Abstract
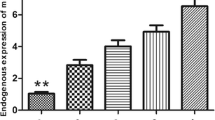
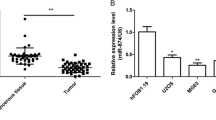
Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common primary malignant bone tumor with high morbidity in young adults and adolescents. Increasing evidence has demonstrated that aberrant microRNA (miRNA) expression is involved in OS occurrence and development. miR-150 has been recently widely studied in many cancers, but not including OS. This study is aimed to investigate the expression and biological role of miR-150 in OS. Here, we found that miR-150 expression was consistently downregulated in OS tissues and cell lines compared with the matched adjacent normal tissues and human normal osteoblast cells (NHOst), and its expression was significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis and tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage. Functional study showed that restoration of miR-150 expression in OS cells could inhibit cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and induced apoptosis in vitro as well as suppressed tumor growth of OS in vivo. Mechanistically, IGF2 mRNA-binding protein 1(IGF2BP1) was confirmed to act as a direct target of miR-150, and the IGF2BP1 mRNA expression was inversely correlated with the level of miR-150 in OS tissues. In addition, downregulation of endogenous IGF2BP1 exhibited similar effects of overexpression of miR-150. Taken together, these findings suggest that miR-150 functions as a tumor suppressor in OS partially by targeting IGF2BP1.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
21 December 2021
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.3233/TUB-219010"
References
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ, Savage SA. Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: data from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program. Cancer. 2009;115:1531–43.
Marina N, Gebhardt M, Teot L, Gorlick R. Biology and therapeutic advances for pediatric osteosarcoma. Oncologist. 2004;9:422–41.
Lamoureux F, Trichet V, Chipoy C, Blanchard F, Gouin F, Redini F. Recent advances in the management of osteosarcoma and forthcoming therapeutic strategies. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2007;7:169–81.
Carrington JC, Ambros V. Role of micrornas in plant and animal development. Science. 2003;301:336–8.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Brodersen P, Voinnet O. Revisiting the principles of microRNA target recognition and mode of action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:141–8.
Garzon R, Marcucci G, Croce CM. Targeting microRNAs in cancer: rationale, strategies and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:775–89.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259–69.
Osada H, Takahashi T. MicroRNAs in biological processes and carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28:2–12.
Namlos HM, Meza-Zepeda LA, Baroy T, Ostensen IH, Kresse SH, Kuijjer ML, et al. Modulation of the osteosarcoma expression phenotype by microRNAs. PLoS One. 2012;7:e48086.
Tian K, Di R, Wang L. MicroRNA-23a enhances migration and invasion through PTEN in osteosarcoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2015;22:351–9.
Liu W, Zhao ZY, Shi L, Yuan WD. Tissue microRNA-126 expression level predicts outcome in human osteosarcoma. Diagn Pathol. 2015;10:116.
Cao M, Hou D, Liang H, Gong F, Wang Y, Yan X, et al. miR-150 promotes the proliferation and migration of lung cancer cells by targeting SRC kinase signalling inhibitor 1. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:1013–24.
Huang S, Chen Y, Wu W, Ouyang N, Chen J, Li H, et al. miR-150 promotes human breast cancer growth and malignant behavior by targeting the pro-apoptotic purinergic P2X7 receptor. PLoS One. 2013;8:e80707.
Li T, Xie J, Shen C, Cheng D, Shi Y, Wu Z, et al. miR-150-5p inhibits hepatoma cell migration and invasion by targeting MMP14. PLoS One. 2014;9:e115577.
Lei Y, Hu X, Li B, Peng M, Tong S, Zu X, et al. miR-150 modulates cisplatin chemosensitivity and invasiveness of muscle-invasive bladder cancer cells via targeting PDCD4 in vitro. Med Sci Monit. 2014;20:1850–7.
Dezhong L, Xiaoyi Z, Xianlian L, Hongyan Z, Guohua Z, Bo S, et al. miR-150 is a factor of survival in prostate cancer patients. J BUON. 2015;20:173–9.
Ma Y, Zhang P, Wang F, Zhang H, Yang J, Peng J, et al. miR-150 as a potential biomarker associated with prognosis and therapeutic outcome in colorectal cancer. Gut. 2012;61:1447–53.
Stoskus M, Gineikiene E, Valceckiene V, Valatkaite B, Pileckyte R, Griskevicius L. Identification of characteristic IGF2BP expression patterns in distinct B-ALL entities. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2011;46:321–6.
Varshney J, Subramanian S. MicroRNAs as potential target in human bone and soft tissue sarcoma therapeutics. Front Mol Biosci. 2015;2:31.
Zhang J, Yan YG, Wang C, Zhang SJ, Yu XH, Wang WJ. MicroRNAs in osteosarcoma. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;444:9–17.
Ziyan W, Shuhua Y, Xiufang W, Xiaoyun L. MicroRNA-21 is involved in osteosarcoma cell invasion and migration. Med Oncol. 2011;28:1469–74.
Zhao G, Cai C, Yang T, Qiu X, Liao B, Li W, et al. MicroRNA-221 induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance through PI3K/Akt pathway in human osteosarcoma. PLoS One. 2013;8:e53906.
Zeng H, Zhang Z, Dai X, Chen Y, Ye J, Jin Z: Increased expression of microrna-199b-5p associates with poor prognosis through promoting cell proliferation, invasion and migration abilities of human osteosarcoma. Pathol Oncol Res 2015
Chong Y, Zhang J, Guo X, Li G, Zhang S, Li C, et al. MicroRNA-503 acts as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma by targeting L1CAM. PLoS One. 2014;9:e114585.
Wei R, Deng Z, Su J. miR-217 targeting Wnt5a in osteosarcoma functions as a potential tumor suppressor. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015;72:158–64.
Shi ZC, Chu XR, Wu YG, Wu JH, Lu CW, Lu RX, Ding MC, Mao NF: Microrna-375 functions as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma by targeting pik3ca. Tumour Biol 2015
Li X, Chen L, Wang W, Meng FB, Zhao RT, Chen Y. MicroRNA-150 inhibits cell invasion and migration and is downregulated in human osteosarcoma. Cytogenetic Genome Res. 2015;146:124–35.
Wang F, Ren X, Zhang X. Role of microRNA-150 in solid tumors. Oncol Lett. 2015;10:11–6.
Nielsen J, Christiansen J, Lykke-Andersen J, Johnsen AH, Wewer UM, Nielsen FC. A family of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding proteins represses translation in late development. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:1262–70.
Vainer G, Vainer-Mosse E, Pikarsky A, Shenoy SM, Oberman F, Yeffet A, et al. A role for VICKZ proteins in the progression of colorectal carcinomas: regulating lamellipodia formation. J Pathol. 2008;215:445–56.
Kobel M, Weidensdorfer D, Reinke C, Lederer M, Schmitt WD, Zeng K, et al. Expression of the RNA-binding protein IMP1 correlates with poor prognosis in ovarian carcinoma. Oncogene. 2007;26:7584–9.
Elcheva I, Tarapore RS, Bhatia N, Spiegelman VS. Overexpression of mRNA-binding protein CRD-BP in malignant melanomas. Oncogene. 2008;27:5069–74.
Ohdaira H, Sekiguchi M, Miyata K, Yoshida K. MicroRNA-494 suppresses cell proliferation and induces senescence in A549 lung cancer cells. Cell Prolif. 2012;45:32–8.
Zhou X, Zhang CZ, Lu SX, Chen GG, Li LZ, Liu LL, et al. miR-625 suppresses tumour migration and invasion by targeting IGF2BP1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2015;34:965–77.
Rebucci M, Sermeus A, Leonard E, Delaive E, Dieu M, Fransolet M, et al. miRNA-196b inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells by targeting IGF2BP1. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:79.
Wang RJ, Li JW, Bao BH, Wu HC, Du ZH, Su JL, et al. MicroRNA-873 (miRNA-873) inhibits glioblastoma tumorigenesis and metastasis by suppressing the expression of IGF2BP1. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:8938–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.3233/TUB-219010"
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Y., Pan, S., Kang, M. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: MicroRNA-150 functions as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma by targeting IGF2BP1. Tumor Biol. 37, 5275–5284 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4389-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4389-8