Abstract
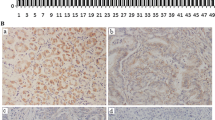
Novel (nua) kinase family 1 (NUAK1) is a member of the human adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinases family, which is overexpressed in multiple human malignancies and thought to be involved in tumor invasion and metastasis ability. Our study is to investigate the association of NUAK1 expression with clinicopathological parameters and prognostic significance of patients with gastric cancer. The expression patterns of the NUAK1 protein in 117 primary archival gastric cancer specimens and 46 adjacent normal epithelial tissues from patients were detected by immunohistochemistry assay. Staining evaluation results were analyzed statistically in relation to various clinicopathological characters, recurrence-free survival and overall survival. High level of NUAK1 expression was detected in gastric cancer, significantly more than in adjacent normal epithelial cells. In gastric cancer, NUAK1 was positively correlated with depth of invasion, lymph node metastasis, pathological stage, surgical resection and histological differentiation. However, no correlations between NUAK1 expression and patients’ age, sex, tumor size, location, CA19-9 or CEA were detected. The recurrence-free survival and overall survival were significantly shorter for patients with NUAK1 higher scores than those with NUAK1 lower scores. Multivariate analysis identified NUAK1 was an independent prognostic factor for both recurrence-free survival and overall survival. Our findings provided convincing evidence for NUAK1 overexpression, which was tightly associated with more aggressive tumor behavior and a poor prognosis, indicating that NUAK1 is a valuable molecular biomarker for gastric cancer progression. It might also act as a promising target for both prognostic prediction and therapeutics.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Parkin DM, Steliarova-Foucher E. Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46(4):765–81. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2009.12.014.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107.
Bernal C, Aguayo F, Villarroel C, Vargas M, Diaz I, Ossandon FJ, et al. Reprimo as a potential biomarker for early detection in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(19):6264–9. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4522.
Marrelli D, Roviello F, De Stefano A, Farnetani M, Garosi L, Messano A, et al. Prognostic significance of CEA, CA 19-9 and CA 72-4 preoperative serum levels in gastric carcinoma. Oncology. 1999;57(1):55–62.
Suzuki A, Kusakai G, Kishimoto A, Shimojo Y, Miyamoto S, Ogura T, et al. Regulation of caspase-6 and FLIP by the AMPK family member ARK5. Oncogene. 2004;23(42):7067–75. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207963.
Kusakai G, Suzuki A, Ogura T, Miyamoto S, Ochiai A, Kaminishi M, et al. ARK5 expression in colorectal cancer and its implications for tumor progression. Am J Pathol. 2004;164(3):987–95.
Chen P, Li K, Liang Y, Li L, Zhu X. High NUAK1 expression correlates with poor prognosis and involved in NSCLC cells migration and invasion. Exp Lung Res. 2013;39(1):9–17. doi:10.3109/01902148.2012.744115.
Lu S, Niu N, Guo H, Tang J, Guo W, Liu Z, et al. ARK5 promotes glioma cell invasion, and its elevated expression is correlated with poor clinical outcome. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(3):752–63. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2012.09.018.
Kinoshita R, Iwadate M, Umeyama H, Taguchi YH. Genes associated with genotype-specific DNA methylation in squamous cell carcinoma as candidate drug targets. BMC Syst Biol. 2014;8(Suppl 1):S4. doi:10.1186/1752-0509-8-S1-S4.
Cui J, Yu Y, Lu GF, Liu C, Liu X, Xu YX, et al. Overexpression of ARK5 is associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2013;34(3):1913–8. doi:10.1007/s13277-013-0735-x.
Ye YZ, Zhang ZH, Fan XY, Xu XL, Chen ML, Chang BW, et al. Notch3 overexpression associates with poor prognosis in human non-small-cell lung cancer. Med Oncol. 2013;30(2):595. doi:10.1007/s12032-013-0595-7.
Cheng WL, Wang CS, Huang YH, Liang Y, Lin PY, Hsueh C, et al. Overexpression of a secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor in human gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 2008;123(8):1787–96. doi:10.1002/ijc.23746.
Yang L. Incidence and mortality of gastric cancer in China. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12(1):17–20.
Hardie DG, Alessi DR. LKB1 and AMPK and the cancer-metabolism link: ten years after. BMC Biol. 2013;11:36. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-11-36.
Sun X, Gao L, Chien HY, Li WC, Zhao J. The regulation and function of the NUAK family. J Mol Endocrinol. 2013;51(2):R15–22. doi:10.1530/JME-13-0063.
Suzuki A, Kusakai G, Kishimoto A, Lu J, Ogura T, Lavin MF, et al. Identification of a novel protein kinase mediating Akt survival signaling to the ATM protein. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(1):48–53. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206025200.
Koh HJ, Toyoda T, Fujii N, Jung MM, Rathod A, Middelbeek RJ, et al. Sucrose nonfermenting AMPK-related kinase (SNARK) mediates contraction-stimulated glucose transport in mouse skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(35):15541–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.1008131107.
Hou X, Liu JE, Liu W, Liu CY, Liu ZY, Sun ZY. A new role of NUAK1: directly phosphorylating p53 and regulating cell proliferation. Oncogene. 2011;30(26):2933–42. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.19.
Suzuki A, Lu J, Kusakai G, Kishimoto A, Ogura T, Esumi H. ARK5 is a tumor invasion-associated factor downstream of Akt signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(8):3526–35.
Humbert N, Navaratnam N, Augert A, Da Costa M, Martien S, Wang J, et al. Regulation of ploidy and senescence by the AMPK-related kinase NUAK1. EMBO J. 2010;29(2):376–86. doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.342.
Liu L, Ulbrich J, Muller J, Wustefeld T, Aeberhard L, Kress TR, et al. Deregulated MYC expression induces dependence upon AMPK-related kinase 5. Nature. 2012;483(7391):608–12. doi:10.1038/nature10927.
Kochi M, Fujii M, Kanamori N, Kaiga T, Kawakami T, Aizaki K, et al. Evaluation of serum CEA and CA19-9 levels as prognostic factors in patients with gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2000;3(4):177–86.
Chu D, Zhang Z, Li Y, Zheng J, Dong G, Wang W, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 is associated with disease-free survival and overall survival in patients with gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 2011;129(4):887–95. doi:10.1002/ijc.25734.
Ying J, Xu Q, Zhang G, Liu B, Zhu L. The expression of CXCL12 and CXCR4 in gastric cancer and their correlation to lymph node metastasis. Med Oncol. 2012;29(3):1716–22. doi:10.1007/s12032-011-9990-0.
Chen W, Wang J, Li X, Li J, Zhou L, Qiu T, et al. Prognostic significance of BRCA1 expression in gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 2013;30(1):423. doi:10.1007/s12032-012-0423-5.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by Key Programs of Educational Commission of Anhui Province (No. KJ2010A181) and Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Anhui Province, China (No. 09A034).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiao-tian Ye and Ai-jun Guo have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Xt., Guo, Aj., Yin, Pf. et al. Overexpression of NUAK1 is associated with disease-free survival and overall survival in patients with gastric cancer. Med Oncol 31, 61 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0061-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0061-1