Abstract
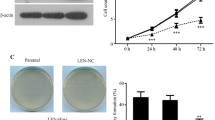
RAF kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) is a negative regulator of the RAS-mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling cascade. We investigated the expression of RKIP in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) K562 cells and the effects of RKIP on the characteristics of K562 cells. The recombinant plasmid pcDNA3.1-RKIP was established and transfected into K562 cells with the help of Lipofectamine 2000. At the same time, the RKIP-siRNA was transfected into K562 cells in another group. The expressions of RKIP in all groups were assayed by Western blot after 48 h. MTT (3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay was used to analyze the cell viability. Flow cytometry (FCM) was used to examine the cell cycle and cell apoptosis. Colony forming unit (CFU) assay was used to analyze the effect of RKIP on the clonogenic growth of CML cells. Western blot or luciferase reporter assay was used to detect the effect of RKIP on the level of phospho-ERK1/2 or the transcriptional activity of NF-κB. Western blot analysis showed that the plasmid pcDNA3.1-RKIP or RKIP-siRNA significantly enhanced or decreased RKIP expression (p < 0.01), respectively. In addition, MTT, FCM, and CFU assay indicated that the overexpression of RKIP significantly lowered the cell viability, cell proliferation and the clonogenic growth (p < 0.05), but improved cell apoptosis (p < 0.01). Western blot analysis or luciferase reporter assay showed that the level of phospho-ERK1/2 or the transcriptional activity of NF-κB was strongly inhibited by overexpression of RKIP. All these results could bring us a new perspective for biological therapy in myelogenous leukemia in the future.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rashidi A, Fisher SI. Therapy-related acute promyelocytic leukemia: a systematic review. Med Oncol. 2013;30:625.
Shah NN, Dave H, Wayne AS. Immunotherapy for pediatric leukemia. Front Oncol. 2013;3:166.
Napper AD, Watson VG. Targeted drug discovery for pediatric leukemia. Front Oncol. 2013;3:170.
Wang C, Wang X. The role of tp53 network in the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013;6:1223–9.
Ferrajoli A, Shanafelt TD, Ivan C, Shimizu M, Rabe KG, Nouraee N, et al. Prognostic value of mir-155 in individuals with monoclonal b-cell lymphocytosis and patients with b-chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2013;122:1891–9.
Koh CP, Wang CQ, Ng CE, Ito Y, Araki M, Tergaonkar V, et al. Runx1 meets mll: epigenetic regulation of hematopoiesis by two leukemia genes. Leukemia. 2013;27:1793–802.
Cianfriglia M. Targeting mdr1-p-glycoprotein (mdr1-pgp) in immunochemotherapy of acute myeloid leukemia (aml). Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2013;49:190–208.
Goldberg SL, Chen L, Guerin A, Macalalad AR, Liu N, Kaminsky M, et al. Association between molecular monitoring and long-term outcomes in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients treated with first line imatinib. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013;29:1075–82.
Chen P, Price C, Li Z, Li Y, Cao D, Wiley A, et al. Mir-9 is an essential oncogenic microrna specifically overexpressed in mixed lineage leukemia-rearranged leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:11511–6.
Smits EL, Anguille S, Berneman ZN. Interferon alpha may be back on track to treat acute myeloid leukemia. Oncoimmunology. 2013;2:e23619.
Lipshultz SE, Lipsitz SR, Kutok JL, Miller TL, Colan SD, Neuberg DS, et al. Impact of hemochromatosis gene mutations on cardiac status in doxorubicin-treated survivors of childhood high-risk leukemia. Cancer. 2013;119:3555–62.
Lin X, Yan J, Tang D. Erk kinases modulate the activation of pi3 kinase related kinases (pikks) in DNA damage response. Histol Histopathol. 2013;28:1547–54.
Chang-Yew Leow C, Gerondakis S, Spencer A. Mek inhibitors as a chemotherapeutic intervention in multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2013;3:e105.
Niba ET, Nagaya H, Kanno T, Tsuchiya A, Gotoh A, Tabata C, et al. Crosstalk between pi3 kinase/pdk1/akt/rac1 and ras/raf/mek/erk pathways downstream pdgf receptor. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;31:905–13.
Escara-Wilke J, Yeung K, Keller ET. Raf kinase inhibitor protein (rkip) in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012;31:615–20.
Deiss K, Kisker C, Lohse MJ, Lorenz K. Raf kinase inhibitor protein (rkip) dimer formation controls its target switch from raf1 to g protein-coupled receptor kinase (grk) 2. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:23407–17.
Tavel L, Jaquillard L, Karsisiotis AI, Saab F, Jouvensal L, Brans A, et al. Ligand binding study of human pebp1/rkip: Interaction with nucleotides and raf-1 peptides evidenced by nmr and mass spectrometry. PLoS One. 2012;7:e36187.
Fu X, Koller S, Abd Alla J, Quitterer U. Inhibition of g-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (grk2) triggers the growth-promoting mitogen-activated protein kinase (mapk) pathway. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:7738–55.
Al-Mulla F, Bitar MS, Taqi Z, Yeung KC. Rkip: much more than raf kinase inhibitory protein. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228:1688–702.
Baritaki S, Huerta-Yepez S, Sahakyan A, Karagiannides I, Bakirtzi K, Jazirehi A, et al. Mechanisms of nitric oxide-mediated inhibition of emt in cancer: inhibition of the metastasis-inducer snail and induction of the metastasis-suppressor rkip. Cell Cycle. 2010;9:4931–40.
Jia B, Liu H, Kong Q, Li B. Rkip expression associated with gastric cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Tumour Biol. 2012;33:919–25.
Zeng L, Imamoto A, Rosner MR. Raf kinase inhibitory protein (rkip): a physiological regulator and future therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008;12:1275–87.
Wu K, Bonavida B. The activated nf-kappab-snail-rkip circuitry in cancer regulates both the metastatic cascade and resistance to apoptosis by cytotoxic drugs. Crit Rev Immunol. 2009;29:241–54.
Kim SO, Ives KL, Wang X, Davey RA, Chao C, Hellmich MR. Raf-1 kinase inhibitory protein (rkip) mediates ethanol-induced sensitization of secretagogue signaling in pancreatic acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:33377–88.
Zhao D, Ma J, Shi J, Cheng L, Li F, Jiang X, et al. Raf kinase inhibitor protein inhibits esophageal cancer cell invasion through downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression. Oncol Rep. 2013;30:304–12.
Li SW, Wang H, Liu ML, Zhang HB, Xiang YQ, Lv X, et al. Positive effect of high rkip expression on reduced distant metastasis by chemotherapy when combined with radiotherapy in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a prospective study. Med Oncol. 2013;30:322.
Ren G, Baritaki S, Marathe H, Feng J, Park S, Beach S, et al. Polycomb protein ezh2 regulates tumor invasion via the transcriptional repression of the metastasis suppressor rkip in breast and prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2012;72:3091–104.
Cardile V, Malaponte G, Loreto C, Libra M, Caggia S, Trovato FM, et al. Raf kinase inhibitor protein (rkip) and phospho-rkip expression in melanomas. Acta Histochem. 2013;115:795–802.
Koelzer VH, Karamitopoulou E, Dawson H, Kondi-Pafiti A, Zlobec I, Lugli A. Geographic analysis of rkip expression and its clinical relevance in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;108:2088–96.
Zheng X, Chang RL, Cui XX, Avila G, Huang MT, Liu Y, et al. Inhibition of nf-kappab by (e)3-[(4-methylphenyl)-sulfonyl]-2-propenenitrile (bay11-7082; bay) is associated with enhanced 12-o-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced growth suppression and apoptosis in human prostate cancer pc-3 cells. Int J Oncol. 2008;32:257–64.
Martinho O, Pinto F, Granja S, Miranda-Goncalves V, Moreira MA, Ribeiro LF, et al. Rkip inhibition in cervical cancer is associated with higher tumor aggressive behavior and resistance to cisplatin therapy. PLoS One. 2013;8:e59104.
Zaravinos A, Chatziioannou M, Lambrou GI, Boulalas I, Delakas D, Spandidos DA. Implication of raf and rkip genes in urinary bladder cancer. Pathol Oncol Res: POR. 2011;17:181–90.
Zaravinos A, Kanellou P, Baritaki S, Bonavida B, Spandidos DA. Braf and rkip are significantly decreased in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:1402–8.
Zaravinos A, Kanellou P, Lambrou GI, Spandidos DA. Gene set enrichment analysis of the nf-kappab/snail/yy1/rkip circuitry in multiple myeloma. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:4987–5005.
Fried I, Wolfler A, Quehenberger F, Hoefler G, Sill H, Zebisch A. Mutations indnmt3a and loss of rkip are independent events in acute monocytic leukemia. Haematologica. 2012;97:1936–7.
Zebisch A, Wolfler A, Fried I, Wolf O, Lind K, Bodner C, et al. Frequent loss of raf kinase inhibitor protein expression in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2012;26:1842–9.
Klysik J, Theroux SJ, Sedivy JM, Moffit JS, Boekelheide K. Signaling crossroads: the function of raf kinase inhibitory protein in cancer, the central nervous system and reproduction. Cell Signal. 2008;20:1–9.
Hagan S, Garcia R, Dhillon A, Kolch W. Raf kinase inhibitor protein regulation of raf and mapk signaling. Methods Enzymol. 2006;407:248–59.
Khamis ZI, Iczkowski KA, Sang QX. Metastasis suppressors in human benign prostate, intraepithelial neoplasia, and invasive cancer: their prospects as therapeutic agents. Med Res Rev. 2012;32:1026–77.
Hao C, Wei S, Tong Z, Li S, Shi Y, Wang X, et al. The effects of rkip gene expression on the biological characteristics of human triple-negative breast cancer cells in vitro. Tumour Biol. 2012;33:1159–67.
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Franklin RA, Montalto G, et al. Ras/raf/mek/erk and pi3k/pten/akt/mtor cascade inhibitors: how mutations can result in therapy resistance and how to overcome resistance. Oncotarget. 2012;3:1068–111.
Britten CD. Pi3k and mek inhibitor combinations: examining the evidence in selected tumor types. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013;71:1395–409.
Beshir AB, Ren G, Magpusao AN, Barone LM, Yeung KC, Fenteany G. Raf kinase inhibitor protein suppresses nuclear factor-kappab-dependent cancer cell invasion through negative regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression. Cancer Lett. 2010;299:137–49.
Ciarmela P, Marzioni D, Islam MS, Gray PC, Terracciano L, Lorenzi T, et al. Possible role of rkip in cytotrophoblast migration: immunohistochemical and in vitro studies. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227:1821–8.
Odabaei G, Chatterjee D, Jazirehi AR, Goodglick L, Yeung K, Bonavida B. Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein: structure, function, regulation of cell signaling, and pivotal role in apoptosis. Adv Cancer Res. 2004;91:169–200.
Jazirehi AR, Vega MI, Chatterjee D, Goodglick L, Bonavida B. Inhibition of the raf-mek1/2-erk1/2 signaling pathway, bcl-xl down-regulation, and chemosensitization of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma b cells by rituximab. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7117–26.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (BK20131199).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Sun, B., Zhu, J. et al. Expression of RKIP in chronic myelogenous leukemia K562 cell and inhibits cell proliferation by regulating the ERK/MAPK pathway. Tumor Biol. 35, 10057–10066 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2312-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2312-3