Abstract
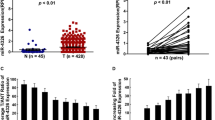
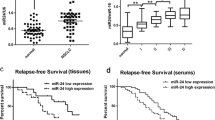
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide; the study of microRNAs gives new hope for lung cancer treatment. miR-411 has been demonstrated to be an independent prognostic factor for lung adenocarcinoma, but the role and regulatory mechanism are largely unknown. In the present study, we found miR-411 was overexpressed in the lung cancer cells; overexpression of miR-411 promoted anchorage-dependent and anchorage-independent growths of lung cancer, while miR-411 knockdown reduced this effect. Further study showed forkhead box O1 (FOXO1) was a target of miR-411. Overexpression of miR-411 suppressed the expression of FOXO1; the effect of suppression was abrogated when the mutation occurred in the 3′UTR of FOXO1. Knockdown of FOXO1 in cells which miR-411 was inhibited recapitulated the phenotype of miR-411 overexpression. Taken together, our study revealed miR-411 promoted cell proliferation of lung cancer by targeting tumor suppressor gene FOXO1 and miR-411 might be a potential target for lung cancer therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2013;63(1):11–30. doi:10.3322/caac.21166.
McDoniels-Silvers AL, Nimri CF, Stoner GD, Lubet RA, You M. Differential gene expression in human lung adenocarcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2002;8(4):1127–38.
Jacks DATT. Modeling human lung cancer in mice: similarities and shortcomings. Oncogene. 1999;18:5318–24.
Ji H, Li D, Chen L, Shimamura T, Kobayashi S, McNamara K, et al. The impact of human EGFR kinase domain mutations on lung tumorigenesis and in vivo sensitivity to EGFR-targeted therapies. Cancer Cell. 2006;9(6):485–95. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.04.022.
Mahoney CL, Choudhury B, Davies H, Edkins S, Greenman C, Haaften G, et al. LKB1/KRAS mutant lung cancers constitute a genetic subset of NSCLC with increased sensitivity to MAPK and mTOR signalling inhibition. Br J Cancer. 2009;100(2):370–5. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604886.
To MD, Wong CE, Karnezis AN, Del Rosario R, Di Lauro R, Balmain A. Kras regulatory elements and exon 4A determine mutation specificity in lung cancer. Nat Genet. 2008;40(10):1240–4. doi:10.1038/ng.211.
Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448(7153):561–6. doi:10.1038/nature05945.
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304(5676):1497–500. doi:10.1126/science.1099314.
Arriagada R, Bergman B, Dunant A, Le Chevalier T, Pignon JP, Vansteenkiste J. Cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(4):351–60. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa031644.
Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(2):121–8. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70364-X.
Shaw AT, Yeap BY, Solomon BJ, Riely GJ, Gainor J, Engelman JA, et al. Effect of crizotinib on overall survival in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring ALK gene rearrangement: a retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(11):1004–12. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70232-7.
Lam EWF, Brosens JJ, Gomes AR, Koo CY. Forkhead box proteins: tuning forks for transcriptional harmony. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(7):482–95. doi:10.1038/Nrc3539.
Zhang X, Yalcin S, Lee DF, Yeh TYJ, Lee SM, Su J, et al. FOXO1 is an essential regulator of pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(9):1092–U1118. doi:10.1038/Ncb2293.
Huang H, Regan KM, Wang F, Wang D, Smith DI, van Deursen JM, et al. Skp2 inhibits FOXO1 in tumor suppression through ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(5):1649–54. doi:10.1073/pnas.0406789102.
Yamagata K, Daitoku H, Takahashi Y, Namiki K, Hisatake K, Kako K, et al. Arginine methylation of FOXO transcription factors inhibits their phosphorylation by Akt. Mol Cell. 2008;32(2):221–31. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.09.013.
Wu L, Li H, Jia CY, Cheng W, Yu M, Peng M, et al. MicroRNA-223 regulates FOXO1 expression and cell proliferation. FEBS Lett. 2012;586(7):1038–43. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2012.02.050.
Wu Z, Sun H, Zeng W, He J, Mao X. Upregulation of MircoRNA-370 induces proliferation in human prostate cancer cells by downregulating the transcription factor FOXO1. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(9), e45825. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0045825.
Zhang L, Quan H, Wang S, Li X, Che X. MiR-183 promotes growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells through FoxO1 inhibition. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med. 2015. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3550-8.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136(2):215–33. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002.
Ke J, Zhao Z, Hong SH, Bai S, He Z, Malik F, et al. Role of microRNA221 in regulating normal mammary epithelial hierarchy and breast cancer stem-like cells. Oncotarget. 2015;6(6):3709–21.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell. 2006;9(3):189–98. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.01.025.
Nadal E, Zhong J, Lin J, Reddy RM, Ramnath N, Orringer MB, et al. A microRNA cluster at 14q32 drives aggressive lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2014;20(12):3107–17. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3348.
Harafuji N, Schneiderat P, Walter M, Chen YW. miR-411 is up-regulated in FSHD myoblasts and suppresses myogenic factors. Orapant Journal of Rare Diseases. 2013;8:55.
van Schooneveld E, Wouters MC, Van der Auwera I, Peeters DJ, Wildiers H, Van Dam PA, et al. Expression profiling of cancerous and normal breast tissues identifies microRNAs that are differentially expressed in serum from patients with (metastatic) breast cancer and healthy volunteers. Breast Cancer Res :BCR. 2012;14(1):R34. doi:10.1186/bcr3127.
Gao Y, Xiao Q, Ma H, Li L, Liu J, Feng Y, et al. LKB1 inhibits lung cancer progression through lysyl oxidase and extracellular matrix remodeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(44):18892–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.1004952107.
Shen G, Jia H, Tai Q, Li Y, Chen D. miR-106b downregulates adenomatous polyposis coli and promotes cell proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34(1):211–9. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgs320.
Malumbres M, Barbacid M. Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(3):153–66. doi:10.1038/nrc2602.
van der Horst A, Burgering BMT. Stressing the role of FoxO proteins in lifespan and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(6):440–50. doi:10.1038/Nrm2190.
Zhang X, Tang N, Hadden TJ, Rishi AK. Akt, FoxO and regulation of apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813(11):1978–86. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.03.010.
Massagué J. G1 cell-cycle control and cancer. Nature. 2004;432:9.
Nakamura N, Ramaswamy S, Vazquez F, Signoretti S, Loda M, Sellers WR. Forkhead transcription factors are critical effectors of cell death and cell cycle arrest downstream of PTEN. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20(23):8969–82.
Seoane J, Le HV, Shen L, Anderson SA, Massague J. Integration of Smad and forkhead pathways in the control of neuroepithelial and glioblastoma cell proliferation. Cell. 2004;117(2):211–23.
Abukhdeir AM, Park BH. P21 and p27: roles in carcinogenesis and drug resistance. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008;10, e19. doi:10.1017/S1462399408000744.
Ramaswamy S, Nakamura N, Sansal I, Bergeron L, Sellers WR. A novel mechanism of gene regulation and tumor suppression by the transcription factor FKHR. Cancer Cell. 2002;2(1):81–91.
Zhang WC, Liu J, Xu X, Wang G. The role of microRNAs in lung cancer progression. Med Oncol. 2013;30(3):675. doi:10.1007/s12032-013-0675-8.
Gao Y, Gao F, Ma JL, Sun WZ, Song LP. The potential clinical applications and prospects of microRNAs in lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2014;7:901–6. doi:10.2147/OTT.S62227.
Marshall AD, Lagutina I, Grosveld GC. PAX3-FOXO1 induces cannabinoid receptor 1 to enhance cell invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011;71(24):7471–80. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0924.
Ailles LE, Weissman IL. Cancer stem cells in solid tumors. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2007;18(5):460–6. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2007.10.007.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Science and technology project of Guangdong Province grant (No.2014A020212640, LM Qin).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Figure 1
miR-411 regulates cell proliferation of BEAS-2B. (A). MTT assay determined the effect on the proliferation after miR-411 was downregulated in BEAS-2B. (B). Colony formation assay determined the effect on the proliferation after miR-411 was downregulated in BEAS-2B. (C). Real-time quantitative PCR analysis determined the expression of cell cycle regulator, p21, p27 and Cyclin D1 transfected miR-411 inhibitor. *p < 0.05, Error bars represent mean ± STDEV . (GIF 4.67 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Z., Qin, L. & Li, S. miR-411 contributes the cell proliferation of lung cancer by targeting FOXO1. Tumor Biol. 37, 5551–5560 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4425-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4425-8