Abstract
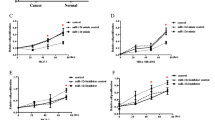
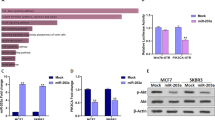
Breast cancer is one of the most common malignancies and a major cause of cancer-related mortality all over the world. A growing body of reports revealed that microRNAs play essential roles in the progression of cancers. Aberrant expression of miR-503 has been reported in several kinds of cancer. The aim of the current study was to elucidate the role of miR-503 in the pathogenesis of breast cancer. In the present study, our results suggested that miR-503 expression was markedly downregulated in breast cancer tissues and cells. Overexpression of miR-503 in breast cancer cell lines reduced cell proliferation through inducing G0/G1 cell cycle arrest by targeting CCND1. Together, our findings provide new knowledge regarding the role of miR-503 in the progression of breast cancer and indicate the role of miR-503 as a tumor suppressor microRNA (miRNA) in breast cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Desantis C, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:104–17.
Park YH, Lee SJ, Jung HA, Kim SM, Kim MJ, Kil WH, Lee JE, Nam SJ, Ahn JS, Im YH. Prevalence and clinical outcomes of young breast cancer (YBC) patients according to intrinsic breast cancer subtypes: single institutional experience in Korea. Breast (Edinburgh, Scotland) 2015.
Krop IE, Kim SB, Gonzalez-Martin A, LoRusso PM, Ferrero JM, Smitt M, et al. Trastuzumab emtansine versus treatment of physician’s choice for pretreated HER2-positive advanced breast cancer (TH3RESA): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:689–99.
Brandt J, Garne JP, Tengrup I, Manjer J. Age at diagnosis in relation to survival following breast cancer: a cohort study. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:429.
Migliaccio I, Malorni L, Hart CD, Guarducci C, Di Leo A. Endocrine therapy considerations in postmenopausal patients with hormone receptor positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 negative advanced breast cancers. BMC Med. 2015;13:280.
Chai J, Wang S, Han D, Dong W, Xie C, Guo H. MicroRNA-455 inhibits proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer by targeting RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. 2015;36:1313–21.
Feng S, Pan W, Jin Y, Zheng J. Mir-25 promotes ovarian cancer proliferation and motility by targeting LATS2. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. 2014;35:12339–44.
Cheng CJ, Bahal R, Babar IA, Pincus Z, Barrera F, Liu C, et al. MicroRNA silencing for cancer therapy targeted to the tumour microenvironment. Nature. 2015;518:107–10.
Dalmay T. Mechanism of miRNA-mediated repression of mRNA translation. Essays Biochem. 2013;54:29–38.
van Kouwenhove M, Kedde M, Agami R. MicroRNA regulation by RNA-binding proteins and its implications for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:644–56.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–66.
Shen S, Yue H, Li Y, Qin J, Li K, Liu Y, et al. Upregulation of miR-136 in human non-small cell lung cancer cells promotes Erk1/2 activation by targeting PPP2R2A. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. 2014;35:631–40.
Hao Z, Yang J, Wang C, Li Y, Zhang Y, Dong X, et al. MicroRNA-7 inhibits metastasis and invasion through targeting focal adhesion kinase in cervical cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:480–7.
Sun B, Yang M, Li M, Wang F. The microRNA-217 functions as a tumor suppressor and is frequently downregulated in human osteosarcoma. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacotherapie. 2015;71:58–63.
Sun Q, Zhao X, Liu X, Wang Y, Huang J, Jiang B, et al. Mir-146a functions as a tumor suppressor in prostate cancer by targeting Rac1. Prostate. 2014;74:1613–21.
Chong Y, Zhang J, Guo X, Li G, Zhang S, Li C, et al. MicroRNA-503 acts as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma by targeting L1CAM. PLoS One. 2014;9, e114585.
Wang T, Ge G, Ding Y, Zhou X, Huang Z, Zhu W, et al. MiR-503 regulates cisplatin resistance of human gastric cancer cell lines by targeting IGF1R and BCL2. Chin Med J. 2014;127:2357–62.
Polioudakis D, Abell NS, Iyer VR. miR-503 represses human cell proliferation and directly targets the oncogene DDHD2 by non-canonical target pairing. BMC Genomics. 2015;16:40.
Ruiz-Llorente L, Ardila-Gonzalez S, Fanjul LF, Martinez-Iglesias O, Aranda A. MicroRNAS 424 and 503 are mediators of the anti-proliferative and anti-invasive action of the thyroid hormone receptor beta. Oncotarget. 2014;5:2918–33.
Peng Y, Liu YM, Li LC, Wang LL, Wu XL. MicroRNA-503 inhibits gastric cancer cell growth and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Lett. 2014;7:1233–8.
Valinezhad Orang A, Safaralizadeh R. Mechanisms of miRNA-mediated gene regulation from common downregulation to mRNA-specific upregulation. 2014;2014:970607.
Vidaurre S, Fitzpatrick C, Burzio VA, Briones M, Villota C, Villegas J, et al. Down-regulation of the antisense mitochondrial non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) is a unique vulnerability of cancer cells and a potential target for cancer therapy. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:27182–98.
Li C, Xiong Q, Zhang J, Ge F, Bi LJ. Quantitative proteomic strategies for the identification of microRNA targets. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2012;9:549–59.
Humphries B, Yang C. The microRNA-200 family: small molecules with novel roles in cancer development, progression and therapy. Oncotarget 2015.
Liang H, Liu M, Yan X, Zhou Y, Wang W, Wang X, et al. miR-193a-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in lung cancer by down-regulating ERBB4. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:926–40.
Jiang J, Lv X, Fan L, Huang G, Zhan Y, Wang M, et al. MicroRNA-27b suppresses growth and invasion of NSCLC cells by targeting Sp1. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. 2014;35:10019–23.
Yang Y, Liu L, Zhang Y, Guan H, Wu J, Zhu X, et al. MiR-503 targets PI3K p85 and IKK-beta and suppresses progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer J Int du Cancer. 2014;135:1531–42.
Malumbres M, Barbacid M. Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:153–66.
Tashiro E, Tsuchiya A, Imoto M. Functions of cyclin D1 as an oncogene and regulation of cyclin D1 expression. Cancer Sci. 2007;98:629–35.
Schaal C, Pillai S, Chellappan SP. The Rb-E2F transcriptional regulatory pathway in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Adv Cancer Res. 2014;121:147–82.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (2012B031800055) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (31400858). All authors designed the study together, performed the experiment together, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper; all authors approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, J., Ou, C., Xia, H. et al. MiR-503 inhibited cell proliferation of human breast cancer cells by suppressing CCND1 expression. Tumor Biol. 36, 8697–8702 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3623-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3623-8