Abstract
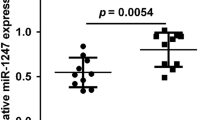
Neuroblastoma, featured by a high rate of spontaneous remissions, is the most common extra-cranial solid tumor in infants and children. Numerous reports have demonstrated that MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play essential roles in cancer progression, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. miR-421 functions as an onco-miR in some malignancies. However, its role in neuroblastoma remains poorly understood. In the present study, we found that miR-421 was increased in neuroblastoma tissues compared with matched adjacent normal tissues. Forced overexpression of miR-421 substantially enhanced cell proliferation, cell-cycle progression, migration, and invasion of neuroblastoma cells. At the molecular level, tumor suppressor menin was found to be a target of miR-421. Furthermore, downregulation of menin by small interfering RNA oligos exhibited similar effects with overexpression of miR-421. On the other hand, overexpression of menin partially reversed the proliferative effects of miR-421 in neuroblastoma cells. Collectively, miR-421 may promote neuroblastoma cell growth and motility partially by targeting menin.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheung NK, Dyer MA. Neuroblastoma: developmental biology, cancer genomics and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:397–411.
Pietras W. Advances and changes in the treatment of children with nephroblastoma. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2012;21:809–20.
Sridhar S, Al-Moallem B, Kamal H, Terrile M, Stallings RL. New insights into the genetics of neuroblastoma. Mol Diagn Ther. 2013;17:63–9.
Ameres SL, Zamore PD. Diversifying microRNA sequence and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14:475–88.
Sun K, Lai EC. Adult-specific functions of animal microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2013;14:535–48.
Ling H, Fabbri M, Calin GA. MicroRNAs and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12:847–65.
Ohira M, Nakagawara A. Global genomic and RNA profiles for novel risk stratification of neuroblastoma. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:2295–301.
Buechner J, Einvik C. N-myc and noncoding RNAs in neuroblastoma. Mol Cancer Res. 2012;10:1243–53.
Xin C, Buhe B, Hongting L, Chuanmin Y, Xiwei H, Hong Z, et al. MicroRNA-15a promotes neuroblastoma migration by targeting reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs (RECK) and regulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. FEBS J. 2013;280:855–66.
Yang H, Li Q, Zhao W, Yuan D, Zhao H, Zhou Y. miR-329 suppresses the growth and motility of neuroblastoma by targeting KDM1A. FEBS Lett. 2014;588:192–7.
Chen L, Tang Y, Wang J, Yan Z, Xu R. miR-421 induces cell proliferation and apoptosis resistance in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma via downregulation of FOXO4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;435:745–50.
Zhou H, Xiao B, Zhou F, Deng H, Zhang X, Lou Y, et al. MiR-421 is a functional marker of circulating tumor cells in gastric cancer patients. Biomarkers. 2012;17:104–10.
Zhong XY, Yu JH, Zhang WG, Wang ZD, Dong Q, Tai S, et al. MicroRNA-421 functions as an oncogenic miRNA in biliary tract cancer through down-regulating farnesoid X receptor expression. Gene. 2012;493:44–51.
Wu X, Hua X. Menin, histone h3 methyltransferases, and regulation of cell proliferation: current knowledge and perspective. Curr Mol Med. 2008;8:805–15.
Lairmore TC, Chen H. Role of menin in neuroendocrine tumorigenesis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;668:87–95.
Balogh K, Patócs A, Hunyady L, Rácz K. Menin dynamics and functional insight: take your partners. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;326:80–4.
Gallo A, Cuozzo C, Esposito I, Maggiolini M, Bonofiglio D, Vivacqua A, et al. Menin uncouples Elk-1, JunD and c-Jun phosphorylation from MAP kinase activation. Oncogene. 2002;21:6434–45.
Wang Y, Ozawa A, Zaman S, Prasad NB, Chandrasekharappa SC, Agarwal SK, et al. The tumor suppressor protein menin inhibits AKT activation by regulating its cellular localization. Cancer Res. 2011;71:371–82.
Swarts DR, Ramaekers FC, Speel EJ. Molecular and cellular biology of neuroendocrine lung tumors: evidence for separate biological entities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1826;2012:255–71.
Agarwal SK. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. Front Horm Res. 2013;41:1–15.
Wu Y, Feng ZJ, Gao SB, Matkar S, Xu B, Duan HB, et al. Interplay between menin and K-Ras in regulating lung adenocarcinoma. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:40003–11.
Gang D, Hongwei H, Hedai L, Ming Z, Qian H, Zhijun L. The tumor suppressor protein menin inhibits NF-κB-mediated transactivation through recruitment of Sirt1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40:2461–6.
Luzi E, Marini F, Giusti F, Galli G, Cavalli L, Brandi ML. The negative feedback-loop between the oncomir Mir-24-1 and menin modulates the Men1 tumorigenesis by mimicking the "Knudson's second hit". PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e39767.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Figure 1
Expression levels of miR-421 were compared in SHSY5Y and SHEP cells by real-time PCR. (A)Expression of miR-421 was determined in SHEP cells after transfection of miR-421 mimics or negative controls (NC). (C) The cell viability of SHEP cells was determined by MTT assays. (D) The growth curve of SHEP cells after miR-421 transfection compared to NC. (E) The cell proliferative potential (BrdU) was determined in SHEP cells. A450 absorption was assayed after transfection for 24 hr. (F) The cell-cycle phase of SHSY5Y cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, compared with NC. (GIF 6 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
(A) Expression levels of miR-421 were determined in three cell lines by real-time PCR. (B)Expression of miR-421 was determined in IMR-32 cells after transfection of miR-421 mimics or negative controls (NC). (C) The cell viability of IMR-32 cells was determined by MTT assays. (D) The growth curve of IMR-32 cells after miR-421 transfection compared to NC. (E) The cell proliferative potential (BrdU) was determined in IMR-32cells. A450 absorption was assayed after transfection for 24 hr. (F) The cell-cycle phase of IMR-32 cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, compared with NC. (GIF 6 kb)
Supplementary Figure 3
Representative Menin protein levels in human NB and adjacent normal tissues from two patients. 40 μg amount of tissue lysates were used in the western blot experiments. (GIF 0 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Li, W., Zhang, JG. et al. Downregulation of tumor suppressor menin by miR-421 promotes proliferation and migration of neuroblastoma. Tumor Biol. 35, 10011–10017 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1921-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1921-1