Abstract
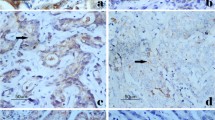
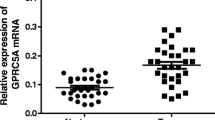
This study investigated the correlation between the expression of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) and the prognosis of gastric carcinoma patients. A total of 156 paired tumor and matched normal samples were collected from patients of gastric carcinoma who underwent surgical resection. The expression of PDK1 was analyzed by real-time quantitative PCR and immunohistochemistry method. Potential correlation between PDK1 protein expression and the clinicopathological characteristics was determined by chi-square test and Spearman correlation analysis. The influence of PDK1 expression on 5-year survival rate and survival length was determined by Kaplan–Meier analysis. The expression of PDK1 mRNA and protein were significantly higher in tumor samples comparing to those in adjacent normal samples (paired t test, P = 0.007). Immunohistochemical staining results indicated that PDK1 protein level was positively correlated with infiltration (P = 0.006). However, no associations with age, sex, clinical stage, lymph node metastasis, and distant metastasis were observed (P > 0.05). The 5-year survival rate was 20.1 and 63.4 % of the patients with high and low expression level of PDK1, respectively (P < 0.05). The median survival length was 32.5 months (95 % CI 22.8–37.6) for patients with high level of PDK1 and 63.1 months (95 % CI 52.3–64.7) for patients with low level of PDK1 (×2 = 20.153, P < 0.05). Kaplan–Meier survival curves demonstrated that elevated expression of PDK1 was an independent negative prognostic factor of gastric carcinoma (P<0.05). Our study indicated that PDK1 might serve as a candidate pro-oncogene and a potential prognostic biomarker for gastric carcinoma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Arsenic R. Immunohistochemical analysis of PDK1 expression in breast cancer. Diagn Pathol. 2014;9:82.
Lu CW, Lin SC, Chien CW, Lee CT, Lin BW, et al. Overexpression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 3 increases drug resistance and early recurrence in colon cancer. Am J Pathol. 2011;179:1405–14.
Galgano MT, Conaway M, Spencer AM, Paschal BM, Frierson Jr HF. PRK1 distribution in normal tissues and carcinomas: overexpression and activation in ovarian serous carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2009;40:1434–40.
Bayascas JR. PDK1: the major transducer of PI 3-kinase actions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;346:9–29.
Williams MR, Arthur JS, Balendran A, van der Kaay J, Poli V, Cohen P, et al. The role of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 in activating AGC kinases defined in embryonic stem cells. Curr Biol. 2000;10(8):439–48.
Cantley LC. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science. 2002;296(5573):1655–7.
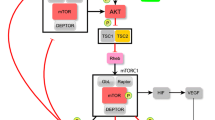
Willems L, Tamburini J, Chapuis N, Lacombe C, Mayeux P, Bouscary D. PI3K and mTOR signaling pathways in cancer: new data on targeted therapies. Curr Oncol Rep. 2012;14(2):129–38.
Nam SY, Lee HS, Jung G-A, Choi J, Cho SJ, Kim MK, et al. Akt/PKB activation in gastric carcinomas correlates with clinicopathologic variables and prognosis. APMIS. 2003;111(12):1105–13.
Manning BD, Cantley LC. AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell. 2007;129(7):1261–74.
Zetter BR. Angiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Annu Rev Med. 1998;49:407–24.
Zhou XD, Chen HX, Guan RN, Lei YP, Shu X, Zhu Y, et al. Protein kinase B phosphorylation correlates with vascular endothelial growth factor A and microvessel density in gastric adenocarcinoma. J Int Med Res. 2012;40(6):2124–34.
Sheng S, Qiao M, Pardee AB. Metastasis and AKT activation. JCell Physiol. 2009;218(3):451–4.
Cinti C, Vindigni C, Zamparelli A, La Sala D, Epistolato MC, Marrelli D, et al. Activated Akt as an indicator of prognosis in gastric cancer. Virchows Arch. 2008;453(5):449–55.
Isakoff SJ, Engelman JA, Irie HY, Luo J, Brachmann SM, Pearline RV, et al. Breast cancer-associated PIK3CA mutations are oncogenic in mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65(23):10992–1000.
Zhou BP, Hu MC, Miller SA, Yu Z, Xia W, Lin SY, et al. HER-2/neu blocks tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis via the Akt/NF-kappaB pathway. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(11):8027–31.
Maurer M, Su T, Saal LH, Koujak S, Hopkins BD, Barkley CR, et al. PDK1 potentiates upstream lesions on the PI3K pathway in breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2009;69(15):6299–306.
Tan J, Li Z, Lee PL, Guan P, Aau MY, Lee ST, et al. PDK1 signaling toward PLK1-MYC activation confers oncogenic transformation, tumor-initiating cell activation, and resistance to mTOR-targeted therapy. Cancer Discov. 2013;3(10):1156–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, X., Li, P., Xie, Y. et al. Overexpression of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 is associated with prognosis of gastric carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37, 2333–2339 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4024-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4024-8