Abstract
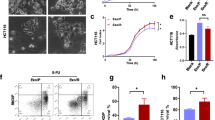
Acquired drug resistance is a major obstacle to chemotherapy of cancers. In this study, we aim to investigate the role of exosomes in drug-resistance transfer between breast cancer cells and detect the probable mechanism. A docetaxel-resistant variant of MCF-7 cell line (MCF-7/DOC) was established and then compared with the drug-sensitive variant (MCF-7/S). Exosomes were expelled from the cell supernatant using ultracentrifugation. Drug resistance was assessed by apoptosis assay and MTT examination. Expressions of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) were analyzed by flow cytometry. Stained exosomes were absorbed by receipt cells. MCF-7/S in the presence of exosomes extracted from the supernatant of MCF-7/DOC (DOC/exo) acquired drug resistance, while MCF-7/S exposed to their own exosomes (S/exo) did not. P-gp expression patterns of exosomes were similar as the originated cells. P-gp expression of MCF-7/S increased after incubation with DOC/exo and was affected by the amount of exosomes. Exosomes are effective in transferring drug resistance as well as P-gp from drug-resistant breast cancer cells to sensitive ones. The delivery of P-gp via exosomes may be a mechanism of exosome-mediated drug resistance transfer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Foo J, Michor F. Evolution of acquired resistance to anti-cancer therapy. J Theor Biol. 2014. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2014.02.025.
Gottesman MM. Mechanisms of cancer drug resistance. Annu Rev Med. 2002;53:615–27. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.53.082901.103929.
Azmi AS, Bao B, Sarkar FH. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and drug resistance: a comprehensive review. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013;32(3–4):623–42. doi:10.1007/s10555-013-9441-9.
Chen WX, Zhong SL, Ji MH, Pan M, Hu Q, Lv MM, et al. MicroRNAs delivered by extracellular vesicles: an emerging resistance mechanism for breast cancer. Tumour Biol J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med. 2013. doi:10.1007/s13277-013-1417-4.
van der Pol E, Boing AN, Harrison P, Sturk A, Nieuwland R. Classification, functions, and clinical relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol Rev. 2012;64(3):676–705. doi:10.1124/pr.112.005983.
Yang X, Weng Z, Mendrick DL, Shi Q. Circulating extracellular vesicles as a potential source of new biomarkers of drug-induced liver injury. Toxicol Lett. 2014;225(3):401–6. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.01.013.
van den Boorn JG, Dassler J, Coch C, Schlee M, Hartmann G. Exosomes as nucleic acid nanocarriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(3):331–5. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2012.06.011.
Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R, Conrad R. Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1820(7):940–8. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.03.017.
Bebawy M, Combes V, Lee E, Jaiswal R, Gong J, Bonhoure A, et al. Membrane microparticles mediate transfer of P-glycoprotein to drug sensitive cancer cells. Leukemia. 2009;23(9):1643–9. doi:10.1038/leu.2009.76.
Pasquier J, Galas L, Boulange-Lecomte C, Rioult D, Bultelle F, Magal P, et al. Different modalities of intercellular membrane exchanges mediate cell-to-cell p-glycoprotein transfers in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(10):7374–87. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.312157.
Vadlapatla RK, Vadlapudi AD, Pal D, Mitra AK. Mechanisms of drug resistance in cancer chemotherapy: coordinated role and regulation of efflux transporters and metabolizing enzymes. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(40):7126–40.
Ambudkar SV, Kimchi-Sarfaty C, Sauna ZE, Gottesman MM. P-glycoprotein: from genomics to mechanism. Oncogene. 2003;22(47):7468–85. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206948.
Zhou SF. Structure, function and regulation of P-glycoprotein and its clinical relevance in drug disposition. Xenobiotica; the fate of foreign compounds in biological systems. 2008;38(7-8):802–32. doi:10.1080/00498250701867889.
Zhong S, Li W, Chen Z, Xu J, Zhao J. MiR-222 and miR-29a contribute to the drug-resistance of breast cancer cells. Gene. 2013;531(1):8–14. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.062.
Lasser C, Eldh M, Lotvall J. Isolation and characterization of RNA-containing exosomes. J Visualized Exp JoVE. 2012;59:e3037. doi:10.3791/3037.
Corcoran C, Rani S, O’Brien K, O’Neill A, Prencipe M, Sheikh R, et al. Docetaxel-resistance in prostate cancer: evaluating associated phenotypic changes and potential for resistance transfer via exosomes. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50999. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050999.
Mathivanan S, Simpson RJ. ExoCarta: a compendium of exosomal proteins and RNA. Proteomics. 2009;9(21):4997–5000. doi:10.1002/pmic.200900351.
Hannafon BN, Ding WQ. Intercellular communication by exosome-derived microRNAs in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(7):14240–69. doi:10.3390/ijms140714240.
Skog J, Wurdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(12):1470–6. doi:10.1038/ncb1800.
Escrevente C, Keller S, Altevogt P, Costa J. Interaction and uptake of exosomes by ovarian cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:108. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-11-108.
Keller S, Konig AK, Marme F, Runz S, Wolterink S, Koensgen D, et al. Systemic presence and tumor-growth promoting effect of ovarian carcinoma released exosomes. Cancer Lett. 2009;278(1):73–81. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.12.028.
Suetsugu A, Honma K, Saji S, Moriwaki H, Ochiya T, Hoffman RM. Imaging exosome transfer from breast cancer cells to stroma at metastatic sites in orthotopic nude-mouse models. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(3):383–90. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2012.08.007.
Kharaziha P, Ceder S, Li Q, Panaretakis T. Tumor cell-derived exosomes: a message in a bottle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1826(1):103–11. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.03.006.
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654–9. doi:10.1038/ncb1596.
Pasquier J, Magal P, Boulange-Lecomte C, Webb G, Le Foll F. Consequences of cell-to-cell P-glycoprotein transfer on acquired multidrug resistance in breast cancer: a cell population dynamics model. Biol Direct. 2011;6:5. doi:10.1186/1745-6150-6-5.
Levchenko A, Mehta BM, Niu X, Kang G, Villafania L, Way D, et al. Intercellular transfer of P-glycoprotein mediates acquired multidrug resistance in tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(6):1933–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0401851102.
He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5(7):522–31. doi:10.1038/nrg1379.
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(30):10513–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0804549105.
Kogure T, Lin WL, Yan IK, Braconi C, Patel T. Intercellular nanovesicle-mediated microRNA transfer: a mechanism of environmental modulation of hepatocellular cancer cell growth. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md). 2011;54(4):1237–48. doi:10.1002/hep.24504.
Chen W-x, Liu X-m, Lv M-m, Chen L, Zhao J-h, Zhong S-l, et al. Exosomes from drug-resistant breast cancer cells transmit chemoresistance by a horizontal transfer of microRNAs. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e95240.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Meng-meng Lv and Xingya Zhu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Mm., Zhu, Xy., Chen, Wx. et al. Exosomes mediate drug resistance transfer in MCF-7 breast cancer cells and a probable mechanism is delivery of P-glycoprotein. Tumor Biol. 35, 10773–10779 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2377-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2377-z