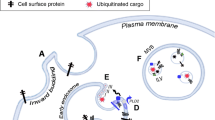
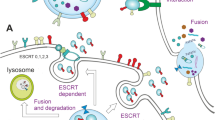
Abstract
Trafficking of biological material across membranes is an evolutionary conserved mechanism and is part of any normal cell homeostasis. Such transport is composed of active, passive, export through microparticles, and vesicular transport (exosomes) that collectively maintain proper compartmentalization of important micro- and macromolecules. In pathological states, such as cancer, aberrant activity of the export machinery results in expulsion of a number of key proteins and microRNAs resulting in their misexpression. Exosome-mediated expulsion of intracellular drugs could be another barrier in the proper action of most of the commonly used therapeutics, targeted agents, and their intracellular metabolites. Over the last decade, a number of studies have revealed that exosomes cross-talk and/or influence major tumor-related pathways, such as hypoxia-driven epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, cancer stemness, angiogenesis, and metastasis involving many cell types within the tumor microenvironment. Emerging evidence suggests that exosome-secreted proteins can also propel fibroblast growth, resulting in desmoplastic reaction, a major barrier in effective cancer drug delivery. This comprehensive review highlights the advancements in the understanding of the biology of exosomes secretions and the consequence on cancer drug resistance. We propose that the successful combination of cancer treatments to tackle exosome-mediated drug resistance requires an interdisciplinary understanding of these cellular exclusion mechanisms, and how secreted biomolecules are involved in cellular cross-talk within the tumor microenvironment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Kitano, H. (2004). Cancer as a robust system: implications for anticancer therapy. Nature Reviews Cancer, 4, 227–235.
Kitano, H. (2003). Cancer robustness: tumour tactics. Nature, 426, 125.
Miyawaki, A. (2011). Proteins on the move: insights gained from fluorescent protein technologies. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 12, 656–668.
Sugano, K., Kansy, M., Artursson, P., Avdeef, A., Bendels, S., Di, L., et al. (2010). Coexistence of passive and carrier-mediated processes in drug transport. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 9, 597–614.
El, A. S., Mager, I., Breakefield, X. O., & Wood, M. J. (2013). Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 12, 347–357.
Staals, R. H., & Pruijn, G. J. (2010). The human exosome and disease. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 702, 132–142.
Schorey, J. S., & Bhatnagar, S. (2008). Exosome function: from tumor immunology to pathogen biology. Traffic, 9, 871–881.
Vlassov, A. V., Magdaleno, S., Setterquist, R., & Conrad, R. (2012). Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1820, 940–948.
Vinciguerra, P., & Stutz, F. (2004). mRNA export: an assembly line from genes to nuclear pores. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 16, 285–292.
Fevrier, B., Vilette, D., Laude, H., & Raposo, G. (2005). Exosomes: a bubble ride for prions? Traffic, 6, 10–17.
Gibbings, D. J., Ciaudo, C., Erhardt, M., & Voinnet, O. (2009). Multivesicular bodies associate with components of miRNA effector complexes and modulate miRNA activity. Nature Cell Biology, 11, 1143–1149.
Finkelstein, A. (1964). Carrier model for active transport of ions across a mosaic membrane. Biophysical Journal, 4, 421–440.
Diekmann, Y., & Pereira-Leal, J. B. (2013). Evolution of intracellular compartmentalization. The Biochemical Journal, 449, 319–331.
Wright, E. M., Hirayama, B., Hazama, A., Loo, D. D., Supplisson, S., Turk, E., et al. (1993). The sodium/glucose cotransporter (SGLT1). Society of General Physiologists Series, 48, 229–241.
Grunwald, D., Singer, R. H., & Rout, M. (2011). Nuclear export dynamics of RNA-protein complexes. Nature, 475, 333–341.
Kim, J., Izadyar, A., Nioradze, N., & Amemiya, S. (2013). Nanoscale mechanism of molecular transport through the nuclear pore complex as studied by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 135, 2321–2329.
Albertini, M., Pemberton, L. F., Rosenblum, J. S., & Blobel, G. (1998). A novel nuclear import pathway for the transcription factor TFIIS. The Journal of Cell Biology, 143, 1447–1455.
Rosenblum, J. S., Pemberton, L. F., Bonifaci, N., & Blobel, G. (1998). Nuclear import and the evolution of a multifunctional RNA-binding protein. The Journal of Cell Biology, 143, 887–899.
Pemberton, L. F., Blobel, G., & Rosenblum, J. S. (1998). Transport routes through the nuclear pore complex. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 10, 392–399.
Rosenblum, J. S., Pemberton, L. F., & Blobel, G. (1997). A nuclear import pathway for a protein involved in tRNA maturation. The Journal of Cell Biology, 139, 1655–1661.
Lee, S. J., Jiko, C., Yamashita, E., & Tsukihara, T. (2011). Selective nuclear export mechanism of small RNAs. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 21, 101–108.
Adam, S. A., Lobl, T. J., Mitchell, M. A., & Gerace, L. (1989). Identification of specific binding proteins for a nuclear location sequence. Nature, 337, 276–279.
Wen, W., Meinkoth, J. L., Tsien, R. Y., & Taylor, S. S. (1995). Identification of a signal for rapid export of proteins from the nucleus. Cell, 82, 463–473.
Denzer, K., Kleijmeer, M. J., Heijnen, H. F., Stoorvogel, W., & Geuze, H. J. (2000). Exosome: from internal vesicle of the multivesicular body to intercellular signaling device. Journal of Cell Science, 113(Pt 19), 3365–3374.
Trams, E. G., Lauter, C. J., Salem, N., Jr., & Heine, U. (1981). Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 645, 63–70.
van den Boorn, J. G., Dassler, J., Coch, C., Schlee, M., & Hartmann, G. (2013). Exosomes as nucleic acid nanocarriers. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 65, 331–335.
Batista, B. S., Eng, W. S., Pilobello, K. T., Hendricks-Munoz, K. D., & Mahal, L. K. (2011). Identification of a conserved glycan signature for microvesicles. Journal of Proteome Research, 10, 4624–4633.
Caby, M. P., Lankar, D., Vincendeau-Scherrer, C., Raposo, G., & Bonnerot, C. (2005). Exosomal-like vesicles are present in human blood plasma. International Immunology, 17, 879–887.
Almqvist, N., Lonnqvist, A., Hultkrantz, S., Rask, C., & Telemo, E. (2008). Serum-derived exosomes from antigen-fed mice prevent allergic sensitization in a model of allergic asthma. Immunology, 125, 21–27.
Chen, C. Y., Hogan, M. C., & Ward, C. J. (2013). Purification of exosome-like vesicles from urine. Methods in Enzymology, 524, 225–241.
Keller, S., Sanderson, M. P., Stoeck, A., & Altevogt, P. (2006). Exosomes: from biogenesis and secretion to biological function. Immunology Letters, 107, 102–108.
Bhatnagar, S., & Schorey, J. S. (2007). Exosomes released from infected macrophages contain Mycobacterium avium glycopeptidolipids and are proinflammatory. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282, 25779–25789.
Bhatnagar, S., Shinagawa, K., Castellino, F. J., & Schorey, J. S. (2007). Exosomes released from macrophages infected with intracellular pathogens stimulate a proinflammatory response in vitro and in vivo. Blood, 110, 3234–3244.
Lee, Y., El, A. S., & Wood, M. J. (2012). Exosomes and microvesicles: extracellular vesicles for genetic information transfer and gene therapy. Human Molecular Genetics, 21, R125–R134.
Fevrier, B., & Raposo, G. (2004). Exosomes: endosomal-derived vesicles shipping extracellular messages. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 16, 415–421.
Cocucci, E., Racchetti, G., Podini, P., & Meldolesi, J. (2007). Enlargeosome traffic: exocytosis triggered by various signals is followed by endocytosis, membrane shedding or both. Traffic, 8, 742–757.
Cocucci, E., Racchetti, G., Rupnik, M., & Meldolesi, J. (2008). The regulated exocytosis of enlargeosomes is mediated by a SNARE machinery that includes VAMP4. Journal of Cell Science, 121, 2983–2991.
Cocucci, E., & Meldolesi, J. (2011). Ectosomes. Current Biology, 21, R940–R941.
Sudhof, T. C. (2004). The synaptic vesicle cycle. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 27, 509–547.
Sudhof, T. C., & Rothman, J. E. (2009). Membrane fusion: grappling with SNARE and SM proteins. Science, 323, 474–477.
Ostrowski, M., Carmo, N. B., Krumeich, S., Fanget, I., Raposo, G., Savina, A., et al. (2010). Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nature Cell Biology, 12, 19–30.
Bobrie, A., Krumeich, S., Reyal, F., Recchi, C., Moita, L. F., Seabra, M. C., et al. (2012). Rab27a supports exosome-dependent and -independent mechanisms that modify the tumor microenvironment and can promote tumor progression. Cancer Research, 72, 4920–4930.
Hsu, C., Morohashi, Y., Yoshimura, S., Manrique-Hoyos, N., Jung, S., Lauterbach, M. A., et al. (2010). Regulation of exosome secretion by Rab35 and its GTPase-activating proteins TBC1D10A-C. The Journal of Cell Biology, 189, 223–232.
Trajkovic, K., Hsu, C., Chiantia, S., Rajendran, L., Wenzel, D., Wieland, F., et al. (2008). Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science, 319, 1244–1247.
Parolini, I., Federici, C., Raggi, C., Lugini, L., Palleschi, S., De, M. A., et al. (2009). Microenvironmental pH is a key factor for exosome traffic in tumor cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284, 34211–34222.
Shen, B., Fang, Y., Wu, N., & Gould, S. J. (2011). Biogenesis of the posterior pole is mediated by the exosome/microvesicle protein-sorting pathway. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286, 44162–44176.
Poliakov, A., Spilman, M., Dokland, T., Amling, C. L., & Mobley, J. A. (2009). Structural heterogeneity and protein composition of exosome-like vesicles (prostasomes) in human semen. The Prostate, 69, 159–167.
Simons, M., & Raposo, G. (2009). Exosomes–vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 21, 575–581.
Mathivanan, S., Ji, H., & Simpson, R. J. (2010). Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. Journal of Proteomics, 73, 1907–1920.
Simpson, R. J., Lim, J. W., Moritz, R. L., & Mathivanan, S. (2009). Exosomes: proteomic insights and diagnostic potential. Expert Review of Proteomics, 6, 267–283.
Gross, J.C., Boutros, M. (2013). Secretion and extracellular space travel of Wnt proteins. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development (in press)
Gross, J. C., Chaudhary, V., Bartscherer, K., & Boutros, M. (2012). Active Wnt proteins are secreted on exosomes. Nature Cell Biology, 14, 1036–1045.
Sheldon, H., Heikamp, E., Turley, H., Dragovic, R., Thomas, P., Oon, C. E., et al. (2010). New mechanism for Notch signaling to endothelium at a distance by Delta-like 4 incorporation into exosomes. Blood, 116, 2385–2394.
Hasegawa, H., Thomas, H. J., Schooley, K., & Born, T. L. (2011). Native IL-32 is released from intestinal epithelial cells via a non-classical secretory pathway as a membrane-associated protein. Cytokine, 53, 74–83.
Vidal, M., Sainte-Marie, J., Philippot, J. R., & Bienvenue, A. (1989). Asymmetric distribution of phospholipids in the membrane of vesicles released during in vitro maturation of guinea pig reticulocytes: evidence precluding a role for "aminophospholipid translocase". Journal of Cellular Physiology, 140, 455–462.
Subra, C., Laulagnier, K., Perret, B., & Record, M. (2007). Exosome lipidomics unravels lipid sorting at the level of multivesicular bodies. Biochimie, 89, 205–212.
Beloribi, S., Ristorcelli, E., Breuzard, G., Silvy, F., Bertrand-Michel, J., Beraud, E., et al. (2012). Exosomal lipids impact notch signaling and induce death of human pancreatic tumoral SOJ-6 cells. PloS One, 7, e47480.
Laulagnier, K., Motta, C., Hamdi, S., Roy, S., Fauvelle, F., Pageaux, J. F., et al. (2004). Mast cell- and dendritic cell-derived exosomes display a specific lipid composition and an unusual membrane organization. The Biochemical Journal, 380, 161–171.
Yuyama, K., Sun, H., Mitsutake, S., & Igarashi, Y. (2012). Sphingolipid-modulated exosome secretion promotes clearance of amyloid-beta by microglia. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287, 10977–10989.
Record, M., Subra, C., Silvente-Poirot, S., & Poirot, M. (2011). Exosomes as intercellular signalosomes and pharmacological effectors. Biochemical Pharmacology, 81, 1171–1182.
Subra, C., Grand, D., Laulagnier, K., Stella, A., Lambeau, G., Paillasse, M., et al. (2010). Exosomes account for vesicle-mediated transcellular transport of activatable phospholipases and prostaglandins. Journal of Lipid Research, 51, 2105–2120.
Corrado, C., Raimondo, S., Chiesi, A., Ciccia, F., De, L. G., & Alessandro, R. (2013). Exosomes as intercellular signaling organelles involved in health and disease: basic science and clinical applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14, 5338–5366.
Mathivanan, S., Fahner, C. J., Reid, G. E., & Simpson, R. J. (2012). ExoCarta 2012: database of exosomal proteins, RNA and lipids. Nucleic Acids Research, 40, D1241–D1244.
Mathivanan, S., & Simpson, R. J. (2009). ExoCarta: a compendium of exosomal proteins and RNA. Proteomics, 9, 4997–5000.
Geminard, C., De, G. A., & Vidal, M. (2002). Reticulocyte maturation: mitoptosis and exosome release. Biocell, 26, 205–215.
Robertson, C., Booth, S. A., Beniac, D. R., Coulthart, M. B., Booth, T. F., & McNicol, A. (2006). Cellular prion protein is released on exosomes from activated platelets. Blood, 107, 3907–3911.
Quah, B., & O'Neill, H. C. (2000). Review: the application of dendritic cell-derived exosomes in tumour immunotherapy. Cancer Biotherapy and Radiopharmaceuticals, 15, 185–194.
Lasser, C., Eldh, M., Lotvall, J. (2012). Isolation and characterization of RNA-containing exosomes. Journal of Visualized Experiments (59):e3037.
Gogolak, P., Rethi, B., Hajas, G., & Rajnavolgyi, E. (2003). Targeting dendritic cells for priming cellular immune responses. Journal of Molecular Recognition, 16, 299–317.
Gyorgy, B., Szabo, T. G., Pasztoi, M., Pal, Z., Misjak, P., Aradi, B., et al. (2011). Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: emerging role of extracellular vesicles. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 68, 2667–2688.
Vickers, K. C., & Remaley, A. T. (2012). Lipid-based carriers of microRNAs and intercellular communication. Current Opinion in Lipidology, 23, 91–97.
Jaiswal, R., Luk, F., Gong, J., Mathys, J. M., Grau, G. E., & Bebawy, M. (2012). Microparticle conferred microRNA profiles—implications in the transfer and dominance of cancer traits. Molecular Cancer, 11, 37.
Gong, J., Jaiswal, R., Mathys, J. M., Combes, V., Grau, G. E., & Bebawy, M. (2012). Microparticles and their emerging role in cancer multidrug resistance. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 38, 226–234.
Gonzalez-Begne, M., Lu, B., Han, X., Hagen, F. K., Hand, A. R., Melvin, J. E., et al. (2009). Proteomic analysis of human parotid gland exosomes by multidimensional protein identification technology (MudPIT). Journal of Proteome Research, 8, 1304–1314.
Akerfelt, M., Morimoto, R. I., & Sistonen, L. (2010). Heat shock factors: integrators of cell stress, development and lifespan. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 11, 545–555.
Akerfelt, M., Trouillet, D., Mezger, V., & Sistonen, L. (2007). Heat shock factors at a crossroad between stress and development. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1113, 15–27.
De, M. A. (1999). Heat shock proteins: facts, thoughts, and dreams. Shock, 11, 1–12.
Bolhassani, A., & Rafati, S. (2013). Mini-chaperones: potential immuno-stimulators in vaccine design. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, 9, 153–161.
Bolhassani, A., & Rafati, S. (2008). Heat-shock proteins as powerful weapons in vaccine development. Expert Review of Vaccines, 7, 1185–1199.
Mathew, A., Bell, A., & Johnstone, R. M. (1995). Hsp-70 is closely associated with the transferrin receptor in exosomes from maturing reticulocytes. The Biochemical Journal, 308(Pt 3), 823–830.
Lancaster, G. I., & Febbraio, M. A. (2005). Exosome-dependent trafficking of HSP70: a novel secretory pathway for cellular stress proteins. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 23349–23355.
Clayton, A., Turkes, A., Navabi, H., Mason, M. D., & Tabi, Z. (2005). Induction of heat shock proteins in B-cell exosomes. Journal of Cell Science, 118, 3631–3638.
Lv, L. H., Wan, Y. L., Lin, Y., Zhang, W., Yang, M., Li, G. L., et al. (2012). Anticancer drugs cause release of exosomes with heat shock proteins from human hepatocellular carcinoma cells that elicit effective natural killer cell antitumor responses in vitro. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287, 15874–15885.
Cho, J. A., Lee, Y. S., Kim, S. H., Ko, J. K., & Kim, C. W. (2009). MHC independent anti-tumor immune responses induced by Hsp70-enriched exosomes generate tumor regression in murine models. Cancer Letters, 275, 256–265.
Mukhopadhyay, U. K., & Mak, A. S. (2009). p53: is the guardian of the genome also a suppressor of cell invasion? Cell Cycle, 8, 2481.
Muller, P. A., & Vousden, K. H. (2013). p53 mutations in cancer. Nature Cell Biology, 15, 2–8.
Wade, M., Li, Y. C., & Wahl, G. M. (2013). MDM2, MDMX and p53 in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 13, 83–96.
Azmi, A. S. (2011). Pharmaceutical reactivation of p53 pathways in cancer. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 17, 534–535.
Yu, X., Harris, S. L., & Levine, A. J. (2006). The regulation of exosome secretion: a novel function of the p53 protein. Cancer Research, 66, 4795–4801.
Yu, X., Riley, T., & Levine, A. J. (2009). The regulation of the endosomal compartment by p53 the tumor suppressor gene. The FEBS Journal, 276, 2201–2212.
Lespagnol, A., Duflaut, D., Beekman, C., Blanc, L., Fiucci, G., Marine, J. C., et al. (2008). Exosome secretion, including the DNA damage-induced p53-dependent secretory pathway, is severely compromised in TSAP6/Steap3-null mice. Cell Death and Differentiation, 15, 1723–1733.
Honegger, A., Leitz, J., Bulkescher, J., Hoppe-Seyler, K., Hoppe-Seyler, F. (2013). Silencing of human papillomavirus (HPV) E6/E7 oncogene expression affects both the contents and amounts of extracellular microvesicles released from HPV-positive cancer cells. International Journal of Cancer (in press)
Hupalowska, A., & Miaczynska, M. (2012). The new faces of endocytosis in signaling. Traffic, 13, 9–18.
Song, M. S., Salmena, L., & Pandolfi, P. P. (2012). The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 13, 283–296.
Wrighton, K. H. (2011). Tumour suppressors: role of nuclear PTEN revealed. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 11, 154.
Vanhaesebroeck, B., Stephens, L., & Hawkins, P. (2012). PI3K signalling: the path to discovery and understanding. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 13, 195–203.
Putz, U., Howitt, J., Doan, A., Goh, C. P., Low, L. H., Silke, J., et al. (2012). The tumor suppressor PTEN is exported in exosomes and has phosphatase activity in recipient cells. Science Signaling, 5, ra70.
Leslie, N. R. (2012). PTEN: an intercellular peacekeeper? Science Signaling, 5, e50.
Ristorcelli, E., Beraud, E., Mathieu, S., Lombardo, D., & Verine, A. (2009). Essential role of Notch signaling in apoptosis of human pancreatic tumoral cells mediated by exosomal nanoparticles. International Journal of Cancer, 125, 1016–1026.
Cho, K. R., & Vogelstein, B. (1992). Suppressor gene alterations in the colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. Supplement, 16G, 137–141.
Aust, D. E., Terdiman, J. P., Willenbucher, R. F., Chang, C. G., Molinaro-Clark, A., Baretton, G. B., et al. (2002). The APC/beta-catenin pathway in ulcerative colitis-related colorectal carcinomas: a mutational analysis. Cancer, 94, 1421–1427.
Lim, J. W., Mathias, R. A., Kapp, E. A., Layton, M. J., Faux, M. C., Burgess, A. W., et al. (2012). Restoration of full-length APC protein in SW480 colon cancer cells induces exosome-mediated secretion of DKK-4. Electrophoresis, 33, 1873–1880.
Seton-Rogers, S. (2013). Microenvironment: making connections. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 13, 222–223.
He, L., & Hannon, G. J. (2004). MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nature Reviews Genetics, 5, 522–531.
Mitchell, P. S., Parkin, R. K., Kroh, E. M., Fritz, B. R., Wyman, S. K., Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E. L., et al. (2008). Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 10513–10518.
Cortez, M. A., Bueso-Ramos, C., Ferdin, J., Lopez-Berestein, G., Sood, A. K., & Calin, G. A. (2011). MicroRNAs in body fluids—the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nature Reviews. Clinical Oncology, 8, 467–477.
Lund, E., Guttinger, S., Calado, A., Dahlberg, J. E., & Kutay, U. (2004). Nuclear export of microRNA precursors. Science, 303, 95–98.
Stoorvogel, W. (2012). Functional transfer of microRNA by exosomes. Blood, 119, 646–648.
Gallo, A., Tandon, M., Alevizos, I., & Illei, G. G. (2012). The majority of microRNAs detectable in serum and saliva is concentrated in exosomes. PloS One, 7, e30679.
Russo, F., Di, B. S., Nigita, G., Macca, V., Lagana, A., Giugno, R., et al. (2012). miRandola: extracellular circulating microRNAs database. PloS One, 7, e47786.
Boon, R. A., & Vickers, K. C. (2013). Intercellular transport of microRNAs. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 33, 186–192.
Valadi, H., Ekstrom, K., Bossios, A., Sjostrand, M., Lee, J. J., & Lotvall, J. O. (2007). Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nature Cell Biology, 9, 654–659.
Lotvall, J., & Valadi, H. (2007). Cell to cell signalling via exosomes through esRNA. Cell Adhesion & Migration, 1, 156–158.
Koga, Y., Yasunaga, M., Moriya, Y., Akasu, T., Fujita, S., Yamamoto, S., et al. (2011). Exosome can prevent RNase from degrading microRNA in feces. Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology, 2, 215–222.
Chen, T. S., Lai, R. C., Lee, M. M., Choo, A. B., Lee, C. N., & Lim, S. K. (2010). Mesenchymal stem cell secretes microparticles enriched in pre-microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Research, 38, 215–224.
Flynt, A. S., Greimann, J. C., Chung, W. J., Lima, C. D., & Lai, E. C. (2010). MicroRNA biogenesis via splicing and exosome-mediated trimming in Drosophila. Molecular Cell, 38, 900–907.
Rabinowits, G., Gercel-Taylor, C., Day, J. M., Taylor, D. D., & Kloecker, G. H. (2009). Exosomal microRNA: a diagnostic marker for lung cancer. Clinical Lung Cancer, 10, 42–46.
Mizoguchi, M., Guan, Y., Yoshimoto, K., Hata, N., Amano, T., Nakamizo, A., et al. (2013). Clinical implications of microRNAs in human glioblastoma. Frontiers in Oncology, 3, 19.
Tanaka, Y., Kamohara, H., Kinoshita, K., Kurashige, J., Ishimoto, T., Iwatsuki, M., et al. (2013). Clinical impact of serum exosomal microRNA-21 as a clinical biomarker in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer, 119, 1159–1167.
Hessvik, N. P., Sandvig, K., & Llorente, A. (2013). Exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers for prostate cancer. Frontiers in Genetics, 4, 36.
Hessvik, N. P., Phuyal, S., Brech, A., Sandvig, K., & Llorente, A. (2012). Profiling of microRNAs in exosomes released from PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1819, 1154–1163.
da Silveira, J. C., Veeramachaneni, D. N., Winger, Q. A., Carnevale, E. M., & Bouma, G. J. (2012). Cell-secreted vesicles in equine ovarian follicular fluid contain miRNAs and proteins: a possible new form of cell communication within the ovarian follicle. Biology of Reproduction, 86, 71.
Lasser, C. (2012). Exosomal RNA as biomarkers and the therapeutic potential of exosome vectors. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 12(Suppl 1), S189–S197.
Tauro, B. J., Greening, D. W., Mathias, R. A., Ji, H., Mathivanan, S., Scott, A. M., et al. (2012). Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods, 56, 293–304.
Alvarez, M. L., Khosroheidari, M., Kanchi, R. R., & DiStefano, J. K. (2012). Comparison of protein, microRNA, and mRNA yields using different methods of urinary exosome isolation for the discovery of kidney disease biomarkers. Kidney International, 82, 1024–1032.
Umezu, T., Ohyashiki, K., Kuroda, M., Ohyashiki, J.H. (2013) Leukemia cell to endothelial cell communication via exosomal miRNAs. Oncogene (in press)
Bobrie, A., Colombo, M., Raposo, G., & Thery, C. (2011). Exosome secretion: molecular mechanisms and roles in immune responses. Traffic, 12, 1659–1668.
Pegtel, D. M., van de Garde, M. D. B., & Middeldorp, J. M. (2011). Viral miRNAs exploiting the endosomal-exosomal pathway for intercellular cross-talk and immune evasion. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1809, 715–721.
Palma, J., Yaddanapudi, S. C., Pigati, L., Havens, M. A., Jeong, S., Weiner, G. A., et al. (2012). MicroRNAs are exported from malignant cells in customized particles. Nucleic Acids Research, 40, 9125–9138.
Yang, M., Chen, J., Su, F., Yu, B., Su, F., Lin, L., et al. (2011). Microvesicles secreted by macrophages shuttle invasion-potentiating microRNAs into breast cancer cells. Molecular Cancer, 10, 117.
Bullerdiek, J., & Flor, I. (2012). Exosome-delivered microRNAs of "chromosome 19 microRNA cluster" as immunomodulators in pregnancy and tumorigenesis. Molecular Cytogenetics, 5, 27.
Meads, M. B., Gatenby, R. A., & Dalton, W. S. (2009). Environment-mediated drug resistance: a major contributor to minimal residual disease. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 9, 665–674.
Shain, K. H., Landowski, T. H., & Dalton, W. S. (2000). The tumor microenvironment as a determinant of cancer cell survival: a possible mechanism for de novo drug resistance. Current Opinion in Oncology, 12, 557–563.
Li, H., Yang, B.B. (2013). Friend or foe: the role of microRNA in chemotherapy resistance. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (in press)
Holzel, M., Bovier, A., & Tuting, T. (2013). Plasticity of tumour and immune cells: a source of heterogeneity and a cause for therapy resistance? Nature Reviews. Cancer, 13, 365–376.
McMillin, D. W., Negri, J. M., & Mitsiades, C. S. (2013). The role of tumour-stromal interactions in modifying drug response: challenges and opportunities. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 12, 217–228.
Khan, S., Aspe, J. R., Asumen, M. G., Almaguel, F., Odumosu, O., cevedo-Martinez, S., et al. (2009). Extracellular, cell-permeable survivin inhibits apoptosis while promoting proliferative and metastatic potential. British Journal of Cancer, 100, 1073–1086.
Pilzer, D., Gasser, O., Moskovich, O., Schifferli, J. A., & Fishelson, Z. (2005). Emission of membrane vesicles: roles in complement resistance, immunity and cancer. Springer Seminars in Immunopathology, 27, 375–387.
Pilzer, D., & Fishelson, Z. (2005). Mortalin/GRP75 promotes release of membrane vesicles from immune attacked cells and protection from complement-mediated lysis. International Immunology, 17, 1239–1248.
Zhang, H. G., Liu, C., Su, K., Yu, S., Zhang, L., Zhang, S., et al. (2006). A membrane form of TNF-alpha presented by exosomes delays T cell activation-induced cell death. The Journal of Immunology, 176, 7385–7393.
Bodey, B., Bodey, B., Jr., & Kaiser, H. E. (1997). Dendritic type, accessory cells within the mammalian thymic microenvironment. Antigen presentation in the dendritic neuro-endocrine-immune cellular network. In Vivo, 11, 351–370.
Aung, T., Chapuy, B., Vogel, D., Wenzel, D., Oppermann, M., Lahmann, M., et al. (2011). Exosomal evasion of humoral immunotherapy in aggressive B-cell lymphoma modulated by ATP-binding cassette transporter A3. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108, 15336–15341.
Hupfeld, T., Chapuy, B., Schrader, V., Beutler, M., Veltkamp, C., Koch, R., et al. (2013). Tyrosinekinase inhibition facilitates cooperation of transcription factor SALL4 and ABC transporter A3 towards intrinsic CML cell drug resistance. British Journal of Haematology, 161, 204–213.
Safaei, R., Larson, B. J., Cheng, T. C., Gibson, M. A., Otani, S., Naerdemann, W., et al. (2005). Abnormal lysosomal trafficking and enhanced exosomal export of cisplatin in drug-resistant human ovarian carcinoma cells. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 4, 1595–1604.
Yin, J., Yan, X., Yao, X., Zhang, Y., Shan, Y., Mao, N., et al. (2012). Secretion of annexin A3 from ovarian cancer cells and its association with platinum resistance in ovarian cancer patients. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 16, 337–348.
Ciravolo, V., Huber, V., Ghedini, G. C., Venturelli, E., Bianchi, F., Campiglio, M., et al. (2012). Potential role of HER2-overexpressing exosomes in countering trastuzumab-based therapy. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 227, 658–667.
Hosseini-Beheshti, E., Pham, S., Adomat, H., Li, N., & Tomlinson Guns, E. S. (2012). Exosomes as biomarker enriched microvesicles: characterization of exosomal proteins derived from a panel of prostate cell lines with distinct AR phenotypes. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 11, 863–885.
Bard, M. P., Hegmans, J. P., Hemmes, A., Luider, T. M., Willemsen, R., Severijnen, L. A., et al. (2004). Proteomic analysis of exosomes isolated from human malignant pleural effusions. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology, 31, 114–121.
Hegmans, J. P., Bard, M. P., Hemmes, A., Luider, T. M., Kleijmeer, M. J., Prins, J. B., et al. (2004). Proteomic analysis of exosomes secreted by human mesothelioma cells. The American Journal of Pathology, 164, 1807–1815.
Mears, R., Craven, R. A., Hanrahan, S., Totty, N., Upton, C., Young, S. L., et al. (2004). Proteomic analysis of melanoma-derived exosomes by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Proteomics, 4, 4019–4031.
Nguyen, D. X., Bos, P. D., & Massague, J. (2009). Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 9, 274–284.
Nguyen, D. X., & Massague, J. (2007). Genetic determinants of cancer metastasis. Nature Reviews Genetics, 8, 341–352.
Grange, C., Tapparo, M., Collino, F., Vitillo, L., Damasco, C., Deregibus, M. C., et al. (2011). Microvesicles released from human renal cancer stem cells stimulate angiogenesis and formation of lung premetastatic niche. Cancer Research, 71, 5346–5356.
Hood, J. L., Pan, H., Lanza, G. M., & Wickline, S. A. (2009). Paracrine induction of endothelium by tumor exosomes. Laboratory Investigation, 89, 1317–1328.
Hood, J. L., San, R. S., & Wickline, S. A. (2011). Exosomes released by melanoma cells prepare sentinel lymph nodes for tumor metastasis. Cancer Research, 71, 3792–3801.
Rana, S., Malinowska, K., & Zoller, M. (2013). Exosomal tumor microRNA modulates premetastatic organ cells. Neoplasia, 15, 281–295.
Di, V. D., Morello, M., Dudley, A. C., Schow, P. W., Adam, R. M., Morley, S., et al. (2012). Large oncosomes in human prostate cancer tissues and in the circulation of mice with metastatic disease. The American Journal of Pathology, 181, 1573–1584.
Bao, B., Azmi, A. S., Ali, S., Ahmad, A., Li, Y., Banerjee, S., et al. (2012). The biological kinship of hypoxia with CSC and EMT and their relationship with deregulated expression of miRNAs and tumor aggressiveness. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1826, 272–296.
Casazza, A., Di, C. G., Wenes, M., Finisguerra, V., Deschoemaeker, S., and Mazzone, M. (2013) Tumor stroma: a complexity dictated by the hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Oncogene.
Salnikov, A. V., Liu, L., Platen, M., Gladkich, J., Salnikova, O., Ryschich, E., et al. (2012). Hypoxia induces EMT in low and highly aggressive pancreatic tumor cells but only cells with cancer stem cell characteristics acquire pronounced migratory potential. PloS One, 7, e46391.
Chaturvedi, P., Gilkes, D. M., Wong, C. C., Luo, W., Zhang, H., Wei, H., et al. (2013). Hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent breast cancer-mesenchymal stem cell bidirectional signaling promotes metastasis. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 123, 189–205.
Wilson, W. R., & Hay, M. P. (2011). Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 11, 393–410.
Rapisarda, A., & Melillo, G. (2012). Overcoming disappointing results with antiangiogenic therapy by targeting hypoxia. Nature Reviews. Clinical Oncology, 9, 378–390.
King, H. W., Michael, M. Z., & Gleadle, J. M. (2012). Hypoxic enhancement of exosome release by breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer, 12, 421.
Kucharzewska, P., Christianson, H.C., Welch, J.E., Svensson, K.J., Fredlund, E., Ringner, M., et al. (2013) Exosomes reflect the hypoxic status of glioma cells and mediate hypoxia-dependent activation of vascular cells during tumor development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (in press)
Borges, F. T., Melo, S. A., Ozdemir, B. C., Kato, N., Revuelta, I., Miller, C. A., et al. (2013). TGF-beta1-containing exosomes from injured epithelial cells activate fibroblasts to initiate tissue regenerative responses and fibrosis. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 24, 385–392.
Park, J. E., Tan, H. S., Datta, A., Lai, R. C., Zhang, H., Meng, W., et al. (2010). Hypoxic tumor cell modulates its microenvironment to enhance angiogenic and metastatic potential by secretion of proteins and exosomes. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 9, 1085–1099.
Svensson, K. J., Kucharzewska, P., Christianson, H. C., Skold, S., Lofstedt, T., Johansson, M. C., et al. (2011). Hypoxia triggers a proangiogenic pathway involving cancer cell microvesicles and PAR-2-mediated heparin-binding EGF signaling in endothelial cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108, 13147–13152.
Svensson, K. J., & Belting, M. (2013). Role of extracellular membrane vesicles in intercellular communication of the tumour microenvironment. Biochemical Society Transactions, 41, 273–276.
Thiery, J. P., & Sleeman, J. P. (2006). Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 7, 131–142.
Thiery, J. P. (2002). Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 2, 442–454.
Masuda, S., & Izpisua Belmonte, J. C. (2013). The microenvironment and resistance to personalized cancer therapy. Nature Reviews. Clinical Oncology, 10.
Garnier, D., Magnus, N., Lee, T. H., Bentley, V., Meehan, B., Milsom, C., et al. (2012). Cancer cells induced to express mesenchymal phenotype release exosome-like extracellular vesicles carrying tissue factor. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287, 43565–43572.
Roccaro, A.M., Sacco, A., Maiso, P., Azab, A.K., Tai, Y.T., Reagan, M., et al. (2013) BM mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes facilitate multiple myeloma progression. Journal of Clinical Investigation (in press)
Katsuno, Y., Lamouille, S., & Derynck, R. (2013). TGF-beta signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer progression. Current Opinion in Oncology, 25, 76–84.
Xu, J., Lamouille, S., & Derynck, R. (2009). TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Research, 19, 156–172.
Lamouille, S., Connolly, E., Smyth, J. W., Akhurst, R. J., & Derynck, R. (2012). TGF-beta-induced activation of mTOR complex 2 drives epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell invasion. Journal of Cell Science, 125, 1259–1273.
Cho, J. A., Park, H., Lim, E. H., & Lee, K. W. (2012). Exosomes from breast cancer cells can convert adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells into myofibroblast-like cells. International Journal of Oncology, 40, 130–138.
Clayton, A., Mitchell, J. P., Court, J., Mason, M. D., & Tabi, Z. (2007). Human tumor-derived exosomes selectively impair lymphocyte responses to interleukin-2. Cancer Research, 67, 7458–7466.
Cheng, C. F., Fan, J., Fedesco, M., Guan, S., Li, Y., Bandyopadhyay, B., et al. (2008). Transforming growth factor alpha (TGFalpha)-stimulated secretion of HSP90alpha: using the receptor LRP-1/CD91 to promote human skin cell migration against a TGFbeta-rich environment during wound healing. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 28, 3344–3358.
Clayton, A., Mitchell, J. P., Court, J., Linnane, S., Mason, M. D., & Tabi, Z. (2008). Human tumor-derived exosomes down-modulate NKG2D expression. The Journal of Immunology, 180, 7249–7258.
Cho, J. A., Park, H., Lim, E. H., Kim, K. H., Choi, J. S., Lee, J. H., et al. (2011). Exosomes from ovarian cancer cells induce adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells to acquire the physical and functional characteristics of tumor-supporting myofibroblasts. Gynecologic Oncology, 123, 379–386.
Klaus, A., & Birchmeier, W. (2008). Wnt signalling and its impact on development and cancer. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 8, 387–398.
Anastas, J. N., & Moon, R. T. (2013). WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 13, 11–26.
Haegel, H., Larue, L., Ohsugi, M., Fedorov, L., Herrenknecht, K., & Kemler, R. (1995). Lack of beta-catenin affects mouse development at gastrulation. Development (Cambridge, England), 121, 3529–3537.
Morin, P. J. (1999). beta-catenin signaling and cancer. BioEssays, 21, 1021–1030.
Korkut, C., Ataman, B., Ramachandran, P., Ashley, J., Barria, R., Gherbesi, N., et al. (2009). Trans-synaptic transmission of vesicular Wnt signals through Evi/Wntless. Cell, 139, 393–404.
Koles, K., Nunnari, J., Korkut, C., Barria, R., Brewer, C., Li, Y., et al. (2012). Mechanism of evenness interrupted (Evi)-exosome release at synaptic boutons. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287, 16820–16834.
Chairoungdua, A., Smith, D. L., Pochard, P., Hull, M., & Caplan, M. J. (2010). Exosome release of beta-catenin: a novel mechanism that antagonizes Wnt signaling. The Journal of Cell Biology, 190, 1079–1091.
Li, D., Ren, Y. N., Yang, J., Yang, Y. M., Li, C. Y., Xie, R. F., et al. (2011). A preliminary study on the influence of human plasma exosomes-like vesicles on macrophage Wnt5A-Ca(2)+ pathway. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi, 32, 404–407.
Hooper, C., Sainz-Fuertes, R., Lynham, S., Hye, A., Killick, R., Warley, A., et al. (2012). Wnt3a induces exosome secretion from primary cultured rat microglia. BMC Neuroscience, 13, 144.
Luga, V., Zhang, L., Viloria-Petit, A. M., Ogunjimi, A. A., Inanlou, M. R., Chiu, E., et al. (2012). Exosomes mediate stromal mobilization of autocrine Wnt-PCP signaling in breast cancer cell migration. Cell, 151, 1542–1556.
Stumpf, W. E. (2005). Drug localization and targeting with receptor microscopic autoradiography. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods, 51, 25–40.
Jones, P. M., & George, A. M. (2004). The ABC transporter structure and mechanism: perspectives on recent research. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 61, 682–699.
Lee, C. H. (2010). Reversing agents for ATP-binding cassette drug transporters. Methods in Molecular Biology, 596, 325–340.
Corcoran, C., Rani, S., O'Brien, K., O'Neill, A., Prencipe, M., Sheikh, R., et al. (2012). Docetaxel-resistance in prostate cancer: evaluating associated phenotypic changes and potential for resistance transfer via exosomes. PloS One, 7, e50999.
Shedden, K., Xie, X. T., Chandaroy, P., Chang, Y. T., & Rosania, G. R. (2003). Expulsion of small molecules in vesicles shed by cancer cells: association with gene expression and chemosensitivity profiles. Cancer Research, 63, 4331–4337.
Kooijmans, S. A., Vader, P., van Dommelen, S. M., van Solinge, W. W., & Schiffelers, R. M. (2012). Exosome mimetics: a novel class of drug delivery systems. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 7, 1525–1541.
Harding, C. V., Heuser, J. E., & Stahl, P. D. (2013). Exosomes: looking back three decades and into the future. The Journal of Cell Biology, 200, 367–371.
Zitvogel, L., Regnault, A., Lozier, A., Wolfers, J., Flament, C., Tenza, D., et al. (1998). Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nature Medicine, 4, 594–600.
Zitvogel, L., Fernandez, N., Lozier, A., Wolfers, J., Regnault, A., Raposo, G., et al. (1999). Dendritic cells or their exosomes are effective biotherapies of cancer. European Journal of Cancer, 35(Suppl 3), S36–S38.
Thery, C., Regnault, A., Garin, J., Wolfers, J., Zitvogel, L., Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P., et al. (1999). Molecular characterization of dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Selective accumulation of the heat shock protein hsc73. The Journal of Cell Biology, 147, 599–610.
Wolfers, J., Lozier, A., Raposo, G., Regnault, A., Thery, C., Masurier, C., et al. (2001). Tumor-derived exosomes are a source of shared tumor rejection antigens for CTL cross-priming. Nature Medicine, 7, 297–303.
Lamparski, H. G., Metha-Damani, A., Yao, J. Y., Patel, S., Hsu, D. H., Ruegg, C., et al. (2002). Production and characterization of clinical grade exosomes derived from dendritic cells. Journal of Immunological Methods, 270, 211–226.
Chaput, N., Schartz, N. E., Andre, F., Taieb, J., Novault, S., Bonnaventure, P., et al. (2004). Exosomes as potent cell-free peptide-based vaccine. II. Exosomes in CpG adjuvants efficiently prime naive Tc1 lymphocytes leading to tumor rejection. The Journal of Immunology, 172, 2137–2146.
Taieb, J., Chaput, N., Schartz, N., Roux, S., Novault, S., Menard, C., et al. (2006). Chemoimmunotherapy of tumors: cyclophosphamide synergizes with exosome based vaccines. The Journal of Immunology, 176, 2722–2729.
Tian, X., Zhu, M., & Nie, G. (2013). How can nanotechnology help membrane vesicle-based cancer immunotherapy development? Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, 9, 222–225.
Hood, J. L., & Wickline, S. A. (2012). A systematic approach to exosome-based translational nanomedicine. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology, 4, 458–467.
Sokolova, V., Ludwig, A. K., Hornung, S., Rotan, O., Horn, P. A., Epple, M., et al. (2011). Characterisation of exosomes derived from human cells by nanoparticle tracking analysis and scanning electron microscopy. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 87, 146–150.
Marchesano, V., Hernandez, Y., Salvenmoser, W., Ambrosone, A., Tino, A., Hobmayer, B., et al. (2013). Imaging inward and outward trafficking of gold nanoparticles in whole animals. ACS Nano, 7, 2431–2442.
Tan, A., De La, P. H., & Seifalian, A. M. (2010). The application of exosomes as a nanoscale cancer vaccine. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 5, 889–900.
Ristorcelli, E., Beraud, E., Verrando, P., Villard, C., Lafitte, D., Sbarra, V., et al. (2008). Human tumor nanoparticles induce apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. The FASEB Journal, 22, 3358–3369.
Lakhal, S., & Wood, M. J. (2011). Exosome nanotechnology: an emerging paradigm shift in drug delivery: exploitation of exosome nanovesicles for systemic in vivo delivery of RNAi heralds new horizons for drug delivery across biological barriers. BioEssays, 33, 737–741.
varez-Erviti, L., Seow, Y., Yin, H., Betts, C., Lakhal, S., & Wood, M. J. (2011). Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nature Biotechnology, 29, 341–345.
Zhu, M., Tian, X., Song, X., Li, Y., Tian, Y., Zhao, Y., et al. (2012). Nanoparticle-induced exosomes target antigen-presenting cells to initiate Th1-type immune activation. Small, 8, 2841–2848.
Halliwell, B. (2007). Dietary polyphenols: good, bad, or indifferent for your health? Cardiovascular Research, 73, 341–347.
Raffoul, J. J., Kucuk, O., Sarkar, F. H., & Hillman, G. G. (2012). Dietary agents in cancer chemoprevention and treatment. Journal of Oncology, 2012, 749310.
Sarkar, F. H., & Li, Y. (2009). Harnessing the fruits of nature for the development of multi-targeted cancer therapeutics. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 35, 597–607.
Asher, G. N., & Spelman, K. (2013). Clinical utility of curcumin extract. Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine, 19, 20–22.
Ahmad, I. U., Forman, J. D., Sarkar, F. H., Hillman, G. G., Heath, E., Vaishampayan, U., et al. (2010). Soy isoflavones in conjunction with radiation therapy in patients with prostate cancer. Nutrition and Cancer, 62, 996–1000.
Heath, E. I., Heilbrun, L. K., Li, J., Vaishampayan, U., Harper, F., Pemberton, P., et al. (2010). A phase I dose-escalation study of oral BR-DIM (BioResponse 3,3′-diindolylmethane) in castrate-resistant, non-metastatic prostate cancer. American Journal of Translational Research, 2, 402–411.
Ahmad, A., Sakr, W. A., & Rahman, K. M. (2012). Novel targets for detection of cancer and their modulation by chemopreventive natural compounds. Frontiers in Bioscience (Elite Edition), 4, 410–425.
Zhang, H. G., Kim, H., Liu, C., Yu, S., Wang, J., Grizzle, W. E., et al. (2007). Curcumin reverses breast tumor exosomes mediated immune suppression of NK cell tumor cytotoxicity. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1773, 1116–1123.
Zhuang, X., Xiang, X., Grizzle, W., Sun, D., Zhang, S., Axtell, R. C., et al. (2011). Treatment of brain inflammatory diseases by delivering exosome encapsulated anti-inflammatory drugs from the nasal region to the brain. Molecular Therapy, 19, 1769–1779.
Escudier, B., Dorval, T., Chaput, N., Andre, F., Caby, M. P., Novault, S., et al. (2005). Vaccination of metastatic melanoma patients with autologous dendritic cell (DC) derived-exosomes: results of thefirst phase I clinical trial. Journal of Translational Medicine, 3, 10.
Marleau, A. M., Chen, C. S., Joyce, J. A., & Tullis, R. H. (2012). Exosome removal as a therapeutic adjuvant in cancer. Journal of Translational Medicine, 10, 134.
Tauro, B. J., Greening, D. W., Mathias, R. A., Mathivanan, S., Ji, H., & Simpson, R. J. (2013). Two distinct populations of exosomes are released from LIM1863 colon carcinoma cell-derived organoids. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 12, 587–598.
Ogawa, Y., Taketomi, Y., Murakami, M., Tsujimoto, M., & Yanoshita, R. (2013). Small RNA transcriptomes of two types of exosomes in human whole saliva determined by next generation sequencing. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 36, 66–75.
Acknowledgements
None
Conflict of interest statements
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azmi, A.S., Bao, B. & Sarkar, F.H. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and drug resistance: a comprehensive review. Cancer Metastasis Rev 32, 623–642 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-013-9441-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-013-9441-9