Abstract
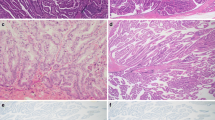
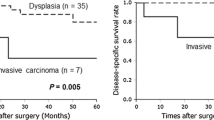
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) of the pancreas are classified into the following four histopathologic subtypes: gastric, intestinal, pancreatobiliary, and oncocytic. However, the clinicopatholgic characteristics of IPMN subtypes have not been fully clarified. Recently, a subgroup classification of minimally invasive intraductal papillary mucinous carcinomas (MI-IPMCs) was suggested in contrast to overt invasive carcinoma from IPMCs (IC-IPMCs). The purpose of this study was to determine whether or not the pathologic subtype classification can predict prognosis and to validate the usefulness of the newly proposed diagnostic criteria of MI-IPMCs. We reviewed the clinicopathologic characteristics of 142 surgically resected cases of IPMNs. There were 54, 56, 30, and two cases of the gastric, intestinal, pancreatobiliary, and oncocytic types of IPMNs, respectively. The intestinal and pancreatobiliary types were more likely to have a main duct type. All gastric type tumors were adenomas or moderate dysplasia, whereas greater than one half of the intestinal and pancreatobiliary types were carcinomas in situ or invasive carcinomas. A significant difference in recurrence and death rate was noted for invasive carcinoma between the intestinal and pancreatobiliary types. The majority of MI-IPMCs were the intestinal type, whereas the majority of IC-IPMCs were the pancreatobiliary type. The IC-IPMC group showed a decreased recurrence-free and overall survival with statistically significance (p < 0.001 and p = 0.001, respectively). Our results suggest that the pathologic subtype classification and the newly proposed diagnostic criteria for minimal invasion may also be useful to predict prognosis of IPMNs of the pancreas.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hruban RH et al. An illustrated consensus on the classification of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:977–87.
Furukawa T, Kloppel G, Volkan Adsay N, Albores-Saavedra J, Fukushima N, Horii A, et al. Classification of types of intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: A consensus study. Virchows Arch. 2005;447:794–9.
Ban S, Naitoh Y, Mino-Kenudson M, Sakurai T, Kuroda M, Koyama I, et al. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) of the pancreas: its histopathologic difference between 2 major types. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30:1561–9.
Takasu N, Kimura W, Moriya T, Hirai I, Takeshita A, Kamio Y, et al. Intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms of the gastric and intestinal types may have less malignant potential than the pancreatobiliary type. Pancreas. 2010;39:604–10.
Adsay NV, Merati K, Basturk O, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Levi E, Cheng JD, et al. Pathologically and biologically distinct types of epithelium in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: Delineation of an “intestinal” pathway of carcinogenesis in the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:839–48.
Hiraoka N, Onozato K, Kosuge T, Hirohashi S. Prevalence of FOXP3+ regulatory t cells increases during the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its premalignant lesions. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:5423–34.
Nara S, Shimada K, Kosuge T, Kanai Y, Hiraoka N. Minimally invasive intraductal papillary-mucinous carcinoma of the pancreas: clinicopathologic study of 104 intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32:243–55.
Sohn TA, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Hruban RH, Lillemoe KD. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: An increasingly recognized clinicopathologic entity. Ann Surg. 2001;234:313–21. discussion 321–2.
Adsay NV, Conlon KC, Zee SY, Brennan MF, Klimstra DS. Intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: an analysis of in situ and invasive carcinomas in 28 patients. Cancer. 2002;94:62–77.
Woo SM, Ryu JK, Lee SH, Yoon WJ, Kim YT, Yoon YB. Branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms in a retrospective series of 190 patients. Br J Surg. 2009;96:405–11.
Tanaka M et al. International consensus guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2006;6(1–2):17–32.
Chari ST, Yadav D, Smyrk TC, DiMagno EP, Miller LJ, Raimondo M, et al. Study of recurrence after surgical resection of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:1500–7.
Wada K, Kozarek RA, Traverso LW. Outcomes following resection of invasive and noninvasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Am J Surg. 2005;189:632–6. discussion 637.
Woo SM, Ryu JK, Lee SH, Yoo JW, Park JK, Kim YT, et al. Survival and prognosis of invasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: comparison with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. 2008;36:50–5.
Japan Pancreas Society. Classification of pancreas Cancer. 2nd ed. Tokyo: Kanehara; 2003.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a Samsung Biomedical Research Institute grant # SBRI C-A9-226-2.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kyu Taek Lee
Jeong Kim and Kee-Taek Jang contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Jang, KT., Mo Park, S. et al. Prognostic relevance of pathologic subtypes and minimal invasion in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Tumor Biol. 32, 535–542 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-010-0148-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-010-0148-z