Abstract
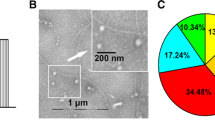
Breast cancer (BCa) remains chemo-unresponsive by inevitable progression of resistance to first-line treatment with docetaxel (doc). Emerging studies indicate that exosomes act as mediators of intercellular communication between heterogeneous populations of tumor cells, engendering a transmitted drug resistance for cancer development. Such modulatory effects have been related to the constant shuttle of biologically active molecules including microRNAs (miRNAs). Here, we aimed to investigate the relevance of exosome-mediated miRNA delivery in resistance transmission of BCa subpopulations. Using microarray and polymerase chain reaction, we found that exosomes from doc-resistant BCa cells (D/exo) loaded cellular miRNAs. Following D/exo transfer to the fluorescent sensitive cells (GFP-S), some miRNAs were significantly increased in recipient GFP-S. Target gene prediction and pathway analysis revealed the involvement of the top 20 most abundant miRNAs of D/exo in pathways implicated in therapy failure. Coculture assays showed that miRNA-containing D/exo increased the overall resistance of GFP-S to doc exposure. Moreover, D/exo was able to alter gene expression in GFP-S. Our results open up an intriguing possibility that drug-resistant BCa cells may spread chemoresistance to sensitive ones by releasing exosomes and that the effects could be partly attributed to the intercellular transfer of specific miRNAs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeSantis C, Siegel R, Bandi P, Jemal A. Breast cancer statistics, 2011. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(6):409–18. doi:10.3322/caac.20134.
Gottesman MM. Mechanisms of cancer drug resistance. Annu Rev Med. 2002;53:615–27. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.53.082901.103929.
Ciravolo V, Huber V, Ghedini GC, Venturelli E, Bianchi F, Campiglio M, et al. Potential role of HER2-overexpressing exosomes in countering trastuzumab-based therapy. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(2):658–67. doi:10.1002/jcp.22773.
Corcoran C, Rani S, O'Brien K, O'Neill A, Prencipe M, Sheikh R, et al. Docetaxel-resistance in prostate cancer: evaluating associated phenotypic changes and potential for resistance transfer via exosomes. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50999. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050999.
Safaei R, Larson BJ, Cheng TC, Gibson MA, Otani S, Naerdemann W, et al. Abnormal lysosomal trafficking and enhanced exosomal export of cisplatin in drug-resistant human ovarian carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4(10):1595–604. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.mct-05-0102.
Simons M, Raposo G. Exosomes—vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21(4):575–81. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.03.007.
Kucharzewska P, Christianson HC, Welch JE, Svensson KJ, Fredlund E, Ringner M, et al. Exosomes reflect the hypoxic status of glioma cells and mediate hypoxia-dependent activation of vascular cells during tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(18):7312–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.1220998110.
Filipazzi P, Burdek M, Villa A, Rivoltini L, Huber V. Recent advances on the role of tumor exosomes in immunosuppression and disease progression. Semin Cancer Biol. 2012;22(4):342–9. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.02.005.
Luga V, Zhang L, Viloria-Petit AM, Ogunjimi AA, Inanlou MR, Chiu E, et al. Exosomes mediate stromal mobilization of autocrine Wnt-PCP signaling in breast cancer cell migration. Cell. 2012;151(7):1542–56. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.024.
Kahlert C, Kalluri R. Exosomes in tumor microenvironment influence cancer progression and metastasis. J Mol Med. 2013;91(4):431–7. doi:10.1007/s00109-013-1020-6. Berlin, Germany.
Azmi AS, Bao B, Sarkar FH. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and drug resistance: a comprehensive review. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013;32(3–4):623–42. doi:10.1007/s10555-013-9441-9.
Chen WX, Zhong SL, Ji MH, Pan M, Hu Q, Lv MM, et al. MicroRNAs delivered by extracellular vesicles: an emerging resistance mechanism for breast cancer. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med. 2014;35(4):2883–92. doi:10.1007/s13277-013-1417-4.
Chiba M, Kimura M, Asari S. Exosomes secreted from human colorectal cancer cell lines contain mRNAs, microRNAs and natural antisense RNAs, that can transfer into the human hepatoma HepG2 and lung cancer A549 cell lines. Oncol Rep. 2012;28(5):1551–8. doi:10.3892/or.2012.1967.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136(2):215–33. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002.
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654–9. doi:10.1038/ncb1596.
Morel L, Regan M, Higashimori H, Ng SK, Esau C, Vidensky S, et al. Neuronal exosomal miRNA-dependent translational regulation of astroglial glutamate transporter GLT1. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(10):7105–16. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.410944.
Xiao X, Yu S, Li S, Wu J, Ma R, Cao H, et al. Exosomes: decreased sensitivity of lung cancer A549 cells to cisplatin. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e89534. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0089534.
Munoz JL, Bliss SA, Greco SJ, Ramkissoon SH, Ligon KL, Rameshwar P. Delivery of functional anti-miR-9 by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes to glioblastoma multiforme cells conferred chemosensitivity. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2013;2:e126. doi:10.1038/mtna.2013.60.
Knaust E, Porwit-MacDonald A, Gruber A, Xu D, Peterson C. Heterogeneity of isolated mononuclear cells from patients with acute myeloid leukemia affects cellular accumulation and efflux of daunorubicin. Haematologica. 2000;85(2):124–32.
Li WJ, Zhong SL, Wu YJ, Xu WD, Xu JJ, Tang JH, et al. Systematic expression analysis of genes related to multidrug-resistance in isogenic docetaxel- and adriamycin-resistant breast cancer cell lines. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40(11):6143–50. doi:10.1007/s11033-013-2725-x.
Zhong S, Li W, Chen Z, Xu J, Zhao J. MiR-222 and miR-29a contribute to the drug-resistance of breast cancer cells. Gene. 2013;531(1):8–14. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.062.
Li XJ, Ji MH, Zhong SL, Zha QB, Xu JJ, Zhao JH, et al. MicroRNA-34a modulates chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells to adriamycin by targeting Notch1. Arch Med Res. 2012;43(7):514–21. doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2012.09.007.
Hu Q, Chen WX, Zhong SL, Zhang JY, Ma TF, Ji H, et al. MicroRNA-452 contributes to the docetaxel resistance of breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med. 2014. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-1834-z.
Miot S, Gianni-Barrera R, Pelttari K, Acharya C, Mainil-Varlet P, Juelke H, et al. In vitro and in vivo validation of human and goat chondrocyte labeling by green fluorescent protein lentivirus transduction. Tissue Eng C Methods. 2010;16(1):11–21. doi:10.1089/ten.TEC.2008.0698.
Yuan A, Farber EL, Rapoport AL, Tejada D, Deniskin R, Akhmedov NB, et al. Transfer of microRNAs by embryonic stem cell microvesicles. PLoS One. 2009;4(3):e4722. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004722.
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg L, Epstein EJ, et al. Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet. 2005;37(5):495–500. doi:10.1038/ng1536.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120(1):15–20. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.035.
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S, Enright AJ. miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(Database issue):D154–8. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm952.
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Gene Ontol Consortium Nat Genet. 2000;25(1):25–9. doi:10.1038/75556.
Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M, Hirakawa M, Itoh M, et al. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(Database issue):D480–4. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm882.
Huang da W, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Kir J, Liu D, Bryant D, et al. DAVID Bioinformatics Resources: expanded annotation database and novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(Web Server issue):W169–75. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm415.
Gusev Y. Computational methods for analysis of cellular functions and pathways collectively targeted by differentially expressed microRNA. Methods. 2008;44(1):61–72. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.10.005. San Diego, Calif.
Sebolt-Leopold JS, Herrera R. Targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade to treat cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(12):937–47. doi:10.1038/nrc1503.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–74. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013.
Harburg GC, Hinck L. Navigating breast cancer: axon guidance molecules as breast cancer tumor suppressors and oncogenes. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2011;16(3):257–70. doi:10.1007/s10911-011-9225-1.
Loh YN, Hedditch EL, Baker LA, Jary E, Ward RL, Ford CE. The Wnt signalling pathway is upregulated in an in vitro model of acquired tamoxifen resistant breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:174. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-174.
Wang SE, Xiang B, Guix M, Olivares MG, Parker J, Chung CH, et al. Transforming growth factor beta engages TACE and ErbB3 to activate phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt in ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancer and desensitizes cells to trastuzumab. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28(18):5605–20. doi:10.1128/mcb.00787-08.
Li X, Liu X, Xu W, Zhou P, Gao P, Jiang S, et al. c-MYC-regulated miR-23a/24-2/27a cluster promotes mammary carcinoma cell invasion and hepatic metastasis by targeting Sprouty2. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(25):18121–33. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.478560.
Koga Y, Yasunaga M, Moriya Y, Akasu T, Fujita S, Yamamoto S, et al. Exosome can prevent RNase from degrading microRNA in feces. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2011;2(4):215–22. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2078-6891.2011.015.
Gibbings DJ, Ciaudo C, Erhardt M, Voinnet O. Multivesicular bodies associate with components of miRNA effector complexes and modulate miRNA activity. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(9):1143–9. doi:10.1038/ncb1929.
Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Ochiya T. Circulating microRNA in body fluid: a new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 2010;101(10):2087–92. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01650.x.
Chen X, Liang H, Zhang J, Zen K, Zhang CY. Secreted microRNAs: a new form of intercellular communication. Trends Cell Biol. 2012;22(3):125–32. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2011.12.001.
Kogure T, Lin WL, Yan IK, Braconi C, Patel T. Intercellular nanovesicle-mediated microRNA transfer: a mechanism of environmental modulation of hepatocellular cancer cell growth. Hepatology. 2011;54(4):1237–48. doi:10.1002/hep.24504. Baltimore, Md.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the funding body for supporting this work: the National Natural Science Foundation of China provided to Jin-hai Tang (81272470). We also thank Jun Zhang, Hao Ji, and Xiao-hui Zhang for their discussion and help in our manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Wei-xian Chen and Yan-qin Cai contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Wx., Cai, Yq., Lv, Mm. et al. Exosomes from docetaxel-resistant breast cancer cells alter chemosensitivity by delivering microRNAs. Tumor Biol. 35, 9649–9659 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2242-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2242-0