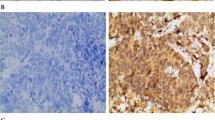
Abstract
Vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) is considered as a prime mediator of lymphangiogenesis and has been implicated in carcinogenesis and metastasis. Various studies examined the relationship between VEGF-C protein overexpression with the clinical outcome in patients with breast cancer but yielded conflicting results. Electronic databases updated to April 2013 were searched to find relevant studies. A meta-analysis was conducted with eligible studies which quantitatively evaluated the relationship between VEGF-C overexpression and survival of patients with breast cancer. Survival data were aggregated and quantitatively analyzed. We performed a meta-analysis of 11 studies (n = 1,357 patients) that evaluated the correlation between VEGF-C overexpression detected by immunohistochemistry and survival in patients with breast cancer. Combined hazard ratios suggested that VEGF-C overexpression was not associated with poor prognosis of disease-free survival (HR [hazard ratio] = 0.80, 95 % CI [confidence interval]: 0.51–1.09), overall survival (OS) (HR = 1.08, 95 % CI: 0.37–1.78) in patients with breast cancer. In the stratified analysis by patient source, significantly risks were not found among Asians or non-Asians. No significant heterogeneity was observed among all studies. VEGF-C overexpression was not associated with poor disease-free survival or overall survival in breast cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Saurel CA, Patel TA, Perez EA. Changes to adjuvant systemic therapy in breast cancer: a decade in review. Clin Breast Cancer. 2010;10:196–208.
Colozza M, Azambuja E, Cardoso F, Sotiriou C, Larsimont D, Piccart MJ. Proliferative markers as prognostic and predictive tools in early breast cancer: where are we now? Ann Oncol. 2005;16:1723–39.
Hayes DF. Prognostic and predictive factors revisited. Breast. 2008;14:493–9.
Callagy GM, Webber MJ, Pharoah PD, Caldas C. Meta-analysis confirms BCL2 is an independent prognostic marker in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:153.
Ferrara N. VEGF and the quest for tumour angiogenesis factors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:795–803.
Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM. Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1011–27.
Karkkainen MJ, Alitalo K. Lymphatic endothelial regulation, lymphoedema, and lymph node metastasis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002;13:9–18.
Da MX, Wu Z, Tian HW. Tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymphangiogenic growth factors. Arch Med Res. 2008;39:365–72.
Cao R, Björndahl MA, Religa P, Clasper S, Garvin S, Galter D, et al. PDGF-BB induces intratumoral lymphangiogenesis and promotes lymphatic metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:333–45.
Chang LK, Garcia-Cardena G, Farnebo F, Fannon M, Chen EJ, Butterfield C, et al. Dose-dependent response of FGF-2 for lymphangiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:11658–63.
Leong SP, Cady B, Jablons DM, Garcia-Aguilar J, Reintgen D, Jakub J, et al. Clinical patterns of metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006;25:221–32.
Altman DG. Systematic reviews of evaluations of prognostic variables. BMJ. 2001;323(7306):224–8.
Zhan P, Qian Q, Yu LK. Prognostic value of COX-2 expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis. 2013;5(1):40–7. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.01.02.
Zhan P, Qian Q, Wan B, Yan TD, Yu LK. Prognostic value of TTF-1 expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Transl Cancer Res. 2013. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2218-676X.2013.02.08.
Zhan P, Wang Q, Qian Q, Yu LK. Megestrol acetate in cancer patients with anorexia-cachexia syndrome: a meta-analysis. Transl Cancer Res. 2013;2(2):74–9. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2218-676X.2013.04.13.
Zhan P, Wang Q, Qian Q, Yu LK. Risk of venous thromboembolism with the erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) for the treatment of cancer-associated anemia: a meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Chin Clin Oncol. 2013. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2304-3865.2013.01.02.
Zhan P, Qian Q, Yu LK. Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue: a meta-analysis. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2013. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2304-3881.2013.06.06.
Zhan P, Qian Q, Yu LK. Serum VEGF level is associated with the outcome of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2013. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2304-3881.2013.06.07.
Zhan P, Ji YN, Yu LK. VEGF is associated with the poor survival of patients with prostate cancer: a meta-analysis. Transl Androl Urol. 2013. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2013.07.01.
Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L. Extracting summary statistics to perform metaanalyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med. 1998;17:2815–34.
Yusuf S, Peto R, Lewis J, et al. Blockade during and after myocardial infarction: an overview of the randomized trials. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1985;27:335–71.
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–88.
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315:629–34.
Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. 1994;50:1088–101.
Kinoshita J, Kitamura K, Kabashima A, Saeki H, Tanaka S, Sugimachi K. Clinical significance of vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2001;66:159–64.
Yang W, Klos K, Yang Y, Smith TL, Shi D, Yu D. ErbB2 overexpression correlates with increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factors A, C, and D in human breast carci-noma. Cancer. 2002;94:2855–61.
Nakamura Y, Yasuoka H, Tsujimoto M, Yang Q, Tsukiyama A, Imabun S, et al. Clinicopathological significance of vascular endothelial growth factor-C in breast carcinoma with long-term follow-up. Mod Pathol. 2003;16:309–14.
Mylona E, Alexandrou P, Mpakali A, Giannopoulou I, Liapis G, Markaki S, et al. Clinico-pathological and prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF)-C and -D and VEGF receptor 3 in inva-sive breast carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2007;33:294–300.
Mohammed RA, Green A, El-Shikh S, Paish EC, Ellis IO, Martin SG. Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial cell growth factors -A, -C and -D in breast cancer and their relationship with angio- and lymphangiogenesis. Br J Cancer. 2007;96:1092–100.
Gisterek I, Matkowski R, Kozlak J, Dus D, Lacko A, Szelachowska J, et al. Evaluation of prognostic value of VEGF-C and VEGF-D in breast cancer—10 years follow-up analysis. Anticancer Res. 2007;27:2797–802.
Zhang XH, Huang DP, Guo GL, Chen GR, Zhang HX, Wan L, et al. Coexpression of VEGF-C and COX-2 and its association with lymphangiogenesis in human breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:4.
Gu Y, Qi X, Guo S. Lymphangiogenesis induced by VEGF-C and VEGF-D promotes metastasis and a poor outcome in breast carcinoma: a retrospective study of 61 cases. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2008;25:717–25.
Tezuka K, Onoda N, Takashima T, Ishikawa T, Wakasa T, Wakasa K, et al. Clinical significance of intra-tumoral sinusoidal structures showing lympho-endothelial immunoreactivity in breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 2008;20:25–32.
Tsutsui S, Matsuyama A, Yamamoto M, Takeuchi H, Oshiro Y, Ishida T, et al. The Akt expression correlates with the VEGF-A and -C expression as well as the microvessel and lymphatic vessel density in breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 2010;23:621–30.
Zhao YC, Ni XJ, Li Y, Dai M, Yuan ZX, Zhu YY, et al. Peritumoral lymphangiogenesis induced by vascular endothelial growth factor C and D promotes lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. World J Surg Oncol. 2012;10:165.
Parikh AA, Ellis LM. The vascular endothelial growth factor family and its receptors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004;18(5):951–71.
Xie K, Wei D, Shi Q, Huang S. Constitutive and inducible expression and regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004;15(5):297–324.
Lee J, Gray A, Yuan J, Luoh SM, Avraham H, Wood WI. Vascular endothelial growth factor-related protein: a ligand and specific activator of the tyrosine kinase receptor Flt4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93(5):1988–92.
Jeltsch M, Kaipainen A, Joukov V, Meng X, Lakso M, Rauvala H, et al. Hyperplasia of lymphatic vessels in VEGF-C transgenic mice. Science. 1997;276(5317):1423–142.
Yulong H, Iiro R, Katri P, et al. Vascular endothelial cell growth factor receptor 3-mediated activation of lymphatic endothelium is crucial for tumor cell entry and spread via lymphatic vessels. Cancer res. 2005;46:4739–46.
Achen MG, Stacker SA. Tumor lymphangiogenesis and metastatic spread-new players begin to emerge. Int J Cancer. 2006;119:1755–60.
Kyzas PA, Cunha IW, Ioannidis JP. Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor immunohistochemical expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(4):1434–40.
Zhan P, Wang J, Lv XJ, Wang Q, Qiu LX, Lin XQ, et al. Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in patients with lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. J Thorac Oncol. 2009;4(9):1094–103.
Des Guetz G, Uzzan B, Nicolas P, Cucherat M, Morere JF, Benamouzig R, et al. Microvessel density and VEGF expression are prognostic factors in colorectal cancer. Meta-analysis of the literature. Br J Cancer. 2006;94(12):1823–32.
Peng L, Zhan P, Zhou Y, Fang W, Zhao P, Zheng Y, et al. Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor immunohistochemical expression in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(10):9473–84.
Schoenleber SJ, Kurtz DM, Talwalkar JA, Roberts LR, Gores GJ. Prognostic role of vascular endothelial growth factor in hepatocellular carcinoma: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 2009;100(9):1385–92.
Kowanetz M, Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathways: therapeutic perspective. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(17):5018–22.
Ferrara N, Hillan KJ, Gerber HP, Novotny W. Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3(5):391–400.
Begg CB, Berlin JA. Publication bias: a problem in interpreting medical data. J R Stat Soc A. 1988;151:419–63.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81172501).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sheng Gao and Jing-jing Ma contributed equally to this work and should be considered as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, S., Ma, JJ. & Lu, C. Prognostic significance of VEGF-C immunohistochemical expression in breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Tumor Biol. 35, 1523–1529 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1211-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1211-3