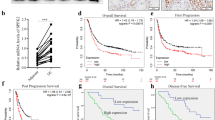
Protein arginine methylation, which is mediated by the protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs), is associated with numerous fundamental cellular processes. Our previous studies have shown that PRMT1 activated Hedgehog signaling in the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells and promoted the growth and migration of cancer cells. However, the detailed mechanisms are unknown. In this study, it was found that PRMT1 interacted with the transcriptional factor Gli1 (glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1) in ESCC cells. The DNA-binding domain (DBD) of Gli1 is responsible for its interaction with PRMT1. Moreover, PRMT1 promoted the methylation of Gli1, and knocking down the expression of PRMT1 impaired the transcriptional activity as well as the biological functions of Gli1. Taken together, our study demonstrated that PRMT1 is a positive regulator of Hedgehog signaling, and PRMT1 might be a therapeutic target for ESCC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rubin LL, de Sauvage FJ. Targeting the Hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5(12):1026–33.
Guha M. Hedgehog inhibitor gets landmark skin cancer approval, but questions remain for wider potential. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11(4):257–8.
Minton K. Cell signalling: putting the brakes on sonic hedgehog. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(3):129.
Eaton S. Multiple roles for lipids in the Hedgehog signalling pathway. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(6):437–45.
Briscoe J, Therond PP, The mechanisms of Hedgehog signalling and its roles in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(7):416–29.
Zhu W et al. Correlation of hedgehog signal activation with chemoradiotherapy sensitivity and survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2011;41(3):386–93.
Mizuarai S, Kawagishi A, Kotani H. Inhibition of p70S6K2 down-regulates Hedgehog/GLI pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Mol Cancer. 2009;8:44.
Min S et al. The glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 promotes epithelial—mesenchymal transition in human esophageal squamous cell cancer by inhibiting E-cadherin via Snail. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013;20(7):379–85.
Isohata N et al. Hedgehog and epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling in normal and malignant epithelial cells of the esophagus. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(5):1212–21.
Yang Y, Bedford MT. Protein arginine methyltransferases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(1):37–50.
Cha B et al. Methylation by protein arginine methyltransferase 1 increases stability of Axin, a negative regulator of Wnt signaling. Oncogene. 2011;30(20):2379–89.
Joost S et al. GLI1 inhibition promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2012;72(1):88–99.
Kuphal S et al. GLI1-dependent transcriptional repression of CYLD in basal cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2011;30(44):4523–30.
Paul P et al. Gli1 transcriptional activity is negatively regulated by AKT2 in neuroblastoma. Oncotarget. 2013;4(8):1149–57.
Singh RR et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway is activated in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2009;69(6):2550–8.
Lee J et al. Gli1 is a target of Sonic hedgehog that induces ventral neural tube development. Development. 1997;124(13):2537–52.
Dery U et al. A glycine-arginine domain in control of the human MRE11 DNA repair protein. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28(9):3058–69.
Boisvert FM et al. The GAR motif of 53BP1 is arginine methylated by PRMT1 and is necessary for 53BP1 DNA binding activity. Cell Cycle. 2005;4(12):1834–41.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Weizheng Zhou and Wenxing Qin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, W., Qin, W., Qiao, F. et al. Protein arginine methyltransferase 1 interacts with Gli1 and regulates its transcriptional activity. Tumor Biol. 37, 9071–9076 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4754-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4754-7