Abstract
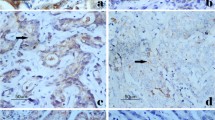
The aim of this study was to investigate the expression and prognostic significance of RIN1 in gastric adenocarcinoma. RIN1 expression was analyzed using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), Western blotting, and immunohistochemical staining on tissue samples from a consecutive series of 315 gastric adenocarcinoma patients who underwent tumor resections between 2003 and 2006. The relationship between RIN1 expression, clinicopathological factors, and patient survival was investigated. qRT-PCR results showed that the RIN1 mRNA expression was higher in tumor tissue samples than in the adjacent normal tissues, and a corresponding increase in protein expression was confirmed by Western blotting. Immunohistochemical staining indicated that RIN1 is highly expressed in 54.3 % of gastric adenocarcinomas. RIN1 expression levels were closely associated with tumor size, histological differentiation, tumor stage, and lymph node involvement. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showed that high RIN1 expression exhibited a significant correlation with poor prognosis for gastric adenocarcinoma patients. Multivariate analysis revealed that RIN1 expression is an independent prognostic parameter for the overall survival rate of gastric adenocarcinoma patients. Our data suggest that RIN1 plays an important role in gastric adenocarcinoma progression and that a high RIN1 expression predicts an unfavorable prognosis in gastric adenocarcinoma patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hohenberger P, Gretschel S. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2003;362:305–15. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13975-X.
Dcken BJ, Bigam DL, Cass C, Mackey JR, Joy AA, Hamilton SM. Gastric adenocarcinoma: review and considerations for future directions. Ann Surg. 2005;241:27–39. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000149300.28588.23.
Zhang B, Cao W, Zhang F, Zhang L, Niu R, Niu Y, Fu L, Hao X, Cao X. Protein interacting with C alpha kinase 1 (PICK1) is involved in promoting tumor growth and correlates with poor prognosis of human breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:1536–42. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01566.x.
Han L, Wong D, Dhaka A, Afar D, White M, Xie W, Herschman H, Witte O, Colicelli J. Protein binding and signaling properties of RIN1 suggest a unique effector function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:4954–9. PMCID: PMC24612.
Tall GG, Barbieri MA, Stahl PD, Horazdovsky BF. Ras-activated endocytosis is mediated by the Rab5 guanine nucleotide exchange activity of RIN1. Dev Cell. 2001;1:73–82.
Barbieri MA, Kong C, Chen PI, Horazdovsky BF, Stahl PD. The SRC homology 2 domain of Rin1 mediates its binding to the epidermal growth factor receptor and regulates receptor endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:32027–36. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304324200.
Hu H, Bliss JM, Wang Y, Colicelli J. RIN1 is an ABL tyrosine kinase activator and a regulator of epithelial-cell adhesion and migration. Curr Biol. 2005;15:815–23. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2005.03.049.
Deininger K, Eder M, Kramer ER, Zieglgänsberger W, Dodt HU, Dornmair K, Colicelli J, Klein R. The Rab5 guanylate exchange factor Rin1 regulates endocytosis of the EphA4 receptor in mature excitatory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:12539–44. doi:10.1073/pnas.0801174105.
Dhaka A, Costa RM, Hu H, Irvin DK, Patel A, Kornblum HI, Silva AJ, O’Dell TJ, Colicelli J. The RAS effector RIN1 modulates the formation of aversive memories. J Neurosci. 2003;23:748–57.
Goi T, Senda K, Yamaguchi A. Expression of RIN1 gene in gastric and colorectal cancers. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 2001;102:783.
Morikawa J, Li H, Kim S, Nishi K, Ueno S, Suh E, Dougherty E, Shmulevich I, Shiku H, Zhang W, Kobayashi T. Identification of signature genes by microarray for acute myeloid leukemia without maturation and acute promyelocytic leukemia with t(15;17) (q22;q12) (PML/RARalpha). Int J Oncol. 2003;23:617–25.
Milstein M, Mooser CK, Hu H, Fejzo M, Slamon D, Goodglick L, Dry S, Colicelli J. RIN1 is a breast tumor suppressor gene. Cancer Res. 2007;67:11510–6. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1147.
Senda K, Goi T, Hirono Y, Katayama K, Yamaguchi A. Analysis of RIN1 gene expression in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2007;17:1171–5.
Tomshine JC, Severson SR, Wigle DA, Sun Z, Beleford DA, Shridhar V, Horazdovsky BF. Cell proliferation and epidermal growth factor signaling in non-small cell lung adenocarcinoma cell lines are dependent on Rin1. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:26331–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.033514.
Chetcuti A, Aktas S, Mackie N, Ulger C, Toruner G, Alkan M, Catchpoole D. Expression profiling reveals MSX1 and EphB2 expression correlates with the invasion capacity of Wilms tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2011;57:950–7. doi:10.1002/pbc.23003.
Fujioka M, Goi T, Hirono Y, Katayama K, Yamaguchi A. Cloning of a novel splicing variant of RIN1 and its expression in gastric and colon cancer. Oncol Res. 2009;17:593–9.
Brown RS, Wahl RL. Overexpression of Glut-1 glucose transporter in human breast cancer. An immunohistochemical study. Cancer. 1993;72:2979–85.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Kelly K, Crowley J, Bunn Jr PA, Presant CA, Grevstad PK, Moinpour CM, Ramsey SD, Wozniak AJ, Weiss GR, Moore DF, Israel VK, Livingston RB, Gandara DR. Randomized phase III trial of paclitaxel plus carboplatin versus vinorelbine plus cisplatin in the treatment of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a Southwest Oncology Group trial. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:3210–8.
Hennessy BT, Hanrahan EO, Daly PA. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma: an update. Lancet Oncol. 2004;5:341–53.
Shuster MI, Han L, Le Beau MM, Davis E, Sawicki M, Lese CM, Park NH, Colicelli J, Gollin SM. A consistent pattern of RIN1 rearrangements in oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines supports a breakage–fusion–bridge cycle model for 11q13 amplification. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2000;28:153–63.
Zainabadi K, Benyamini P, Chakrabarti R, Veena MS, Chandrasekharappa SC, Gatti RA, Srivatsan ES. A 700-kb physical and transcription map of the cervical cancer tumor suppressor gene locus on chromosome 11q13. Genomics. 2005;85:704–14.
Hu H, Milstein M, Bliss JM, Thai M, Malhotra G, Huynh LC, Colicelli J. Integration of transforming growth factor beta and RAS signaling silences a RAB5 guanine nucleotide exchange factor and enhances growth factor-directed cell migration. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:1573–83. doi:10.1128/MCB.01087-07.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Hai-Feng Yu, Gang Zhao, and Zhi-Jun Ge contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, HF., Zhao, G., Ge, ZJ. et al. High RIN1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma. Tumor Biol. 33, 1557–1563 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0409-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0409-0