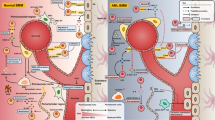
Abstract
Hematoproliferative neoplasias like chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) progressively affect bone marrow niche; however, there are only few specific clinical markers for prediction of disease progression. Here, we review the myeloproliferative niche and molecular changes including signaling pathways as well as microRNA (miRNA) in CML in order to better understand the therapeutic approaches. CML is a three-stage myeloproliferative disorder caused by reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22. There has been a new interest on treatment of this disorder. Therefore, in order to develop the appropriate therapy, an analysis of the molecular changes involved in malignant cells can be effective. A review of the signaling pathways, miRNA, and related targets can be helpful for better understanding of molecular pathogenesis of CML. Characterizing malignant cells and molecular changes with a focus on their targets may help researchers use molecular targets as effective therapeutic means for CML. On the other hand, interactions between leukemic stem cells and CML niche will help researchers investigate the causes of drug resistance in this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Celso CL, Fleming HE, Wu JW, Zhao CX, Miake-Lye S, Fujisaki J, et al. Live-animal tracking of individual haematopoietic stem/progenitor cells in their niche. Nature. 2009;457(7225):92–6.
Azizidoost S, Babashah S, Rahim F, Shahjahani M, Saki N. Bone marrow neoplastic niche in leukemia. Hematology. 2014;19(4):232–8.
Yasumizu R, Toki J, Asou H, Nishino T, Komatsu Y, Ikehara S. Production of hematopoietic stem cell-chemotactic factor by bone marrow stromal cells. Blood. 1994;83(4):964–71.
Williams DA, Cancelas JA. Leukaemia: niche retreats for stem cells. Nature. 2006;444(7121):827–8.
Saki N, Abroun S, Farshdousti Hagh M, Asgharei F. Neoplastic bone marrow niche: hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells. Cell J. 2011;13(3):131–6.
Azizidoost S, Shanaki Bavarsad M, Shanaki Bavarsad M, Shahrabi S, Jaseb K, Rahim F, et al. The role of notch signaling in bone marrow niche. Hematology. 2014. doi:10.1179/1607845414y.0000000167.
Schepers K, Pietras EM, Reynaud D, Flach J, Binnewies M, Garg T, et al. Myeloproliferative neoplasia remodels the endosteal bone marrow niche into a self-reinforcing leukemic niche. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;13(3):285–99.
Oehler VG, Yeung KY, Choi YE, Bumgarner RE, Raftery AE, Radich JP. The derivation of diagnostic markers of chronic myeloid leukemia progression from microarray data. Blood. 2009;114(15):3292–8.
Nwajei F, Konopleva M. The bone marrow microenvironment as niche retreats for hematopoietic and leukemic stem cells. Adv Hematol. 2013;2013.
Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, Peng B, Buchdunger E, Ford JM, et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. New Engl J Med. 2001;344(14):1031–7.
Gordon JE, Wong JJL, Rasko JE. MicroRNAs in myeloid malignancies. Br J Haematol. 2013;162(2):162–76.
Flamant S, Ritchie W, Guilhot J, Holst J, Bonnet ML, Chomel JC, et al. Micro-RNA response to imatinib mesylate in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2010;95(8):1325–33.
Sipkins DA, Wei X, Wu JW, Runnels JM, Cote D, Means TK, et al. In vivo imaging of specialized bone marrow endothelial microdomains for tumour engraftment. Nature. 2005;435(7044):969–73.
Agirre X, Jiménez-Velasco A, San José-Enériz E, Garate L, Bandrés E, Cordeu L, et al. Down-regulation of hsa-miR-10a in chronic myeloid leukemia CD34+ cells increases USF2-mediated cell growth. Mol Cancer Res. 2008;6(12):1830–40.
Melo JV, Deininger MW. Biology of chronic myelogenous leukemia-signaling pathways of initiation and transformation. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004;18(3):545–68.
Ahmed W, Van Etten RA. Signal transduction in the chronic leukemias: implications for targeted therapies. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2013;8(1):71–80.
Zhang B, Ho YW, Huang Q, Maeda T, Lin A, S-u L, et al. Altered microenvironmental regulation of leukemic and normal stem cells in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2012;21(4):577–92.
Krause DS, Lazarides K, von Andrian UH, Van Etten RA. Requirement for CD44 in homing and engraftment of BCR-ABL-expressing leukemic stem cells. Nat Med. 2006;12(10):1175–80.
Ninomiya S, Kanemura N, Tsurumi H, Kasahara S, Hara T, Yamada T, et al. Coexistence of inversion 16 and the Philadelphia chromosome comprising P190 BCR/ABL in chronic myeloid leukemia blast crisis. Int J Hematol. 2011;93(6):806–10.
Werner M, Kaloutsi V, Buhr T, Delventhal S, Vykoupil K-F, Georgii A. Cytogenetics of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) correlated to the histopathology of bone marrow biopsies. Ann Hematol. 1991;63(4):201–5.
Van der Plas D, Grosveld G, Hagemeijer A. Review of clinical, cytogenetic, and molecular aspects of Ph-negative CML. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1991;52(2):143–56.
Provan A, Majer RV, Herbert A, Smith AG. del (15) (q11q15) associated with transformation of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1991;55(1):35–8.
Wessels J, Fibbe W, Van Der Keur D, Landegent J, Van Der Plas D, Den Ottolander G, et al. t(5; 12)(q31; p12). A clinical entity with features of both myeloid leukemia and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1993;65(1):7–11.
Sherrington P, Nacheva E, Fischer P, Rees J, Hoyle C, Dyer M, et al. Translocation 5;21 and interstitial deletion of chromosome 7 in a case of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988;31(2):247–52.
Medeiros BC, Markovic V, Kamel-Reid S, Lipton JH. Presence of t(1;14)(p13;p11.2) in Philadelphia chromosome-negative cells in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2007;173(1):83–4.
Thompson P, Whittaker J. Translocation 3;21 in Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia at diagnosis. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1989;39(2):143–6.
Vaidya S, Joshi D, Ghosh K, Chakrabarti P, Vundinti BR. A novel 5-way translocation t(9;11;13;19;22) in a case of chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Hum Pathol. 2013;44(10):2365–9.
Gerber JM, Qin L, Kowalski J, Smith BD, Griffin CA, Vala MS, et al. Characterization of chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells. Am J Hematol. 2011;86(1):31–7.
Gerber JM, Gucwa JL, Esopi D, Gurel M, Haffner MC, Vala M, et al. Genome-wide comparison of the transcriptomes of highly enriched normal and chronic myeloid leukemia stem and progenitor cell populations. Oncotarget. 2013;4(5):715.
Naka K, Hoshii T, Muraguchi T, Tadokoro Y, Ooshio T, Kondo Y, et al. TGF-β–FOXO signalling maintains leukaemia-initiating cells in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 2010;463(7281):676–80.
Corrêa S, Binato R, Du Rocher B, Castelo-Branco MT, Pizzatti L, Abdelhay E. Wnt/β-catenin pathway regulates ABCB1 transcription in chronic myeloid leukemia. BMC Cancer. 2012;12(1):303.
Sengupta A, Banerjee D, Chandra S, Banerji S, Ghosh R, Roy R, et al. Deregulation and cross talk among Sonic hedgehog, Wnt, Hox and Notch signaling in chronic myeloid leukemia progression. Leukemia. 2007;21(5):949–55.
Danisz K, Blasiak J. Role of anti-apoptotic pathways activated by BCR/ABL in the resistance of chronic myeloid leukemia cells to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Acta Biochim Pol. 2013;60:503–14.
Yang Z, Yang C, Zhang S, Li Y, Chen J. Notch2 inhibits proliferation of chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Oncol Lett. 2013;5(4):1390–4.
Chang G, Zhang H, Wang J, Zhang Y, Xu H, Wang C, et al. CD44 targets Wnt/β-catenin pathway to mediate the proliferation of K562 cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2013;13(1):117.
Helgason GV, Young GA, Holyoake TL. Targeting chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2010;5(2):81–7.
Zhang L, Huang J, Yang N, Greshock J, Megraw MS, Giannakakis A, et al. microRNAs exhibit high frequency genomic alterations in human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2006;103(24):9136–41.
Bueno MJ, Perez de Castro I, Gomez de Cedron M, Santos J, Calin GA, Cigudosa JC, et al. Genetic and epigenetic silencing of microRNA-203 enhances ABL1 and BCR-ABL1 oncogene expression. Cancer Cell. 2008;13(6):496–506.
Polakova KM, Lopotová T, Klamová H, Burda P, Trněný M, Stopka T, et al. Expression patterns of microRNAs associated with CML phases and their disease related targets. Mol Cancer. 2011;10(1):41–53.
Eiring AM, Harb JG, Neviani P, Garton C, Oaks JJ, Spizzo R, et al. miR-328 functions as an RNA decoy to modulate hnRNP E2 regulation of mRNA translation in leukemic blasts. Cell. 2010;140(5):652–65.
Albano F, Anelli L, Zagaria A, Liso V, Rocchi M, Specchia G. MIRN199B downregulation in chronic myeloid leukaemia is associated with deletions on der(9). Br J Haematol. 2009;144(2):271–3.
Kong W, He L, Richards E, Challa S, Xu C, Permuth-Wey J, et al. Upregulation of miRNA-155 promotes tumour angiogenesis by targeting VHL and is associated with poor prognosis and triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene. 2013;33(6):679–89.
San José-Enériz E, Román-Gómez J, Jiménez-Velasco A, Garate L, Martin V, Cordeu L, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia patients without clinically significant ABL1-mutations. Mol Cancer. 2009;8(1):69–72.
Zhu X, Lin Z, Du J, Zhou X, Yang L, Liu G. Studies on microRNAs that are correlated with the cancer stem cells in chronic myeloid leukemia. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;390(1–2):75–84.
Babashah S, Sadeghizadeh M, Hajifathali A, Tavirani MR, Zomorod MS, Ghadiani M, et al. Targeting of the signal transducer Smo links microRNA‐326 to the oncogenic Hedgehog pathway in CD34+ CML stem/progenitor cells. Int J Cancer. 2013;133(3):579–89.
Venturini L, Battmer K, Castoldi M, Schultheis B, Hochhaus A, Muckenthaler MU, et al. Expression of the miR-17–92 polycistron in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) CD34+ cells. Blood. 2007;109(10):4399–405.
Li Y, Wang H, Tao K, Xiao Q, Huang Z, Zhong L, et al. miR-29b suppresses CML cell proliferation and induces apoptosis via regulation of BCR/ABL1 protein. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(8):1094–101.
Yin H, Liu Y, Zheng W-L, Song Y-B. Effects of miRNA-196b overexpression on proliferation, apoptosis and survivin, Cox-2 expression of K562 cells. China Oncol. 2013;5:007.
Labbaye C, Testa U. The emerging role of MIR-146A in the control of hematopoiesis, immune function and cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2012;5(1):13.
Chomel J, Aggoune D, Sorel N, Turhan A. [Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells: cross-talk with the niche]. Med Sci: M/S. 2014;30(4):452–61.
Corrado C, Raimondo S, Saieva L, Flugy AM, De Leo G, Alessandro R. Exosome-mediated crosstalk between chronic myelogenous leukemia cells and human bone marrow stromal cells triggers an interleukin 8-dependent survival of leukemia cells. Cancer Lett. 2014;348(1):71–6.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank all our colleagues in Shafa Hospital and Allied Health Sciences School, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences.
Authors’ contributions
N. S. and Sh. A. conceived the manuscript and revised it; S. Sh., F. R., and M. Sh. wrote the manuscript. N. S and A. A. prepared the tables.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahrabi, S., Azizidoost, S., Shahjahani, M. et al. New insights in cellular and molecular aspects of BM niche in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Tumor Biol. 35, 10627–10633 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2610-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2610-9